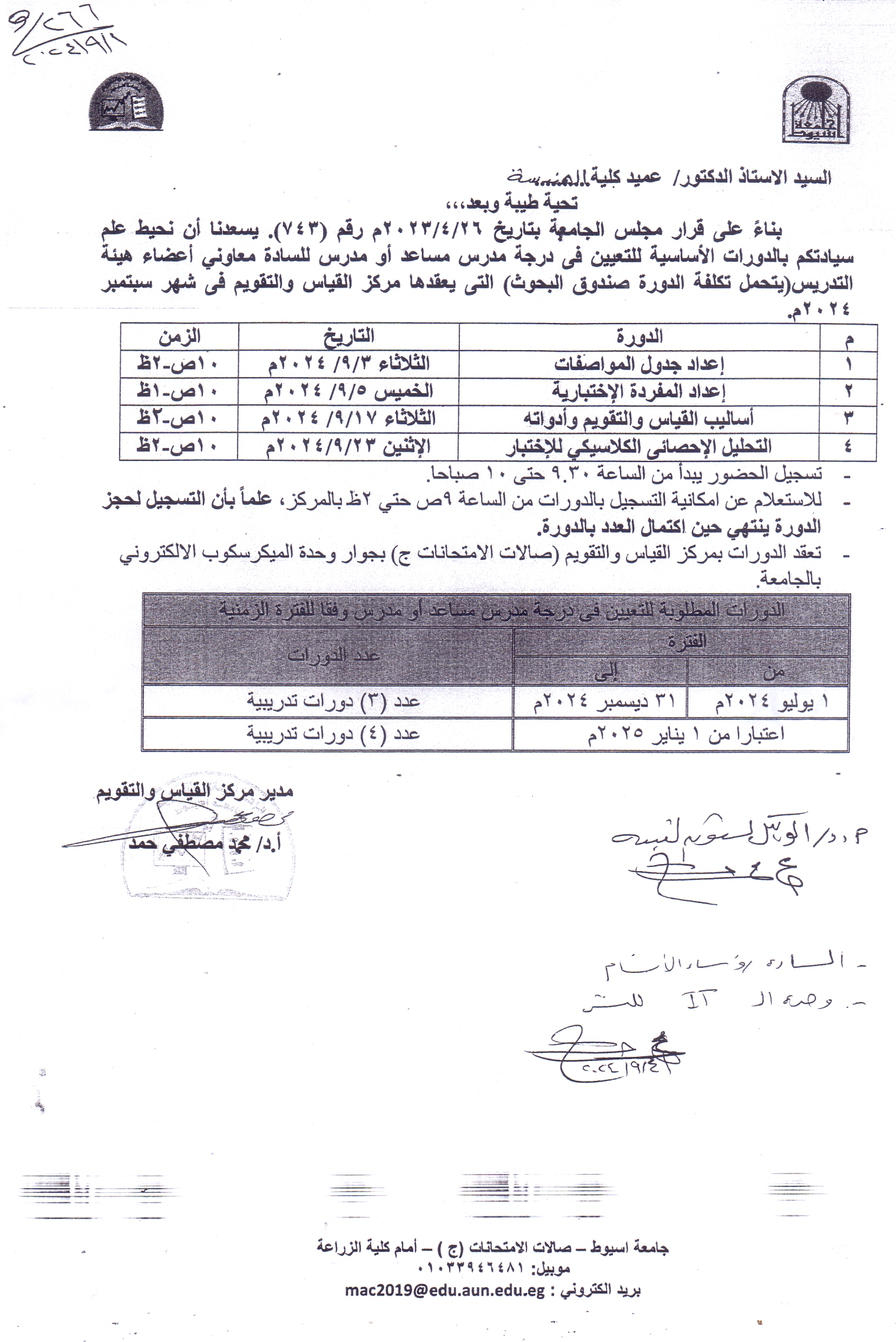
Assiut University President announces international accreditation of the "Electronics and Communications Engineering" program at Assiut University by the American ABET Institution

- Dr. Al-Minshawy: The program is the first of its kind to achieve this international accreditation at the republic level.
- The international accreditation of the program confirms the compatibility of engineering education at Assiut University with international quality standards.
Dr. Ahmed El-Minshawy, President of Assiut University, announced the international accreditation of the “Electronics and Communications Engineering” program in the Electrical Engineering Department - Faculty of Engineering, from the American ABET Foundation, as the first program of its kind (general - free) in engineering faculties across the country to be internationally accredited by this institution.
Dr. Al-Minshawy congratulated the Faculty of Engineering family, all those in charge of the Electrical Engineering Department, and the Electronics and Communications Engineering Program, for their distinguished efforts in achieving this accomplishment, which reflects the success of the Faculty in achieving the highest international standards and specifications, and reflects the distinguished engineering education and scientific research it provides, keeping pace with modern developments and linked to local and regional needs.
The President of Assiut University explained that this achievement came as one of the fruits of cooperation between the university - represented by the Faculty of Engineering, and the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research - represented by the Higher Education Development Projects Management Unit, through one of the joint projects that aims to support academic programs with the aim of obtaining international accreditation.
Dr. Ahmed El-Minshawy stressed that the Electronics and Communications Engineering Program obtaining international accreditation from ABET places it in a competitive global position for excellence in the field of electronics and communications, and raises the university’s position in global rankings. It is also a confirmation of the compatibility of engineering education at Assiut University with global quality standards, as the evaluation is done by meeting a set of academic standards specific to the American ABET Foundation.
For more information, please visit the following link:https://www.aun.edu.eg/main/ar/ryys-jamt-asywt-yln-alatmad-aldwly-lbrnamj-hndst-alalktrwnyat-walatsalatbhndst-asywt-mn-mwsst-abet