The Department of Pharmacognosy announces the holding of a seminar for the pharmacist/ Tasneem Zidan Zaid Ibrahim, who is enrolled to obtain a Master's degree in Pharmaceutical Sciences (Pharmacognosy) on Sunday, April 6, 2025

 Do you have any questions? (088) 2080369 - 2345622 Pharmacy_QAAU@pharm.aun.edu.eg
Do you have any questions? (088) 2080369 - 2345622 Pharmacy_QAAU@pharm.aun.edu.eg

Introduction: Tick-borne diseases represent a major threat to both
animal and human health globally. This study explores the prevalence of
tick infestation and associated piroplasm infections specifically Theileria
and Babesia species in cattle, in addition to evaluating the acaricidal
effectiveness of Chrysanthemum extract (Dendranthema grandiflora) and
neem oil emulsion (Azadirachta indica).
Methods: Among 130 cattle examined, 61 were infested with ticks and
subsequently screened for piroplasm infections. Molecular analysis identified
infections caused by Theileria annulata and Babesia bigemina.
Results: A strong association was found between tick infestation and Babesia
species, while T. annulata infection showed a slight correlation. Hemolymph
examination confirmed the critical role of ticks in the life cycle of piroplasm
infection. Chrysanthemum extract and neem oil were tested for their acaricidal
properties against adult ticks (Rhipicephalus annulatus). Chrysanthemum extract
(0.5 mg/mL) caused tick mortality within 24 h. However, neem oil induced
rapid and significant tick mortality at (20 mg/L) and (15 mg/L), achieving 100%
mortality within the same time frame. Both treatments demonstrated high
effectiveness, with results indicating strong dose-and time-dependent effects
compared to controls. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) revealed extensive
morphological damage to treated ticks. This damage included destruction of
the hypostome, loss of surface striations, wrinkling with pore formation, and
cracking following exposure to neem oil and Chrysanthemum extract.
Discussion: These findings highlight the potential of D. grandiflora extract and
neem oil emulsion as effective natural acaricides for controlling tick infestations
and reducing tick-borne diseases.
Silver-based metal organic frameworks (MOFs) have recently acquired considerable interest due to their potential applications in sensing and detection, bioimaging, and light-emitting devices. Incorporating specific linkers or functional groups into the MOF structure can tailor their fluorescence characteristics and thus can selectively respond to target analytes. Herein, we report the synthesis of a novel luminescent silver-based MOFs (SOF1) derived from 2,3-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (2,3-DHBDC). The formation of SOF1 was established via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and elemental analysis. The synthesis conditions i.e. molar ratio of Ag to 2,3-DHBDC and temperature played a crucial role in the formation of clean SOF with no formation of silver nanoparticles (NPs). High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) revealed various shapes depending on the synthesis conditions. Mostly, octahedrons and hexagons were observed for SOFs obtained utilizing molar ratio of 1:1 and 1:2, respectively. Furthermore, the selected area electron diffraction (SAED) revealed its high crystallinity. The synthesized SOF1 showed a distinct and strong fluorescent signal that is much higher than that produced from SOF2 based on the isomeric ligand; 2,5-dihydroxyterephthalic acid (2,5-DHBDC). The designed sensor was utilized for the sensitive detection of trifluralin (TRF) pesticide in river water samples. The achieved limit of detection of TRF was found to be 8 μg/L. The fluorescence quenching was experimentally and mathematically confirmed to primarily occur through the mechanisms of inner-filter effect (IFE), static quenching (SQ) and photoinduced electron transfer (PET). Moreover, a thin film of SOF1 was synthesized for selective visualization of TRF.
A novel and selective analytical method has been developed for doxycycline (DOX) determination, addressing the critical need for monitoring this widely used antibiotic in environmental samples. The method employs a hybrid sensing system combining orange-emitting carbon dots (O-CDs) with a calcium-murexide (Ca@Mu) complex, offering a unique dual-mode detection approach. Unlike conventional methods that rely on direct fluorescence quenching by DOX, which often suffer from poor selectivity, this system utilizes the competitive binding between DOX and murexide for Ca2+ ions. Initially, the pink-colored Ca@Mu complex formed under alkaline conditions causes fluorescence quenching of O-CDs at 552 nm. Upon introduction of DOX, its stronger Ca2+-binding affinity leads to the formation of a calcium-DOX complex, liberating free Mu and triggering both colorimetric (pink to orange) and fluorometric (restoration of O-CDs emission) responses. Comprehensive characterization and mechanistic investigations employing different spectroscopic techniques confirmed the sensing mechanism. The method demonstrates excellent selectivity for DOX among other tetracyclines and potential interferents, along with impressive analytical performance including good linearity (1.0-35.0 μM), low detection limit (325 nM), and high precision. Additionally, a smartphone-based colorimetric platform was developed for convenient on-site analysis. The practical utility of this method was validated through successful determination of DOX in environmental water samples with excellent recovery rates, offering a reliable and user-friendly approach for environmental monitoring of this important antibiotic.
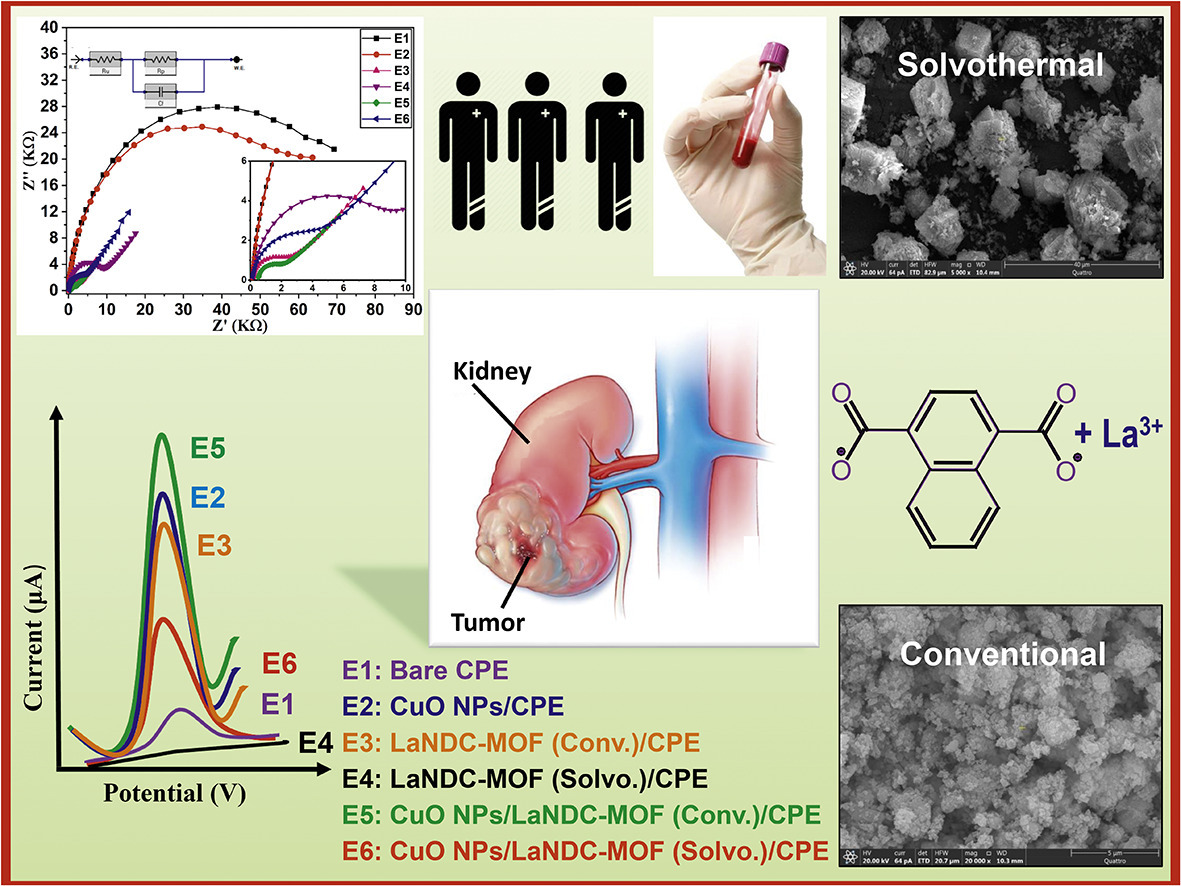
This study uniquely emphasizes the crucial role of MOF synthesis techniques in optimizing electrocatalytic properties and enhancing electroanalytical performance. The main aim of this work is to develop a highly sensitive, selective, and cost-effective electrochemical sensor for detecting sunitinib malate (SUN) in serum samples collected from renal cancer patients. The designed sensor was based on using CuO nanoparticles/lanthanum 1,4-napthalene dicarboxylic acid (NDC) MOF-modified carbon paste electrode (CuO NPs/LaNDC-MOF/CPE) coupled with square-wave adsorptive anodic stripping voltammetry (SW-AdASV) as the electrochemical technique. Two MOF synthetic approaches were utilized i.e. conventional (Conv.) and solvothermal (Solvo.). The synthesized La-MOFs were characterized using X-ray Diffraction analysis (XRD), Fourier transform IR spectroscopy (FTIR), Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and Nitrogen adsorption/desorption isotherm (BET). LaNDC-MOF (Conv.) has a higher surface area (four times) than LaNDC-MOF (Solvo.). Moreover, the modified electrode based on LaNDC-MOF (Conv.) exhibited better electrocatalytic activity and improved sensitivity towards the oxidation of SUN than that prepared through solvothermal route. Various experimental parameters, including accumulation potential, accumulation time, and pH of the supporting electrolyte, were optimized to obtain the best analytical performance. The fabricated sensor based on CuO NPs/LaNDC-MOF/CPE showed an oxidation peak of SUN at 0.66 V vs Ag/AgCl. Under the optimized conditions, SW-AdASV method exhibited a linear response over a concentration range of 0.01–1.0 μmol l-1 with a detection limit of 0.002 μmol l-1 for SUN. The proposed method was successfully applied for the determination of SUN in pharmaceutical formulations and serum samples of renal cancer patients. Moreover, the proposed methodology via modification of CPE with the synthesized MOFs tailors them to be applied for clinical analysis and therapeutic drug monitoring of SUN, providing a valuable tool for personalized medicine and improving the treatment outcomes for renal cancer patients.
Among the all possible isomers of triazolopyrimidines, 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines are the most important
isomers owing to their vast activities in agriculture and medicinal chemistry. Herein, we present an overview of
the most used synthetic pathways of this scaffold to assist researchers design new drug molecules with expected
pharmacological activities
Two new series of quinazoline‐chalcone hybrids were designed, synthesized as histone deacetylase (HDAC)/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) dual inhibitors, and screened in vitro against the NCI 60 human cancer cell line panel. The most potent derivative, compound 5e bearing a 3,4,5‐trimethoxyphenyl chalcone moiety, showed the most effective growth inhibition value against the panel of NCI 60 human cancer
cell lines. Thus, it was selected for further investigation for NCI 5 log doses. Interestingly, this trimethoxy‐substituted analog inhibited the proliferation of Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI)‐8226 cells by 96%, at 10 μMwith IC50 = 9.09 ± 0.34μM and selectivity index = 7.19 against normal blood cells. To confirm the selectivity of this compound, it was evaluated against a panel of tyrosine kinase enzymes. Mechanistically, it successfully and selectively inhibited HDAC6, HDAC8, and EGFR with IC50=0.41±0.015, 0.61 ± 0.027, and 0.09 ± 0.004 μM, respectively. Furthermore, the selected derivative induced apoptosis via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway by raising the Bax/Bcl‐2 ratio and activating caspases 3, 7, and 9. Also, the flow cytometry analysis of RPMI‐8226 cells showed that the trimethoxy‐substituted analog produced cell cycle arrest in the G1 and S phases at 55.82%. Finally, an in silico study was performed to explore the binding interaction of the most active compound within the zinc‐containing binding site of HDAC6 and HDAC8.

The department announces the mid-term exam for the "Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-2" course, which will be held on Saturday, April 5, 2025, from 3:00 PM to 4:00 PM, covering the following topics:
Please adhere to the specified time, as the exam will not be rescheduled.
Location:

Novel 3-(4-methylsulfonylphenyl) pyrazole derivatives with different substitutions at position four were
designed, synthesized, characterized by spectroscopic techniques, and investigated as potential anticancer agents via inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 and cyclooxygenase-2 enzymes. All the synthesized compounds were screened against three cancer cell line panels, hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG-2), mammary gland breast cancer (MCF-7), and colorectal carcinoma (HCT-116), to determine their antiproliferative properties by MTT assay. Compounds 5a, 6a, 6c, and 10c exhibited a considerable antiproliferative effect on HepG-2 cell line with IC50 value of 2.88 to 8.57 μM, on HCT-116 cell line with IC50 value of 6.34 to 17.84 μM, and on MCF-7 cell line with IC50 value of 1.75 to 9.58 μM. Compounds 5a, 6a, 6c, and 10c had weak toxicity towards normal HEK-293T, especially 10c displayed the highest IC50 with a value of 101.21 μM against normal cells. Furthermore, mechanistic studies for the antiproliferative activity were performed on the most active compounds 5a, 6a, 6c, and 10c. Compound 6c exhibited significant inhibitory activity against CDK2 enzyme with IC50 value of 0.614 μM compared to R-roscovitine (IC50 = 0.533 μM) as a reference drug. Additionally, compounds 5a, 6a, 6c, and 10c have significant potency and selectivity for the COX-2 enzyme (IC50 = 0.058 – 0.089 μM) over COX-1 enzyme (IC50 = 9.7 – 11.6 μM) compared to celecoxib and indomethacin. Accordingly, compounds 5a and 6c showed potent COX-2 inhibitory activity with IC50 values of 0.058 and 0.075 μM with a selectivity index of 198.27 and 154.66, respectively, in comparison to celecoxib and indomethacin with COX-2 IC50 value of 0.046 and 0.079 μM and a selectivity index of 315.21 and 1.25. compound 6c, with the potent CDK2 and COX-2 inhibitory activity, demonstrated apoptotic activity on HepG-2 cancer cells by inducing a strong G1 phase cell cycle arrest. Also, compound 6c significantly elevated the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio by 14.54 folds compared to the untreated control, which is clearly correlated with its sensitivity to apoptosis. Molecular docking and dynamics simulations were conducted to illustrate the binding modes inside the active sites. Finally, the hit compound 6c was discovered to
have antiproliferative activity against HepG-2, MCF-7, and HCT-116 cancer cell lines by inhibiting CDK2 and
COX-2 enzymes as proposal mechanisms.

