Assiut University Club announces the group iftar parties throughout the month of Ramadan
A Training Course on Microsoft Excel from 20 to 27 Mar 2024
A Training Course on Microsoft Word from 19 to 28 March 2024
Financial Reward to the University Employee in recognition of their efforts.
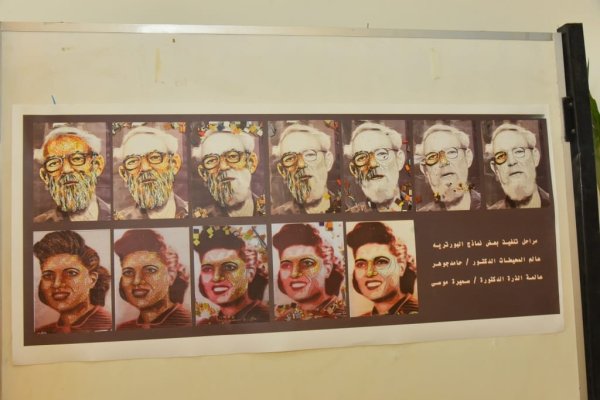
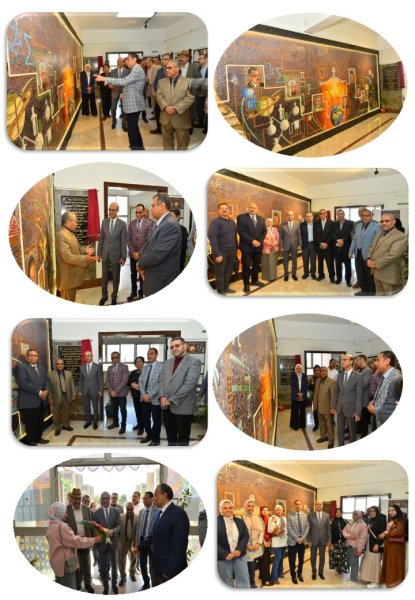
Follow-up by Dean of the Faculty of Implementation Phases of the Faculty of Science Art Mural
Invitation to attend the opening of the Faculty of Science Art Mural on Tuesday 19 - 3 – 2024
The visit of Prof. Dr. Ahmed El-Manshawi President of Assiut University to the Faculty of Science to witness the Art Mural.
Graduate Study Result for the Academic Year 2024 (MSc - PhD - Ph.D. Qualification).

نتيجة دكتوراه تأهيلى فبراير 2024 م
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1CC9cegPN2j7_T_3o10qmSMiupIbp4fOX/view?usp=sharing
نتيجة دكتوراه فبراير 2024 م
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1CPwRa1S-PDBy0T3wDU0p7FEIvfordPct/view?usp=sharing
نتيجة ماجستير فبراير 2024 م
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1IGeU4WNU1xW9xpn0Ov6yam4lj1Z-g8y9/view?usp=sharing