Do you have any questions? (088) 2345643 - 2412000 sci_dean@aun.edu.eg
Biodiesel Production from the Marine Alga Nannochloropsis oceanica Grown on Yeast Wastewater and the Effect on Its Biochemical Composition and Gene Expression
Microalgae-based biodiesel synthesis is currently not commercially viable due to the high costs of culture realizations and low lipid yields. The main objective of the current study was to determine the possibility of growing Nannochloropsis oceanica on Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast wastewater for biodiesel generation at an economical rate. N. oceanica was grown in Guillard F/2 synthetic medium and three dilutions of yeast wastewater (1, 1.25, and 1.5%). Biodiesel properties, in addition to carbohydrate, protein, lipid, dry weight, biomass, lipid productivity, amino acids, and fatty acid methyl ester (FAMEs) content, were analyzed and the quality of the produced biodiesel is assessed. The data revealed the response of N. oceanica to nitrogen-deficiency in the three dilutions of yeast wastewater. N. oceanica in Y2 (1.25%) yeast wastewater dilution exhibited the highest total carbohydrate and lipid percentages (21.19% and 41.97%, respectively), and the highest lipid productivity (52.46 mg L−1 day −1) under nitrogen deficiency in yeast wastewater. The fatty acids profile shows that N. oceanica cultivated in Y2 (1.25%) wastewater dilution provides a significant level of TSFA (47.42%) and can be used as a feedstock for biodiesel synthesis. In addition, N. oceanica responded to nitrogen shortage in wastewater dilutions by upregulating the gene encoding delta-9 fatty acid desaturase (Δ9FAD). As a result, the oleic and palmitoleic acid levels increased in the fatty acid profile of Y2 yeast wastewater dilution, highlighting the increased activity of Δ9FAD enzyme in transforming stearic acid and palmitic acid into oleic acid and palmitoleic acid. This study proved that the Y2 (1.25%) yeast wastewater dilution can be utilized as a growth medium for improving the quantity of specific fatty acids and lipid productivity in N. oceanica that affect biodiesel quality to satisfy global biodiesel requirements.
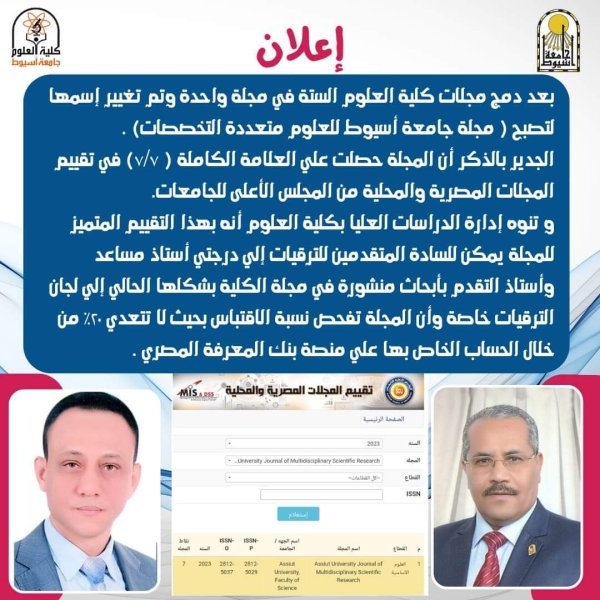
Announcement
Condolences
ic3 courses
Congratulation
Condolences
Application of Gravity and Remote Sensing data to groundwater potential in Wadi Ar-Ramah, Saudi Arabia
Water scarcity is developing in the Middle East as a result of the region's growing population and tremendously advanced agricultural and industrial sectors. Saudi Arabia is the Middle East country with the highest water consumption, so there is an urgent need to take action, and new technology advancements in geophysical measurements allow for the monitoring of groundwater. Wadi Ar-Ramah is one region that has witnessed significant agricultural expansion as well as a serious over-exploitation of the groundwater resources that are available there. Depletion rate in groundwater of the Wadi Ar-Ramah basin at eastern Saudi Arabia was determined for the time interval of 04/2002 to 12/2021 using a combination of gravity data from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) mission and results of land surface models. The findings are: (1) the average yearly rainfall rate was computed at 87.7 mm yr -1 over the Wadi Ar-Ramah; (2) the terrestrial water storage variation (ΔTWS) was computed at -1.216±0.013 cm yr -1 ; (3) the GLDAS-derived soil moisture (ΔSMS) was minimal at -0.32±0.025 mm yr -1 ; (4) the GRACE-derievd groundwater decreasing rate was calculated at 1.212±0.012 cm yr -1 ; (5) the relief of the ground surface is producing northeasterly streams that carry the minimal surface water to the east; (6) our integrated method provides a repeatable and cost-effective approach
Geophysical investigations for the identification of subsurface features influencing mineralization zones
The numerous hydrothermal alteration zones and subsurface structures affecting the mineralized deposits
of the Dungash region were identified using aeromagnetic data. The Center of Exploration Targeting
(CET) approach and several filters, such as reduction-to-pole, Tilt derivative, First Vertical Derivative,
Horizontal gradient map, Downward continuation, analytical signal methods, regional, and residual separation,
were used to analyze the aeromagnetic data. The research region is impacted by several structural
trends running in the N-S, E-W, NW-SE, and NE-SW directions, and these trends are strongly
related to the gold mineralization and surrounding hydrothermal alteration zones. In the NW-SE direction,
four alteration zones have been identified. The research region’s northern and eastern regions have
shallower basement relief, with depths of only approximately 100 m, and those depths show that the
area is rootless. Conversely, the basement relief and surface depths are lower in the study region’s western
and southern regions. The routes taken by the ascending hydrothermal fluids can be seen as aeromagnetic
lineaments at the hydrothermal alteration zones. Mineralization appears to be linked to structural
lineaments, as evidenced by airborne magnetic data. For gold prospecting, the aeromagnetic technique
seems to be the most effective and efficient geophysical method because gold is typically found in
severely deformed shear zones and faults.
Structural, vibrational and opto-nonlinear properties of spin coater derived PbI2 films: Effect of solute concentrations
Herein, PbI2 nanostructured thin films were grown on glass substrates with different (0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 g) solute concentrations using a spin coating technique. The impact of the solute concentration on the structural, optical, nonlinear optical properties was examined thoroughly and was analyzed as a function of solute concentrations. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the films confirm a hexagonal wurtzite structure with a preferred orientation along (001) plane. The band gap of the films was calculated using absorbance spectra and found to be about 2.41–2.56 eV. The refractive index (n), extinction coefficient (k), optical dielectric constant, SELF and VELF were investigated and analyzed. In addition, third order optical susceptibility (χ(3)), nonlinear refractive index (n2) were also calculated. The obtained data shows that the prepared films are promising for optoelectronics applications.










