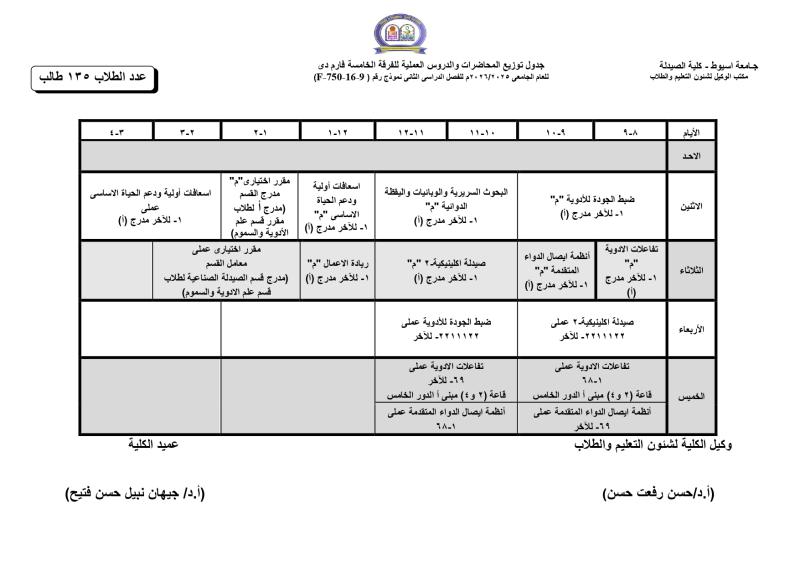
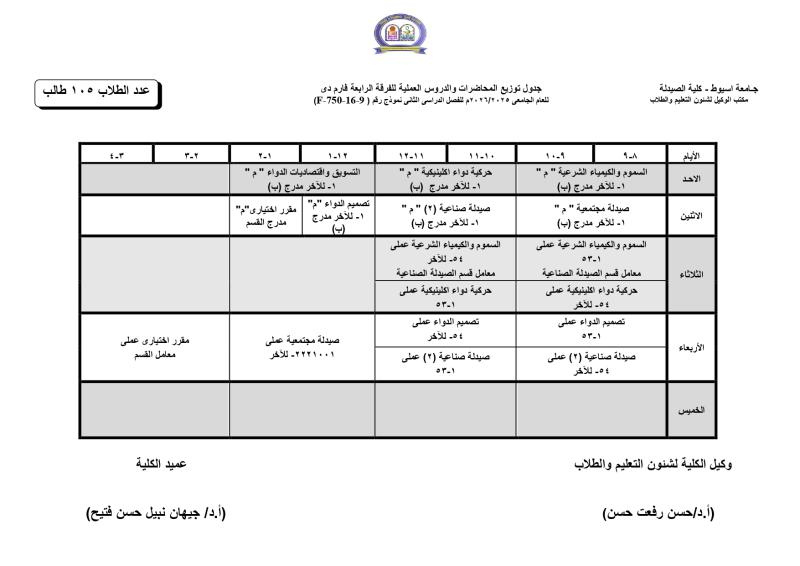
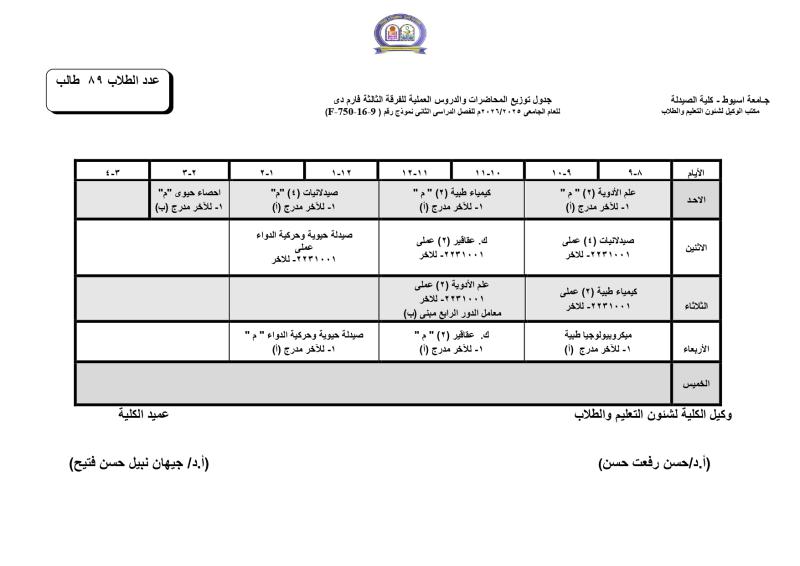
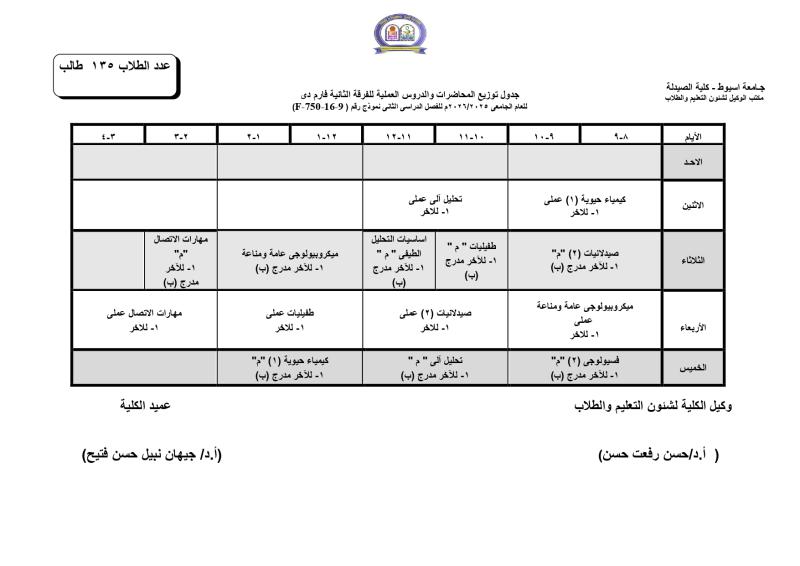

 Do you have any questions? (088) 2080369 - 2345622 Pharmacy_QAAU@pharm.aun.edu.eg
Do you have any questions? (088) 2080369 - 2345622 Pharmacy_QAAU@pharm.aun.edu.eg



God willing, the 67th meeting of the Department of Pharmacognosy Council at the Faculty of Pharmacy This will take place on Thursday, February 5, 2026.26, at 11:00 AM.
in the department council meeting room.

