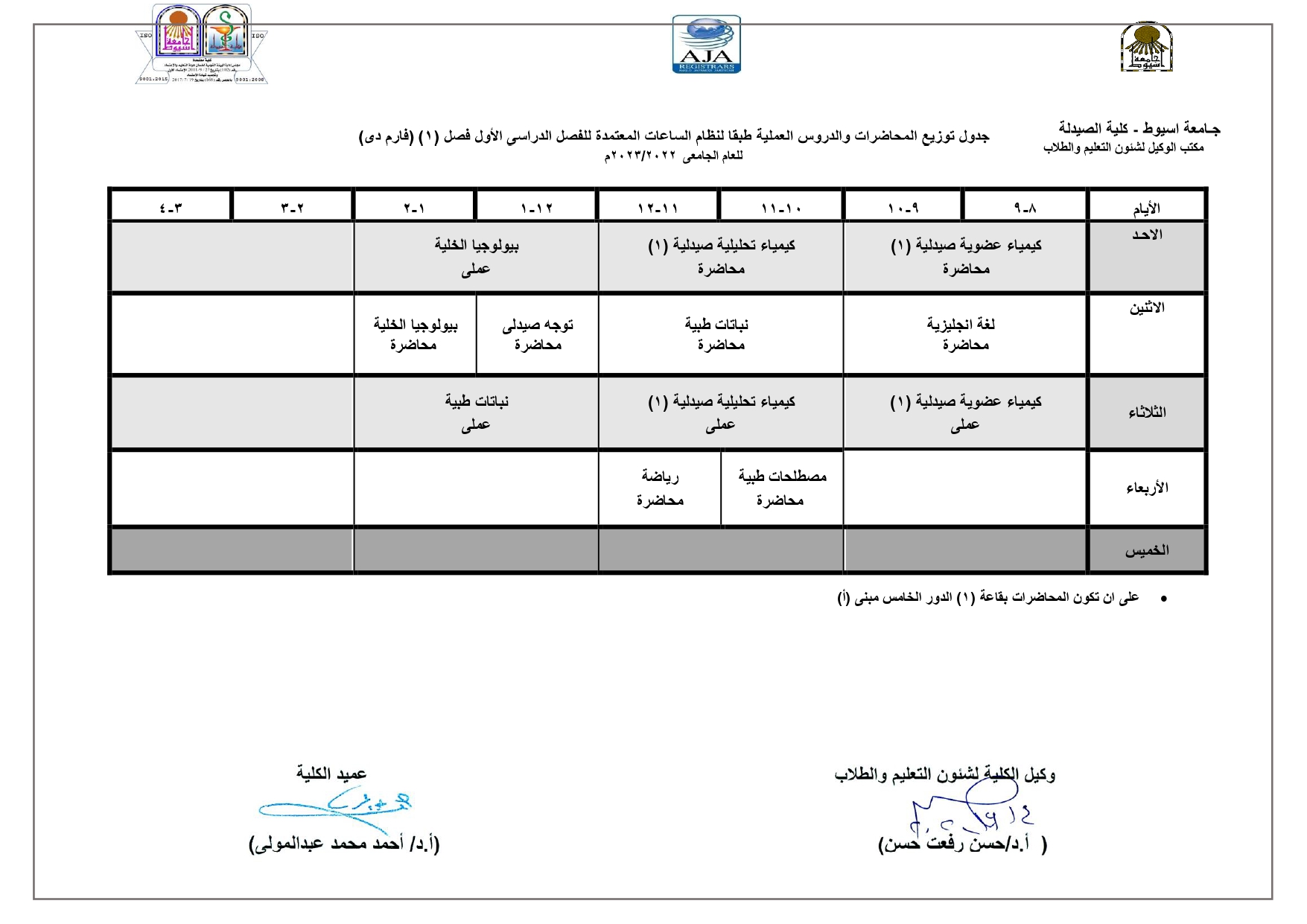
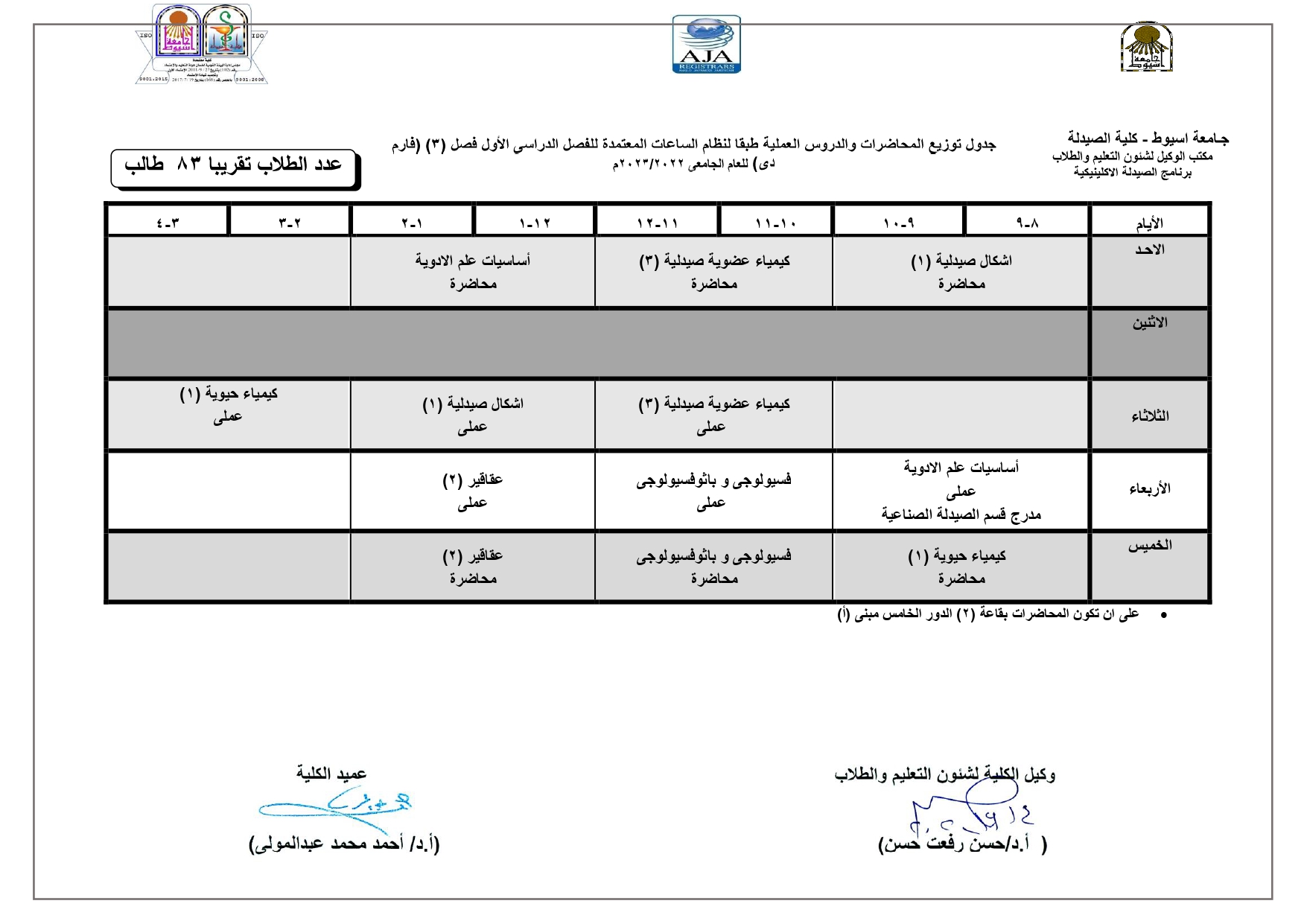
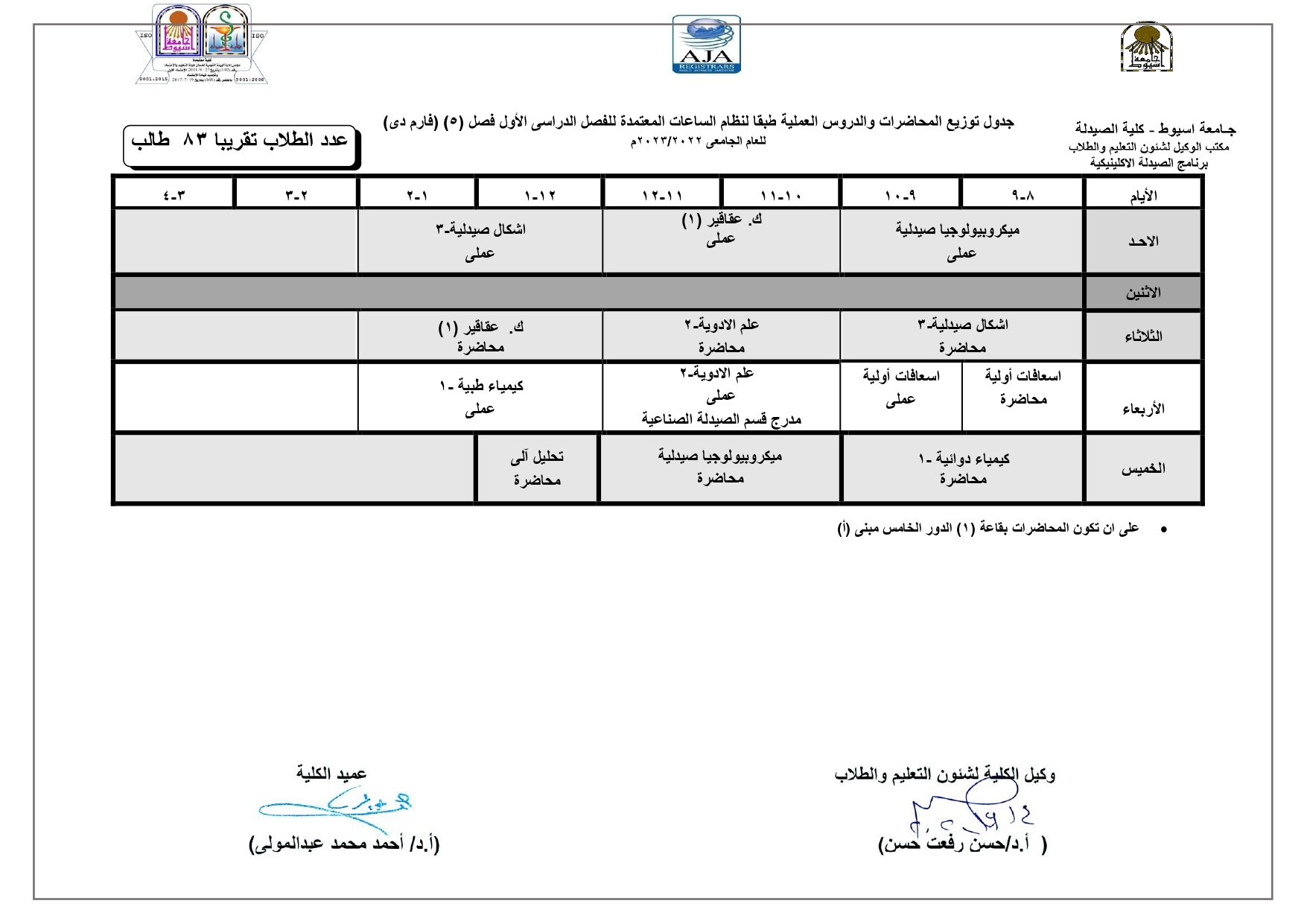
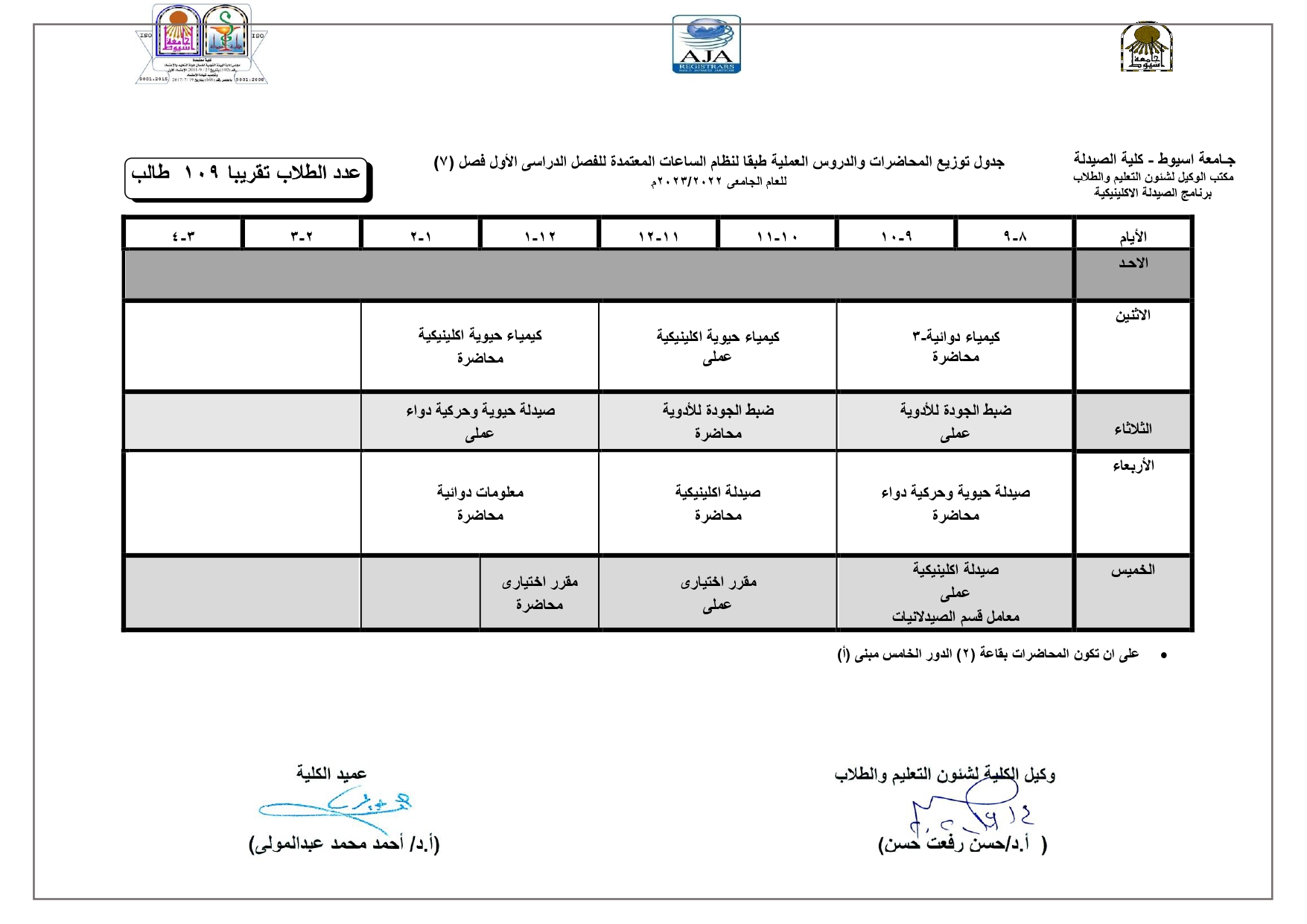
Exploration of components contributing to potent cytotoxicity of Gardenia thunbergia L. f. against human leukemia and hepatoma
Promising cytotoxic effects of several Gardenia species (Rubiaceae) have been established
by many studies. The current study evaluated MTT-based cytotoxic activities of the crude
extract from Gardenia thunbergia L. f. aerial parts and four fractions thereof, including n-hexane, dichloromethane (DCM), ethyl acetate, and aqueous, against human leukemia (HL-60)
and hepatoma (HepG2) cell lines, as well as the normal (WI38) cell line. Both non-polar
fractions, n-hexane and dichloromethane, showed tumor-selective toxicities against both tested
cancerous cell lines. These results sparked our interest in chemically characterising these
bioactive fractions to reveal their cytotoxic components. The composition of n-hexane-soluble
fraction was investigated via GC-MS analysis, while column chromatographic separation was
used to isolate the components of DCM-soluble fraction. These isolated phytochemicals were
identified via spectroscopic analyses. Besides, the chemotaxonomic value of the detected
phytochemicals and their reported cytotoxic profiles were discussed