Acceptance of the master's thesis of the researcher/ Mohamed Khaled Ali Abdel Gawad, a nursing specialist at Al-Adisat Hospital, Luxor Health Care Authority
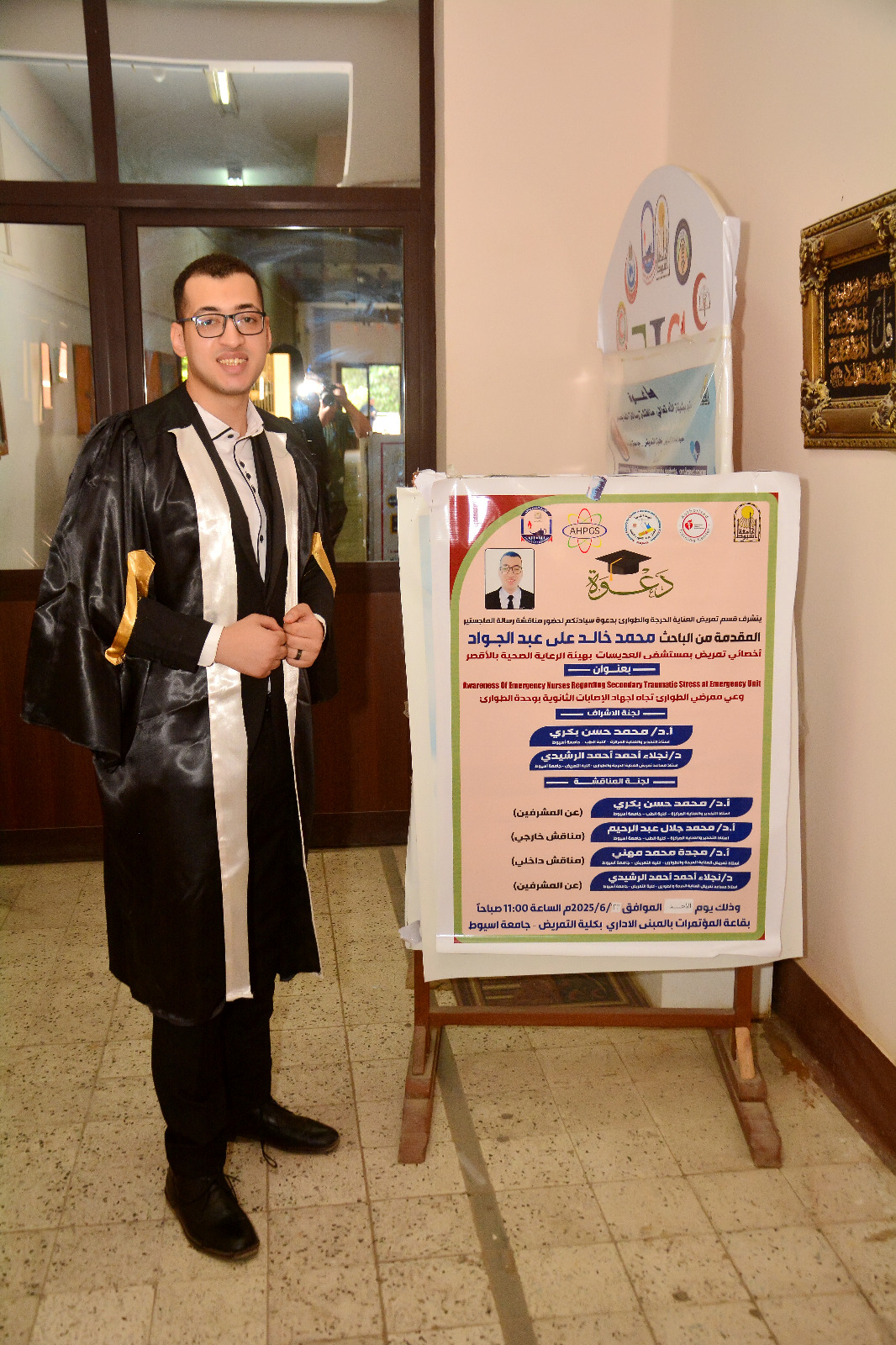

The subject of the submitted thesis was:
(Emergency Nurses' Awareness of Secondary Trauma Stress in the Emergency Unit)
The jury and supervisory committee for the thesis were:
Prof. Dr. Mohamed Hassan Bakry, Professor of Anesthesia and Intensive Care, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University. (On behalf of the supervisors)
Prof. Dr. Mohamed Galal Abdel Rahim, Professor of Anesthesia and Intensive Care, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University. (External examiner)
Prof. Dr. Magda Mohamed Mahni, Professor of Critical Care and Emergency Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Assiut University. (Internal examiner)
Dr. Naglaa Ahmed Ahmed Al-Rashidi, Assistant Professor of Critical Care and Emergency Nursing, Faculty of Nursing, Assiut University. (On behalf of the supervisors)
We wish everyone the best of luck and success.