A series of awareness seminars to combat the spread of narcotic substances among students
under the care of
Dr. Nevin Riad Al-Qabbaj, Minister of Social Solidarity
Professor Dr. Ahmed Al-Minshawy, President of the University
Professor Dr. Ahmed Abdel Mawla, Vice President of the University for Education and Student Affairs
Dr. Amr Othman, First Assistant Minister of Social Solidarity
Professor Dr. Tayseer Hassan Abdel Hamid, Dean of the College of Computers and Information
Professor Dr. Khaled Fathi Hussein, Vice Dean of the College for Education and Student Affairs
Professor Dr. Madiha Darwish, General Supervisor of Student Activities at the University
Dr. Haitham Ibrahim, Director General of the General Administration of Youth Welfare
Preparation and implementation
Mr. Omaima Ibrahim, Director of the Social Activity and Trips Department
Mr. Mohamed Mahran, university communication officer
The Social Activity Department of the General Administration of Youth Welfare is implemented in cooperation with the university colleges and with the participation of the Supreme Council of Universities and the Fund for Combating and Treating Addiction.
A series of awareness seminars to combat the spread of narcotic substances among students
Within Egypt's Vision 2030 at the level of university colleges
During the first semester 2023/2024
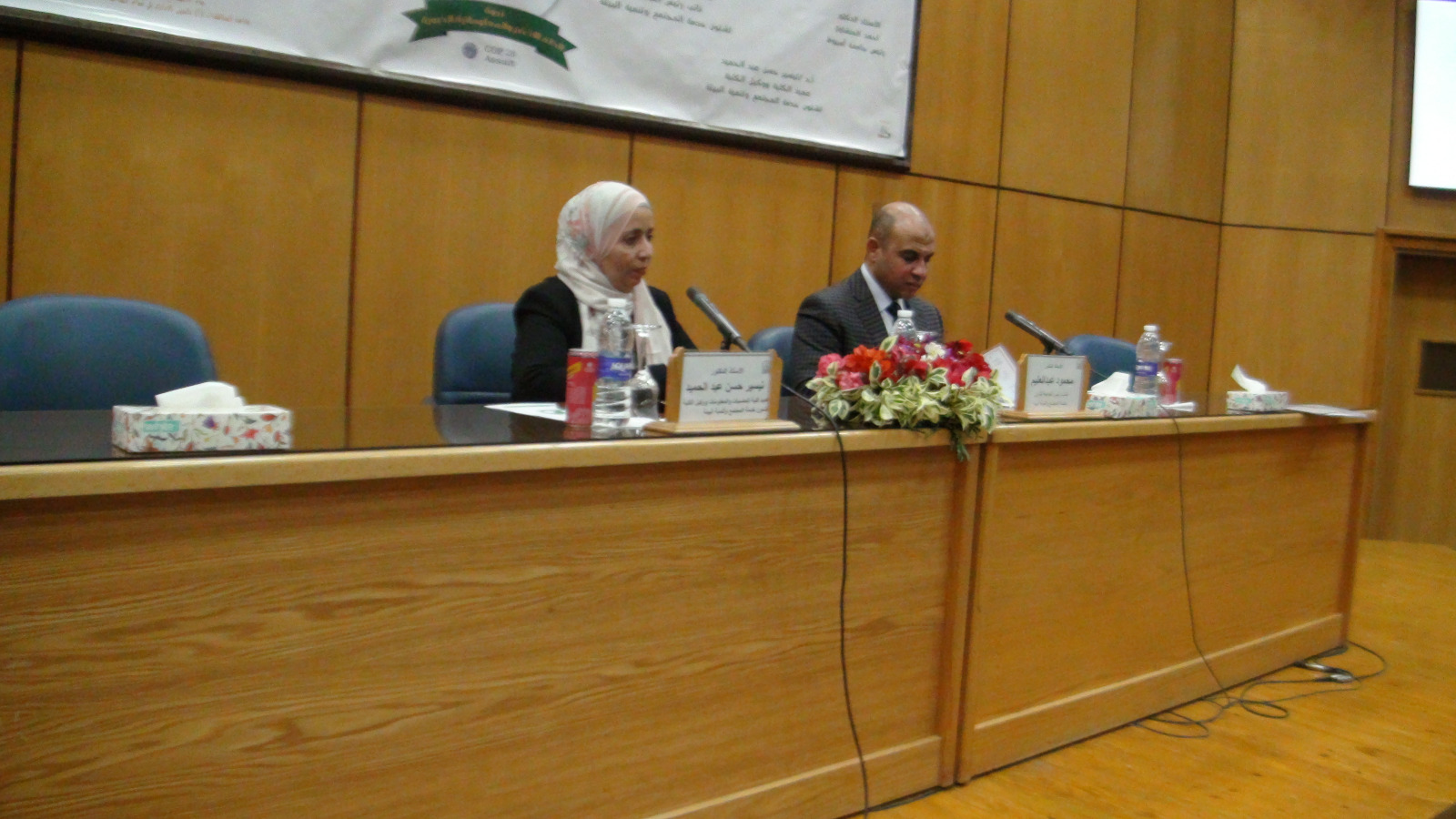
Activities of the second day of the November 2023 awareness seminars against drugs at the College of Computers and Information
with the presence of:
Professor Dr. Tayseer Hassan Abdel Hamid, Dean of the College of Computers and Information, and Professor Dr. Khaled Fathi Hussein, Vice Dean of the College for Education and Student Affairs.
Professor Dr. Nady Sayed Ali, advisor to the Fund for Combating and Treating Addiction and Abuse, and former head of the Forensic Medicine Department in Assiut
Mr. Mohamed Sayed Mohamed, Assiut Governorate Supervisor at the Fund for Combating and Treating Addiction and Abuse
And the youth care department at the college




 دعوة لحضور مناقشة رسالة الدكتوراه للباحثة / مروة حسين محمد المدرس المساعد بقسم نظم المعلومات
دعوة لحضور مناقشة رسالة الدكتوراه للباحثة / مروة حسين محمد المدرس المساعد بقسم نظم المعلومات










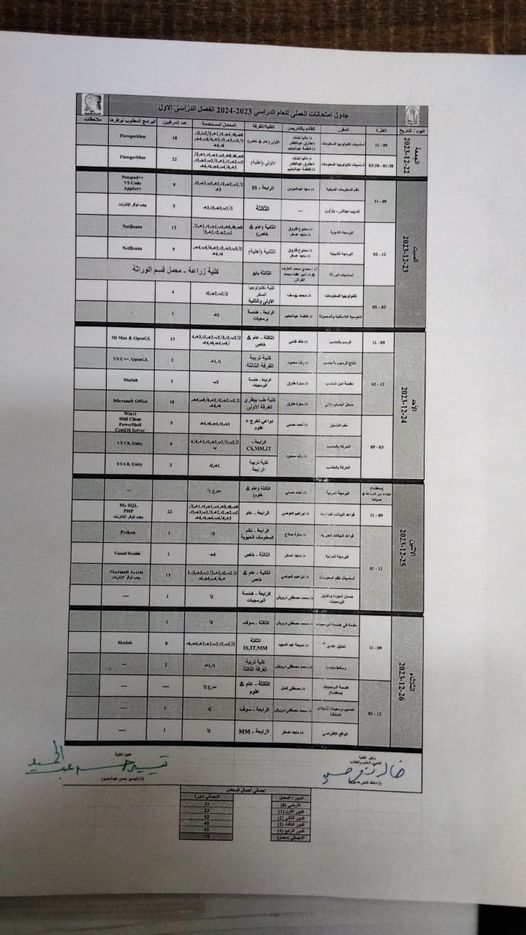
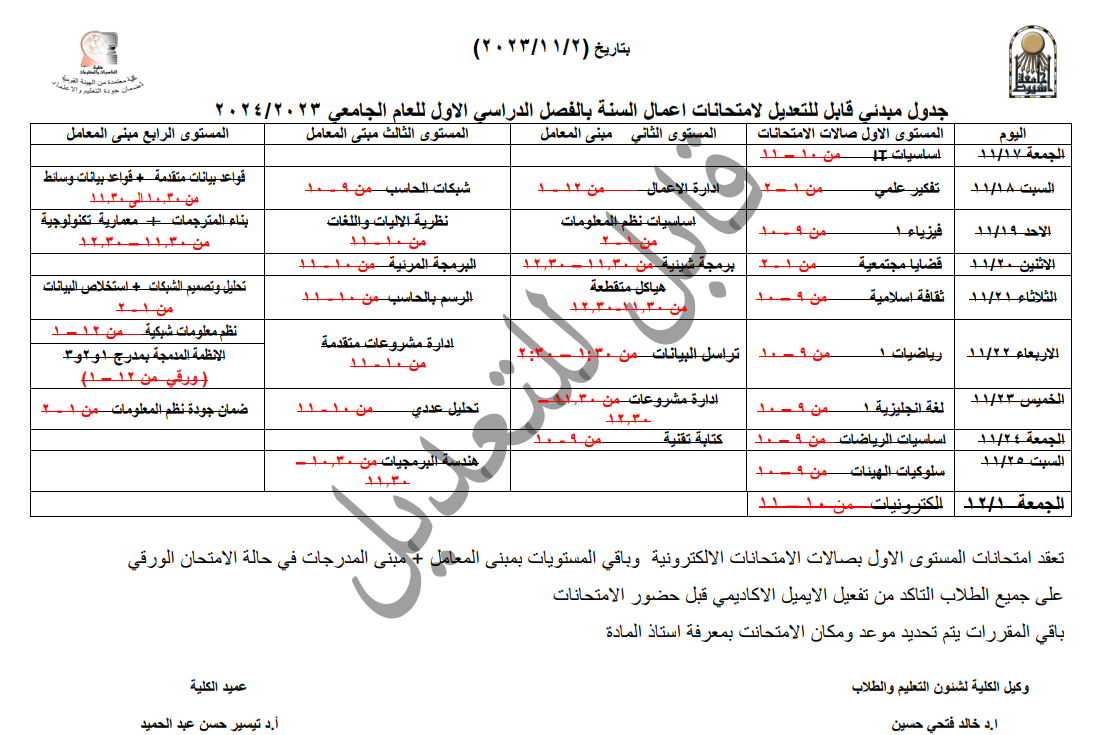
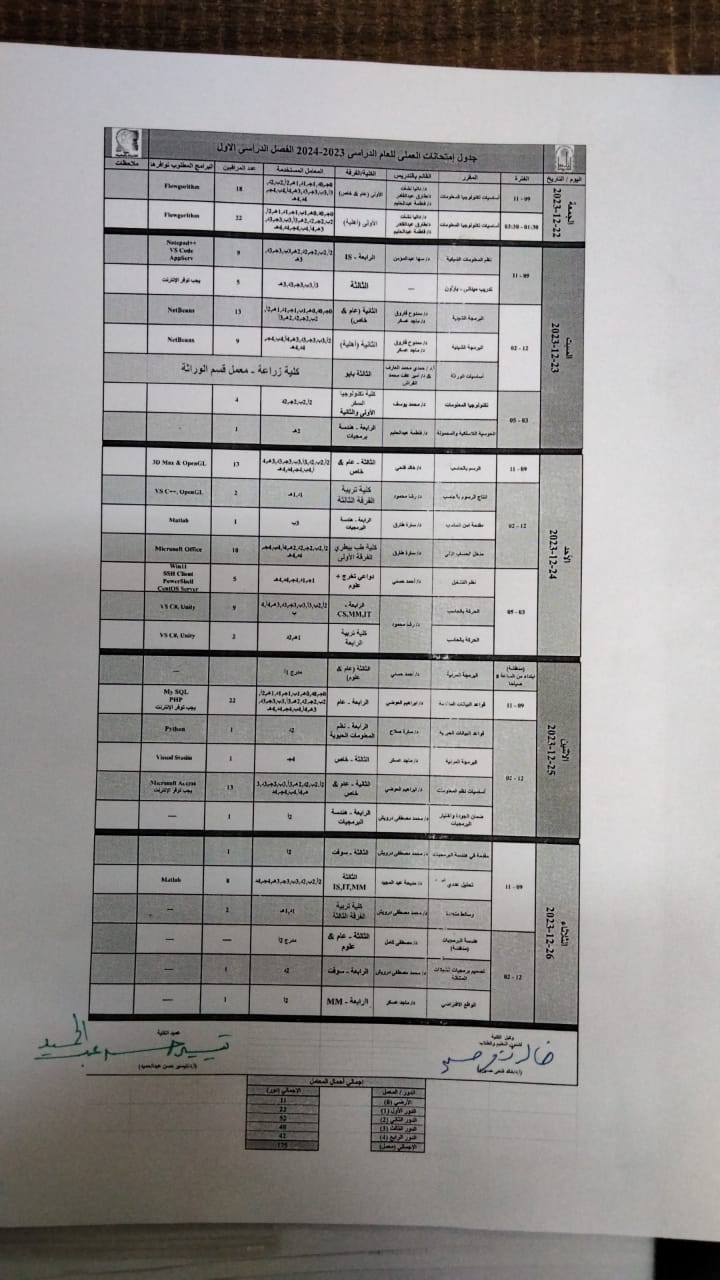 https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1PrmnY7c-MolyMYrqTdSxz_irjDrrfbRN5s0tDnl9x6E/edit?usp=sharing
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1PrmnY7c-MolyMYrqTdSxz_irjDrrfbRN5s0tDnl9x6E/edit?usp=sharing