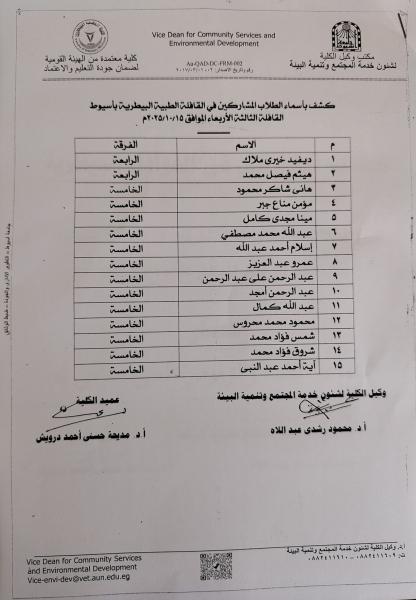
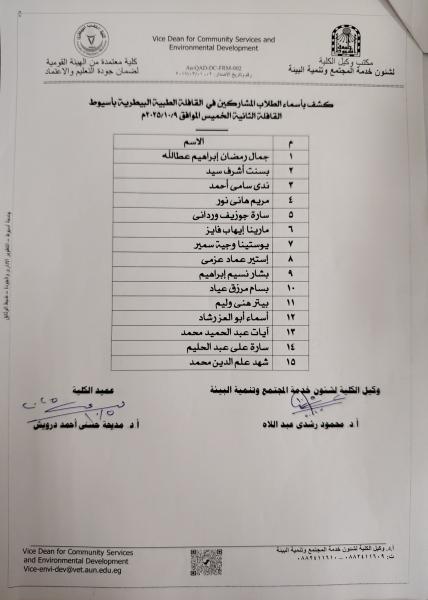
The Faculty of Veterinary Medicine at Assiut University launches a blood donation campaign for the benefit of the South Egypt Cancer Institute under the slogan "A drop of blood equals a human life".
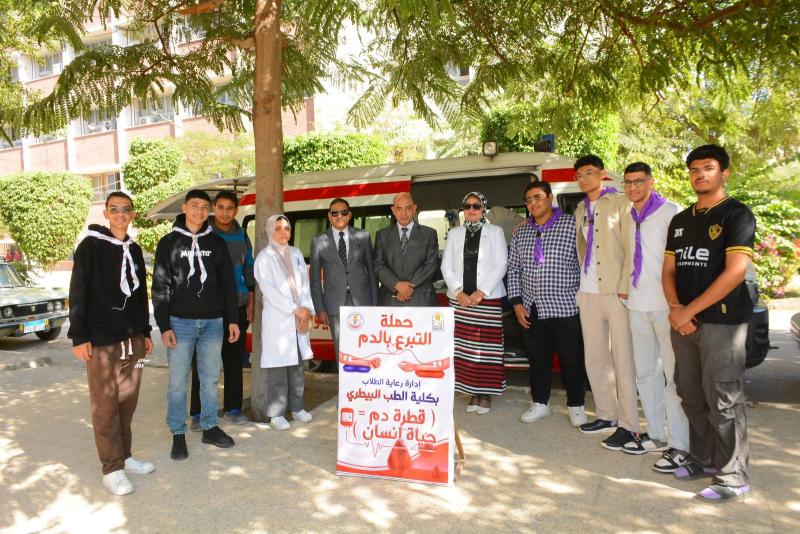

كلية الطب البيطري بجامعة أسيوط تطلق حملة للتبرع بالدم لصالح معهد جنوب مصر للأورام تحت شعار «قطرة دم تساوي حياة إنسان»
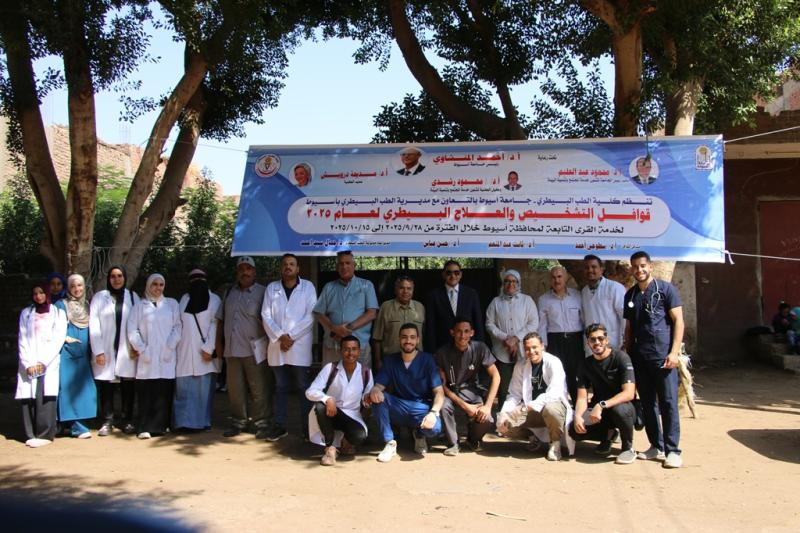
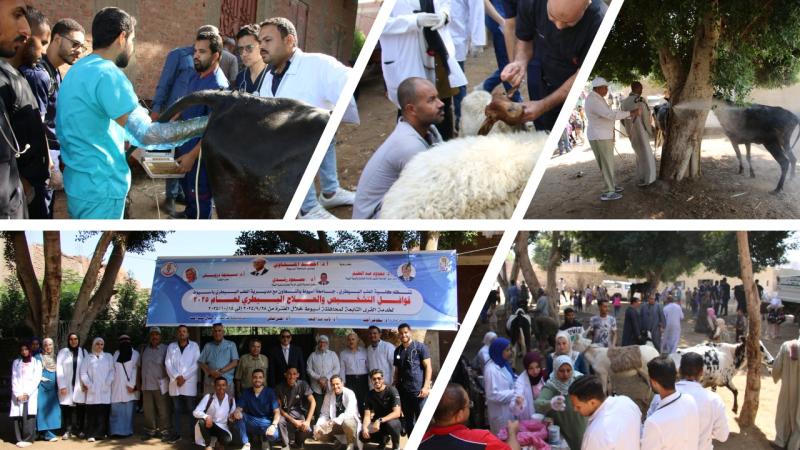
تحت رعاية الدكتور أحمد المنشاوي رئيس جامعة أسيوط، نظمت إدارة رعاية الطلاب بكلية الطب البيطري حملة للتبرع بالدم تحت شعار «قطرة دم تساوي حياة إنسان»، وذلك لصالح مرضى معهد جنوب مصر للأورام، خلال الفترة من 19 إلى 21 نوفمبر. جاءت الفعاليات تحت إشراف الدكتور محمد أحمد عدوي نائب رئيس الجامعة لشئون خدمة المجتمع وتنمية البيئة، والدكتورة إيناس أحمد عبد الحافظ عميد كلية الطب البيطري، والدكتور محمود رشدي وكيل الكلية لشئون خدمة المجتمع وتنمية البيئة.
وأقيمت الحملة بالتعاون مع معهد جنوب مصر للأورام، تحت إشراف الدكتور محمد أبو المجد عميد المعهد، وبمشاركة الدكتورة آية عماد الدين الطبيب المقيم بالمعهد، والدكتور أحمد ثابت مدير رعاية الطلاب بالكلية، إلى جانب عدد من أعضاء هيئة التدريس، وطاقم التمريض، ومسؤولي رعاية الطلاب.
وأكد الدكتور أحمد المنشاوي أن هذه الحملة تعكس روح التكافل الإنساني التي تحرص جامعة أسيوط على ترسيخها بين طلابها، مشيراً إلى أن التبرع بالدم يمثل عملاً تطوعياً نبيلاً يسهم في إنقاذ حياة المرضى، ولا سيما مرضى الأورام الذين يحتاجون بصورة مستمرة إلى دعم المجتمع.
وأشاد الدكتور محمد أحمد عدوي بجهود كلية الطب البيطري في دعم دور الجامعة تجاه المجتمع، مؤكداً التزامها بتعزيز المشاركة المجتمعية وتقديم خدمات تعليمية وتوعوية فعالة، مشيراً إلى أهمية هذه المبادرات في دعم مرضى السرطان وتخفيف معاناتهم، وداعياً الطلاب إلى المشاركة الفاعلة في الحملة.
ومن جانبها، أوضحت الدكتورة إيناس عبد الحافظ أن الحملة تهدف إلى توفير فصائل الدم المختلفة لخدمة مرضى السرطان بالمعهد، لاسيما في ظل تزايد أعداد المترددين عليه من مختلف محافظات صعيد مصر، مضيفةً أن الفريق الطبي قام بإجراء الفحوصات اللازمة للطلاب قبل التبرع، إلى جانب تقديم إرشادات حول أهمية التبرع بالدم وفوائده الصحية للمتبرعين.