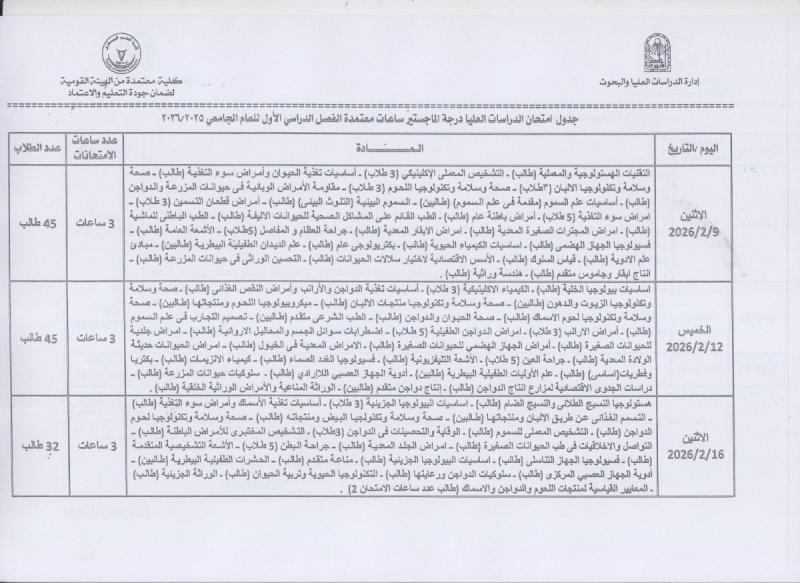
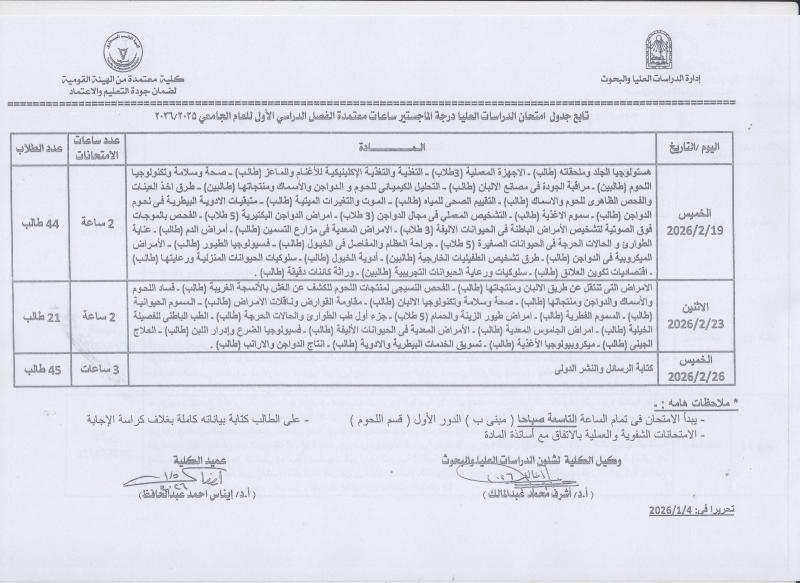
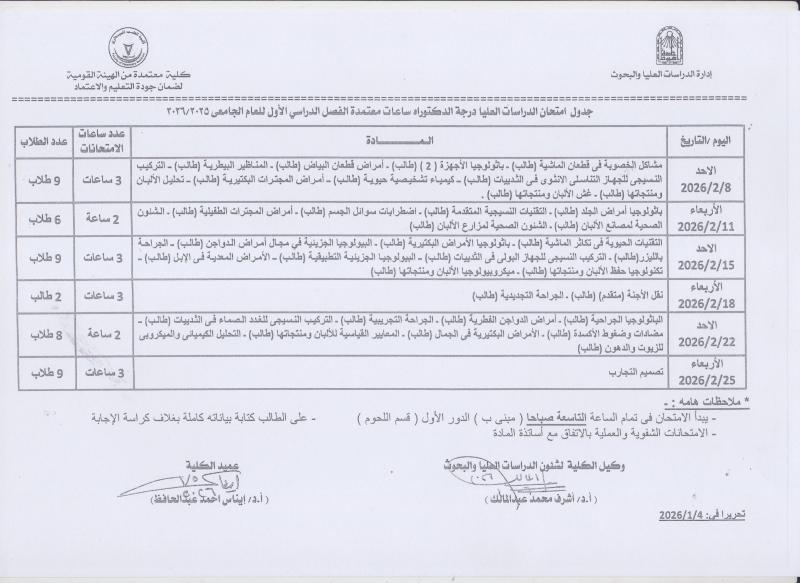
Graduate Studies Examination Schedules: PhD Degree
جداول امتحانات الدراسات العليا : الدرجة دكتوراه
Clostridium perfringens is the primary cause of necrotic enteritis (NE), one of the most economically destructive illnesses in broiler production. The virulence of this pathogen has recently been linked to the NetB toxin gene, a pore-producing cytotoxin recognized as a key determinant in NE pathogenesis. Despite its global significance, molecular data on NetB-positive C. perfringens from Upper Egypt are extremely limited. Therefore, this investigation was carried out to isolate C. perfringens recovered from broiler chickens in Assiut Governorate, Egypt, with a focus on the detection, sequencing, and genetic analysis of the NetB gene. Out of 60 intestinal samples, 40 isolates (66.7 %) were identified as C. perfringens by cultural and biochemical methods. PCR screening revealed that 20 isolates (50 %) harbored both alpha (cpa) and NetB toxin genes. Two representative NetB-positive isolates (Assiut1 and Assiut2) were sequenced and compared with global reference strains. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that the Egyptian isolates were closely associated to those from Egypt (KJ724530) and Iran (GU581173), forming a distinct Middle Eastern clade. Multiple sequence alignment revealed several nucleotide substitutions and amino acid variations, particularly when compared with strains from India, Brazil, and Denmark, suggesting the occurrence of unique regional mutations within the NetB gene. Experimental infection of broiler chickens confirmed the pathogenic potential of these isolates, producing classical NE lesions including gas-filled intestines, necrotic patches, and hemorrhagic ceca in Eimeria-preinfected birds, along with a significant reduction in body weight gain and feed intake (p < 0.05). To our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive molecular investigation of NetB-positive C. perfringens isolates from Upper Egypt. The findings underscore the genetic diversity and virulence of circulating strains and highlight the urgent need for regional surveillance and preventive strategies against necrotic enteritis in poultry.
Pattern matching is a fundamental operation in computational biology, information retrieval, and text processing. Despite advances in algorithms, efficiently searching large-scale texts, particularly genomic sequences spanning billions of base pairs, remains a significant challenge. Existing approaches face substantial limitations including Boyer-Moore algorithm's poor worst-case performance of O(mn) and limited scalability on large datasets, KMP algorithm's high memory overhead and poor cache locality despite O(m+n) complexity, traditional suffix array methods' expensive O(mlogn) search time with costly preprocessing, and hash-based approaches like Rabin-Karp's vulnerability to hash collisions and poor performance on repetitive sequences common in genomic data. This paper presents LCP-Optimized Suffix Array (LOSA), a high-performance pattern matching algorithm that combines suffix arrays with Longest …
The Identification of various mycobacterial species is critical for understanding their pathogenicity and epidemiology. Despite the existence of several established methods for identifying mycobacterial species, each of these methods has several significant limitations, including high costs, substantial time demands, and a restricted ability to detect a wide range of recoverable species. This study presents an in silico method using restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) to differentially identify 75 clinically important mycobacterial species.The present investigation employed specific primer combinations to identify and generate a distinct hypervariable sequence across the ribosomal RNA gene. This unique sequence using appropriate restriction enzyme digestion followed by gel electrophoresis enabled the creation of highly precise and distinct patterns or profiles for each of the 75 medically relevant …

