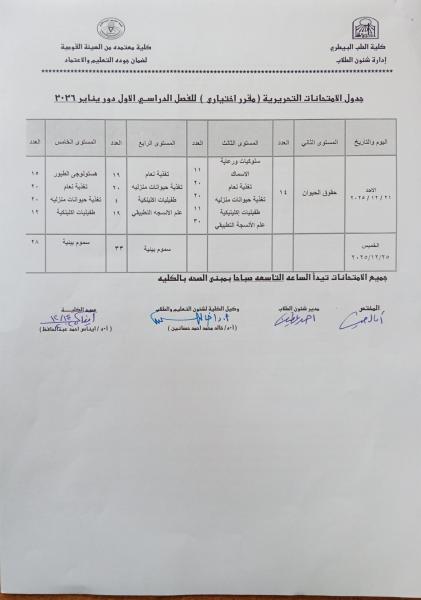
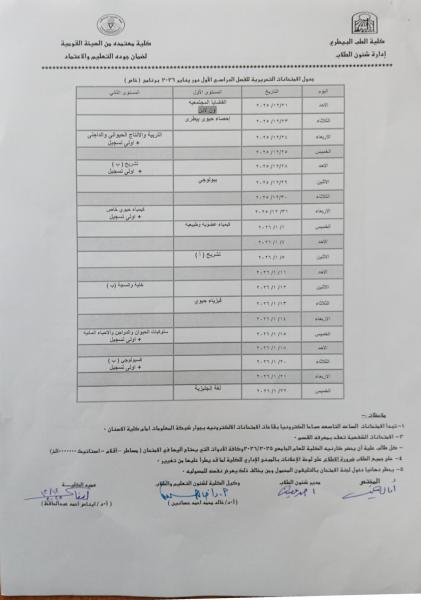
First semester exam schedules (special program) for the academic year 2025-2026
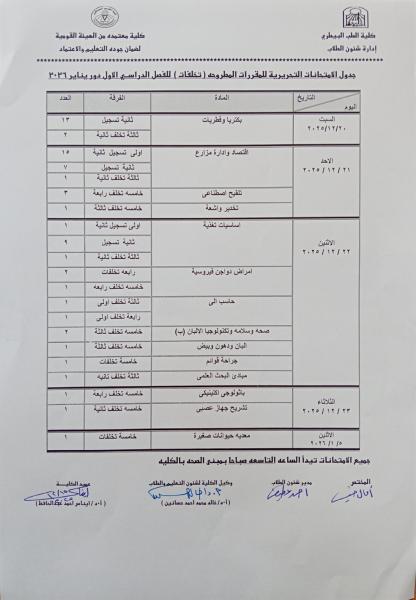
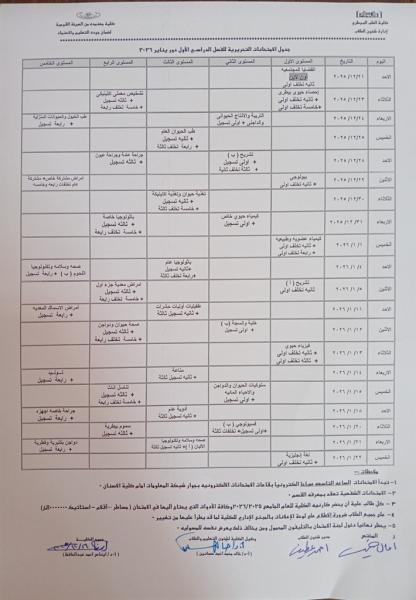
First semester written exam schedules for courses offered for the academic year 2025-2026
ثلاث منح لعام 2015 من دولة المكسيك
First semester written exam schedules for the academic year 2025-2026
سيتم بمشيئة الله تعالي
عقد سيمنار صلاحية رسالة الدكتوراه الخاصة
بالطالب / وضاح محمد محمد النيني
وذلك يوم الأثنين الموافق 2014/06/30م فى تمام الساعة الحادية عشر صباحاً
بقاعة السيمنار بالدور الرابع بقسم الرياضيات بالكلية
Condolences are due

سيتم بمشيئة الله تعالي
عقد سيمنار صلاحية رسالة الدكتوراه الخاصة
بالطالبة / سهير محمد محمود رجب
المدرس المساعد بقسم علم الحيوان - بكلية العلوم - جامعة أسيوط
وذلك يوم الخميس الموافق 2014/06/26م فى تمام الساعة الثانية عشر صباحاً
بقاعة المؤتمرات بالدور الخامس بالمبني الإداري بكلية العلوم - جامعة أسيوط
Invitation to attend researcher Ahmed Abdel-Majeed's seminar to register for his doctoral dissertation topic
The Dean of the College extends her heartfelt congratulations on the occasion of the New Year 2026