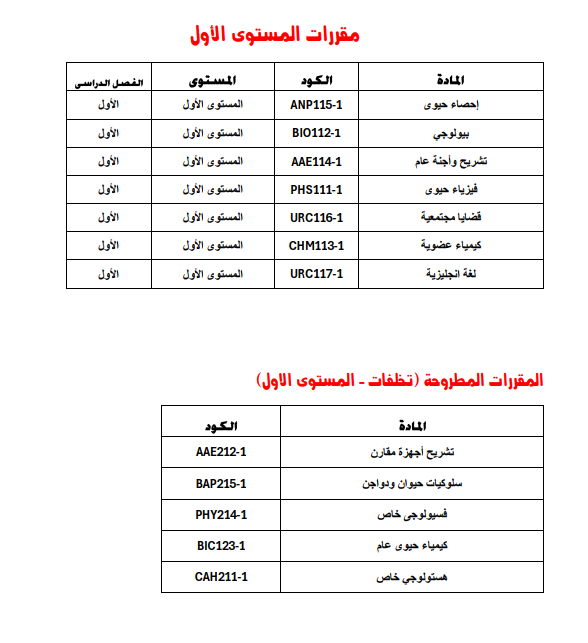
Course codes on the Thinqi platform - Level Two - First Semester 2024-2025

For more details:
http://www.aun.edu.eg/faculty_science/arabic/news.php?id=501537283&screen=5
news category
student
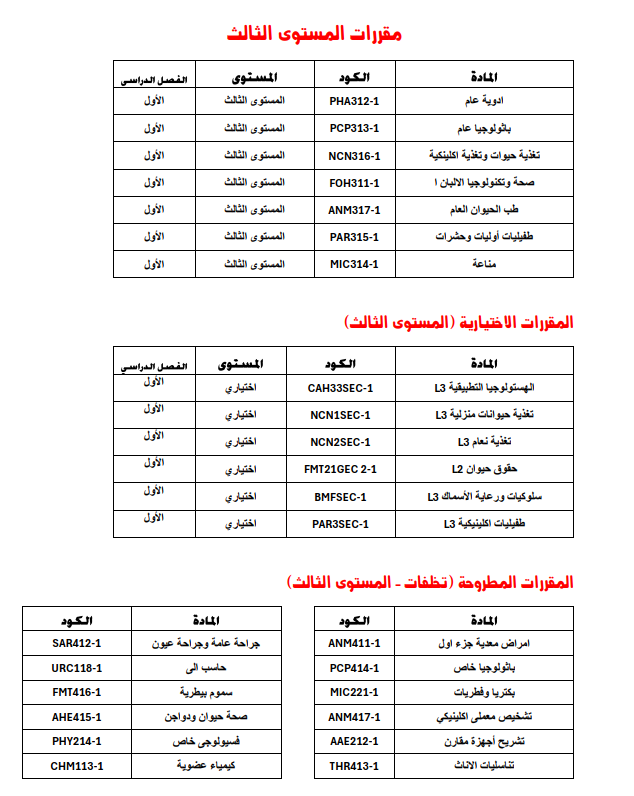
Course codes on the Thinqi platform - Third level - First semester 2024-2025
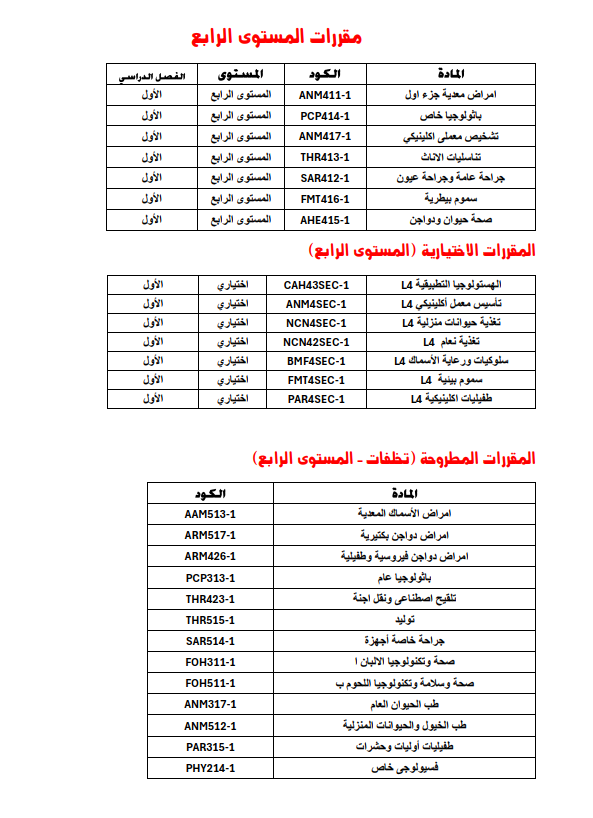
Course codes on the Thinqi platform - Fourth level - First semester 2024-2025
Course codes on the Thinqi platform - Fifth level - First semester 2024-2025
Congratulations to the student Malak Ramadan for winning third place in the Karate Championship
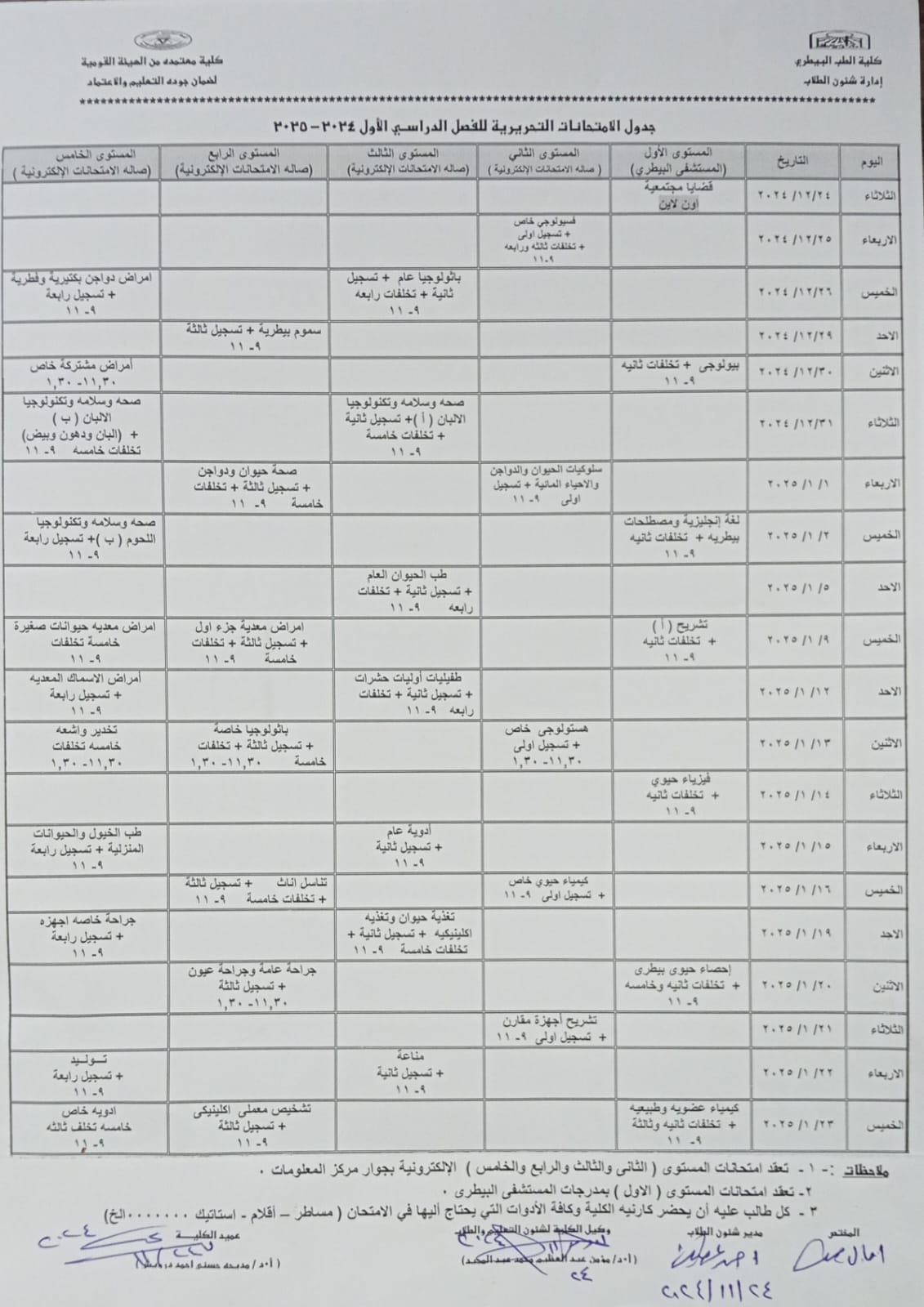
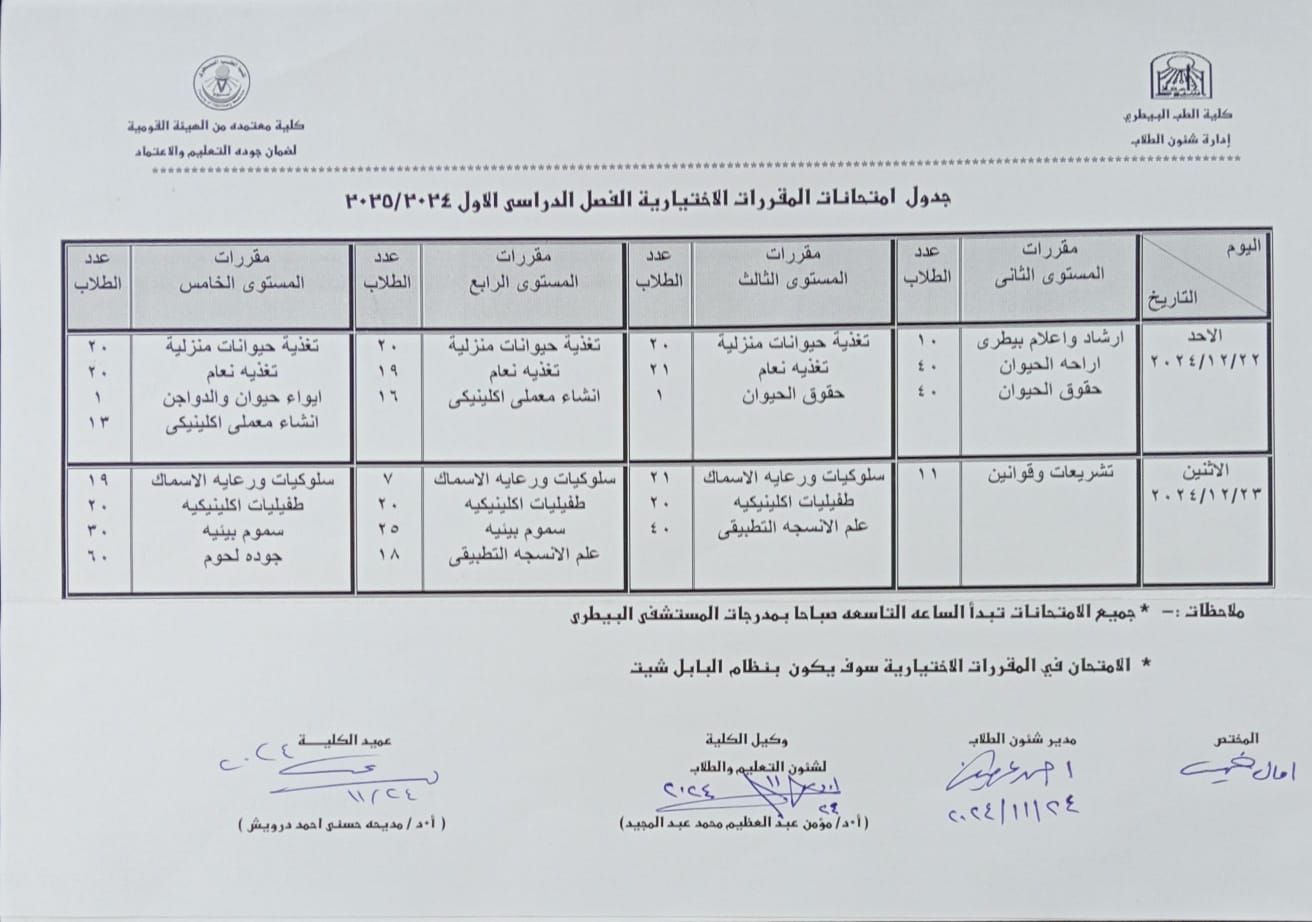
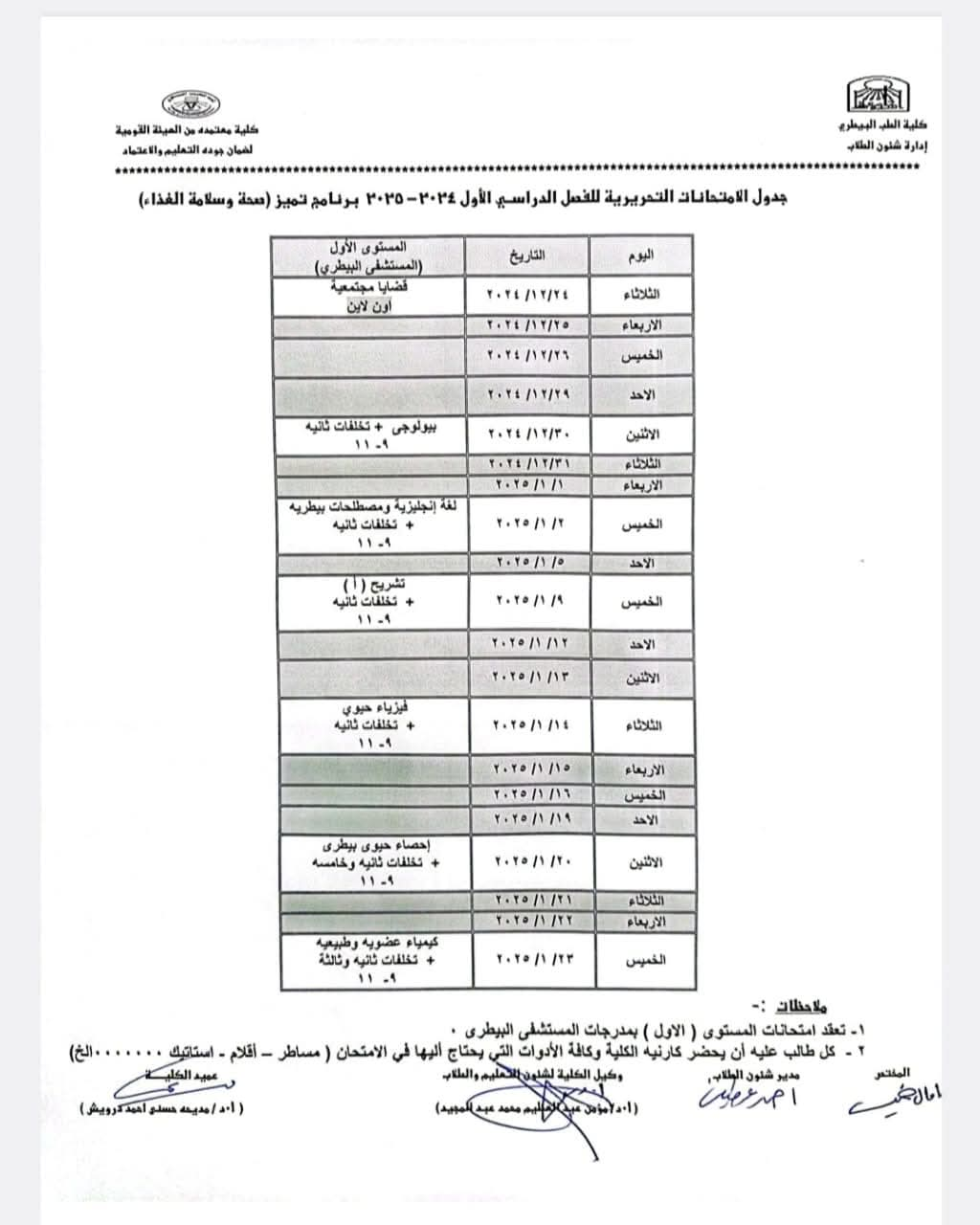
Final Exam Schedule for the First Semester 2024-2025
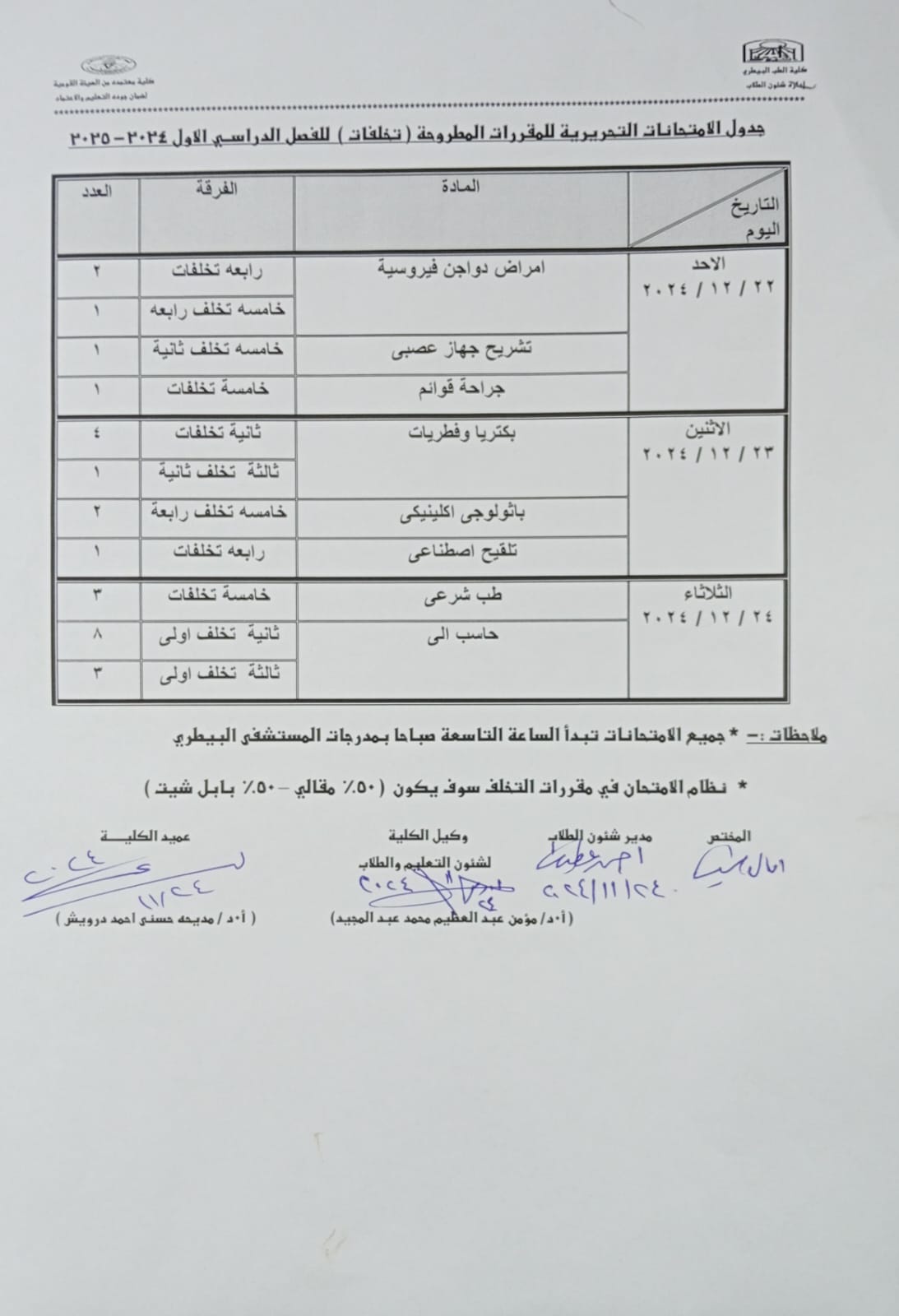
Written Exam Schedule (Offered Courses) First Semester 2024-2025
news category
student