تحت شعار «ابدأ قويًا… استمر قويًا»..
قسم طب الأطفال بالتعاون مع قسم الأمراض الباطنة ينظمان المؤتمر الأول لعلم المناعة والروماتيزم للأطفال والبالغين والكبار
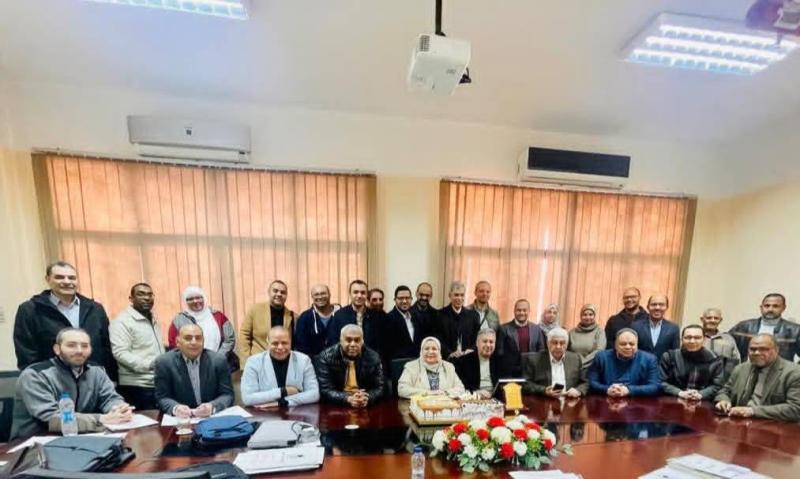
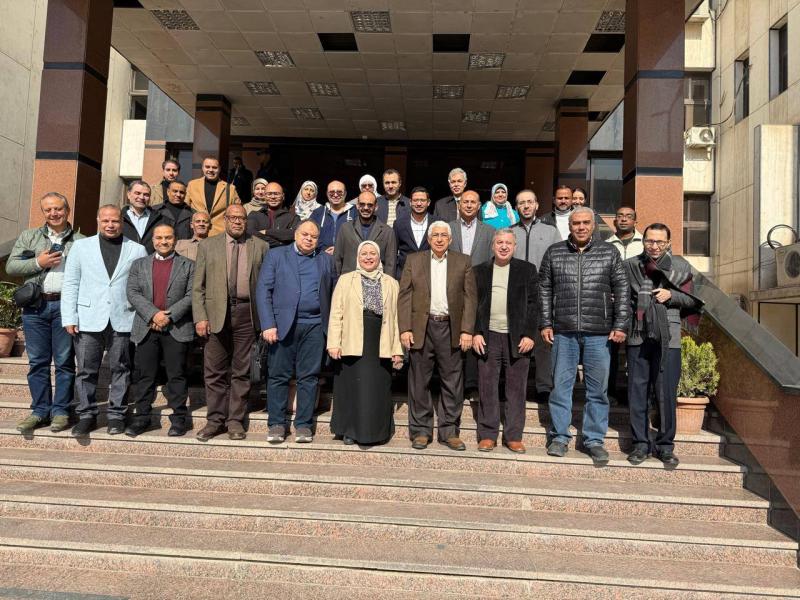
في خطوة علمية رائدة تهدف إلى تعزيز أحدث المفاهيم العلاجية والتشخيصية والتعاون المثمر بين التخصصات العلمية، تنظم وحدتي الحساسية والروماتيزم والمناعة بقسمي طب الأطفال، والأمراض الباطنة بكلية الطب جامعة أسيوط، المؤتمر الأول لعلم المناعة والروماتيزم للأطفال والبالغين والكبار، 1st PAIR، تحت شعار «ابدأ قويًا… استمر قويًا»، وذلك يوم ١٨ يناير، تحت رعاية الأستاذ الدكتور أحمد المنشاوي، رئيس جامعة أسيوط، والأستاذ الدكتور علاء عطية، عميد كلية الطب ورئيس مجلس إدارة المستشفيات الجامعية، والأستاذ الدكتور محمد عبد الباسط خلاف، وكيل كلية الطب لشئون الدراسات العليا والبحوث، والأستاذ الدكتور محمد اليمني، رئيس قسم الأمراض الباطنة، والأستاذ الدكتور جمال عسكر رئيس قسم طب الأطفال.
يشهد المؤتمر مشاركة نخبة من خبراء أمراض المناعة والروماتيزم لدى الأطفال والبالغين والكبار، لمناقشة أحدث المستجدات العلمية والتطبيقات الإكلينيكية في مجال أمراض المناعة والروماتيزم، وفقًا للبروتوكولات العالمية المعتمدة.
يتضمن المؤتمر عددًا من المحاضرات العلمية المتنوعة، منها؛ محاضرة حول التأكيد على أهمية العلاج المبكر والقوي لمرض الذئبة الحمراء وأمراض الروماتيزم، خاصة لدى الأطفال، ومحاضرة يستعرض فيها أحدث التطورات العلاجية في الروماتيزم مجهول السبب، والروماتويد، وأمراض المناعة المختلفة لدى الأطفال والكبار، كما سيشهد المؤتمر جلسة تتضمن مناقشة آليات التشخيص المبكر لنقص المناعة الأولية، وضمان استمرارية الرعاية الصحية عند انتقال المرضى من تخصص طب الأطفال إلى الباطنة، هذا بالإضافة إلى محاضرة حول تسليط الضوء على الأمراض النادرة التي قد تتشابه أعراضها مع أمراض الروماتيزم، مع وضع أسس واضحة لتشخيص حمى البحر المتوسط، مع مناقشة سبل الحفاظ على الخصوبة لدى الفتيات والذكور الذين يحتاجون إلى علاجات مثبطة للمناعة، ومحاضرة حول أحدث ما توصل إليه الطب في تشخيص وعلاج الوذمة الوعائية في ظل تزايد معدلات اكتشاف الحالات في مصر، مع عرض المستجدات الحديثة في علاج مرض بهجت عبر مختلف المراحل العمرية.
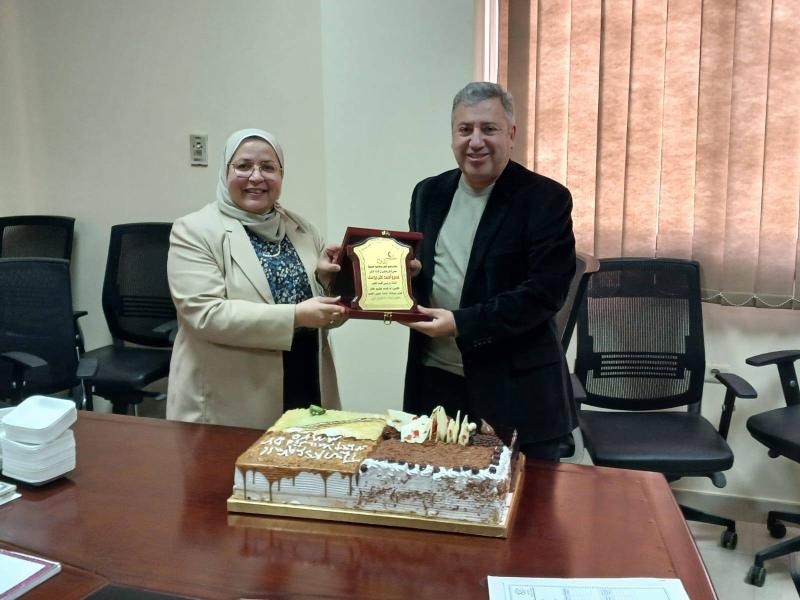
يأتي المؤتمر تحت إشراف الأستاذة الدكتورة نبوية محمود توفيق، أستاذ علم الروماتيزم والباطنة، والأستاذ الدكتور مصطفى السعيد، أستاذ طب الأطفال، رؤساء شرف المؤتمر، والأستاذ الدكتور عمر حردان، أستاذ أمراض الروماتيزم بقسم الأمراض الباطنة، والأستاذة الدكتورة نجلاء سامي عثمان، أستاذ الروماتيزم بقسم طب الأطفال، رؤساء المؤتمر، والأستاذة الدكتورة منال حسانين، أستاذ طب الروماتيزم والتأهيل، سكرتير عام للمؤتمر، فيما تكونت اللجنة المنظمة من الدكتورة آيات صلاح، مدرس أمراض الروماتيزم بقسم الأمراض الباطنة، والدكتورة إيناس محمد، مدرس أمراض الروماتيزم بقسم طب الأطفال.
يأتي هذا المؤتمر تأكيدًا على الدور الريادي لجامعة أسيوط في دعم البحث العلمي والتدريب الطبي المستمر، والارتقاء بمستوى الخدمات الصحية المقدمة لمرضى المناعة والروماتيزم في صعيد مصر وعلى مستوى الجمهورية.
تنطلق فعاليات المؤتمر في التاسعة صباحا، بالمبنى الإداري بجامعة أسيوط .