وحدة أمراض الدم تناقش التحديات القادمة في علم أمراض الدم خلال النسخة الرابعة لمؤتمرها بجامعة أسيوط
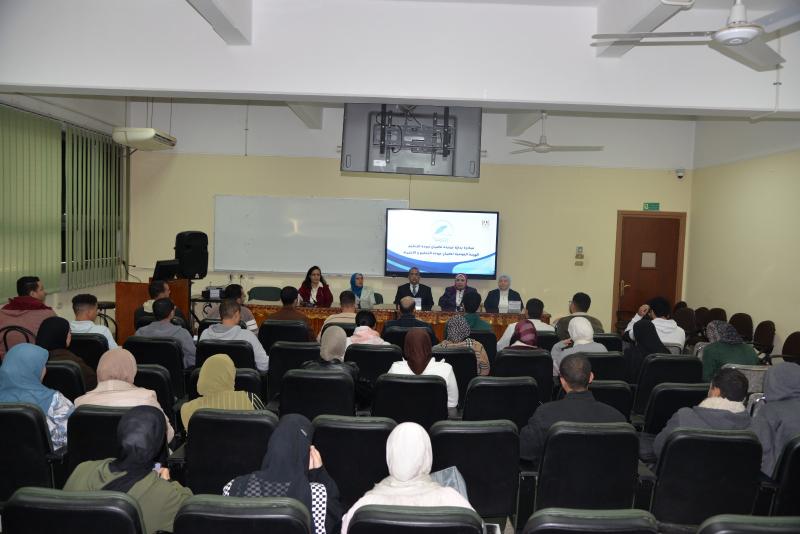
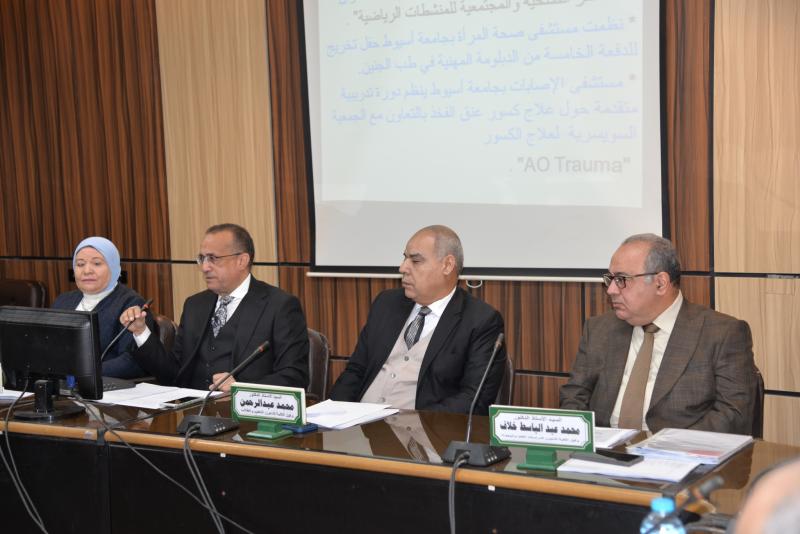
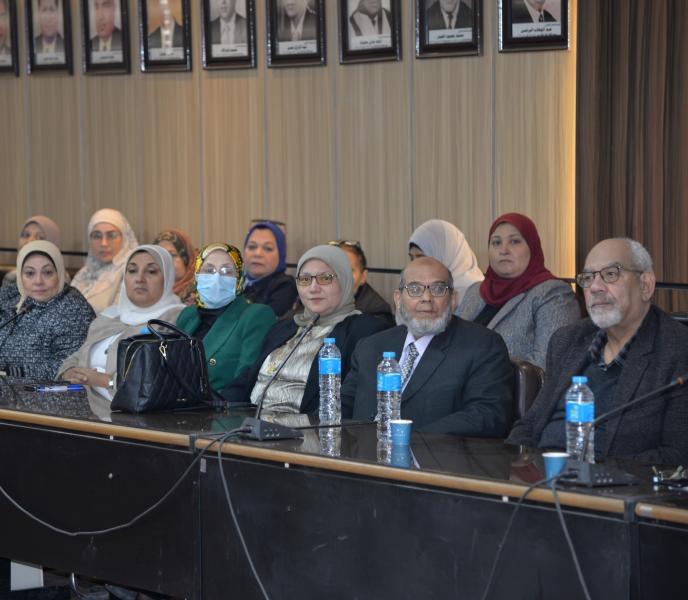
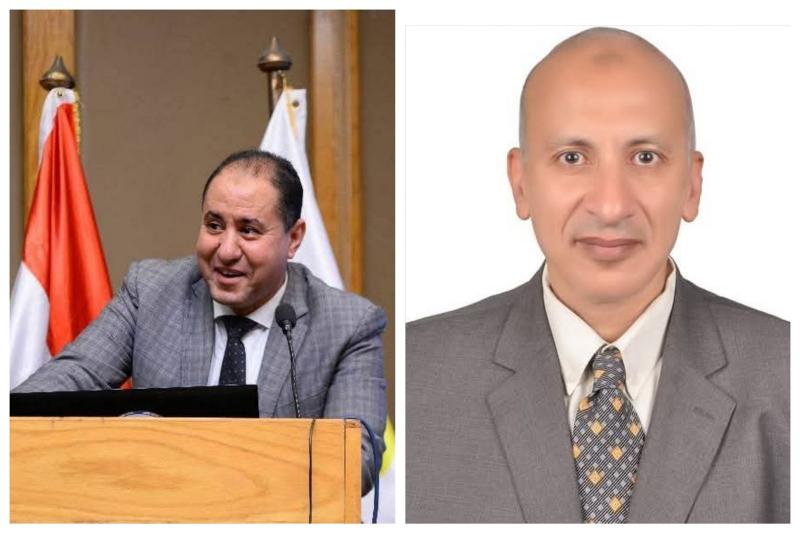
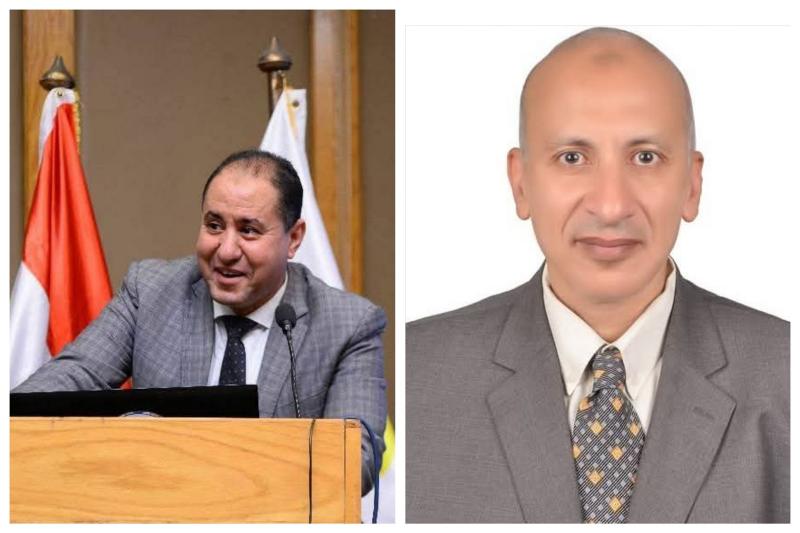
انطلقت فعاليات المؤتمر السنوي الرابع لوحدة أمراض الدم الإكلينيكية بقسم الأمراض الباطنة بجامعة أسيوط، تحت عنوان «التحديات القادمة في أمراض الدم – Upcoming Challenges in Hematology»، وذلك برعاية الأستاذ الدكتور أحمد المنشاوي رئيس جامعة أسيوط، والأستاذ الدكتور علاء عطية، عميد كلية الطب ورئيس مجلس إدارة المستشفيات الجامعية، والأستاذ الدكتور محمد عبد الباسط خلاف، وكيل كلية الطب لشئون الدراسات العليا والبحوث، وتحت إشراف الأستاذ الدكتور محمد اليمني، رئيس قسم الأمراض الباطنة ورئيس المؤتمر، والأستاذ الدكتور محمد رمضان رئيس، وحدة أمراض الدم الإكلينيكية وسكرتير عام المؤتمر.
شهد المؤتمر حضور الأستاذ الدكتور أحمد عبد المولى، نائب رئيس الجامعة لشئون التعليم والطلاب، والأستاذ الدكتور ضياء الدين عبد الحميد، نقيب الأطباء بأسيوط، والأستاذ الدكتور محمد زين، مستشار محافظ أسيوط لشئون السياسات الصحية، إلى جانب نخبة من الأساتذة والأطباء والمتخصصين في مجال أمراض الدم.
خلال كلمته، أشاد الأستاذ الدكتور أحمد عبد المولى، بالدور المحوري والبارز لكلية الطب وما تضمه من أقسام علمية متميزة، مؤكدًا أنها تمثل منبرًا علميًا رائدًا في إعداد كوادر طبية مؤهلة على أعلى مستوى، مشيرا إلى أن جامعة أسيوط تضم منظومة طبية متكاملة تحتوي على ١١ مستشفى جامعي في مختلف التخصصات، وهو ما جعلها تقدم خدماتها الطبية بأعلى جودة لجميع المترددين عليها، مؤكدًا ًعلى حرص إدارة الجامعة على دعم الفعاليات العلمية التي تسهم في تدريب شباب الأطباء ورفع كفاءتهم ومواكبة أحدث المستجدات العلمية.
من جانبه، أكد الأستاذ الدكتور علاء عطية على أن كلية الطب تحرص على تنظيم العديد من الفعاليات العلمية ودعم مختلف الأنشطة، للارتقاء بمستوى الخدمات الطبية والعلاجية المقدمة للمرضى، مضيفا أن أبرز ما يميز كلية الطب هو تكامل خدماتها البحثية والإكلينيكية، مشيرًا إلى أن قسم الأمراض الباطنة من أبرز وأعرق الأقسام بالكلية، ويقدم نموذجًا متميزًا في التفوق العلمي والأكاديمي، حيث يقوم القسم بمنح ١١ درجة علمية ما بين الماجستير والدكتوراه، بما يعكس مدى التقدم العلمي بالقسم.
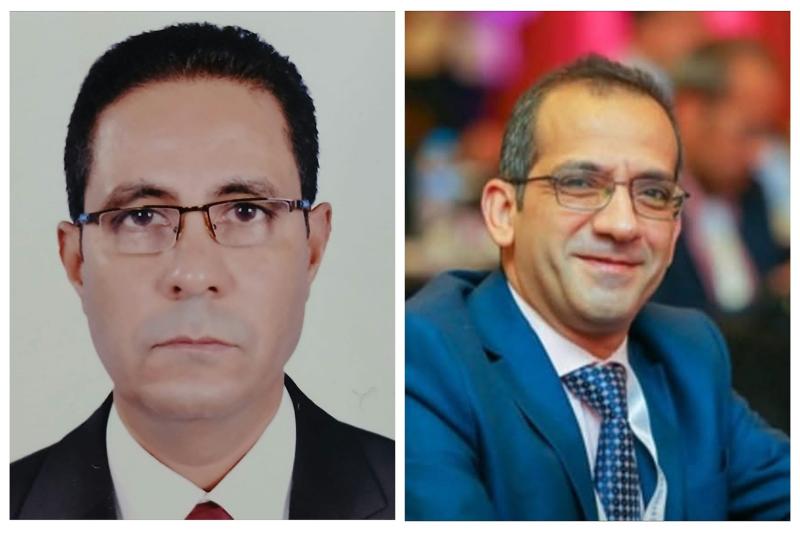
وأكد الأستاذ الدكتور محمد زين أن مستشفيات وزارة الصحة تشهد تعاونا مشتركا ومثمرا مع مستشفيات جامعة أسيوط، مشيرا إلى أن هذا التعاون ساهم في رفع كفاءة الخدمات الصحية المقدمة، وتعزيز التكامل بين المؤسسات الصحية لخدمة المواطنين.
وأوضح الأستاذ الدكتور ضياء عبد الحميد أن جامعة أسيوط تزخر بنخبة متميزة من أعضاء هيئة التدريس في مختلف التخصصات الطبية، الذين يحرصون على تقديم أفضل مستويات الرعاية الصحية للمرضى، مشيرا إلى أن تعدد الروابط العلمية، والتعاون بين التخصصات الطبية المختلفة، يعكس الدور الريادي للجامعة في خدمة المجتمع والارتقاء بالمنظومة الصحية.
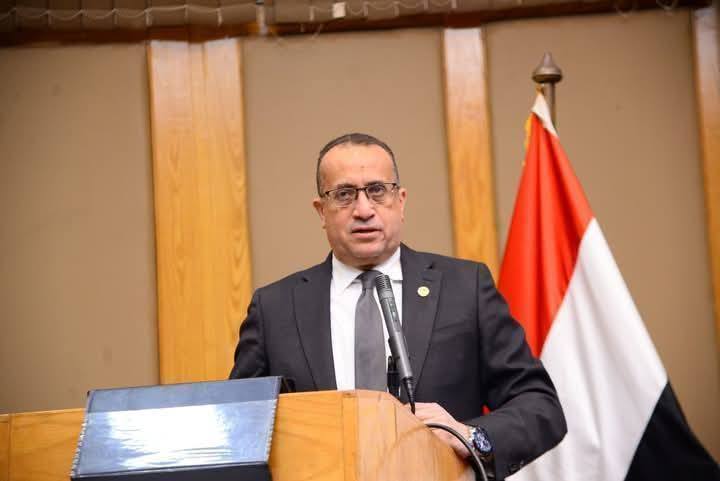
وأضاف الأستاذ الدكتور محمد اليمني أن قسم الأمراض الباطنة يعد بمثابة «القسم الأم» الذي تفرعت منه العديد من التخصصات الدقيقة، ويشكل إحدى الركائز الأساسية بكلية الطب، مشيرًا إلى أن وحدة أمراض الدم تعد من الوحدات المهمة بالقسم، لما تقوم به من دور بارز في تدريب الأطباء، إلى جانب تقديم خدمات طبية ومجتمعية متميزة تخدم المرضى وتلبي احتياجات المجتمع.
وذكر الأستاذ الدكتور محمد رمضان أن مؤتمر هذا العام جاء لمناقشة أحدث المستجدات والتحديات في تشخيص وعلاج أمراض الدم الإكلينيكية، باعتباره مجالا متجددا يشهد تطورا مستمرًا، فضلا عن إتاحة الفرصة لتبادل الخبرات بين المتخصصين بما يسهم في الارتقاء بمستوى الرعاية الصحية المقدمة للمرضى، موجها الشكر لجميع القائمين على تنظيم المؤتمر ودعمهم لنجاح فعالياته.
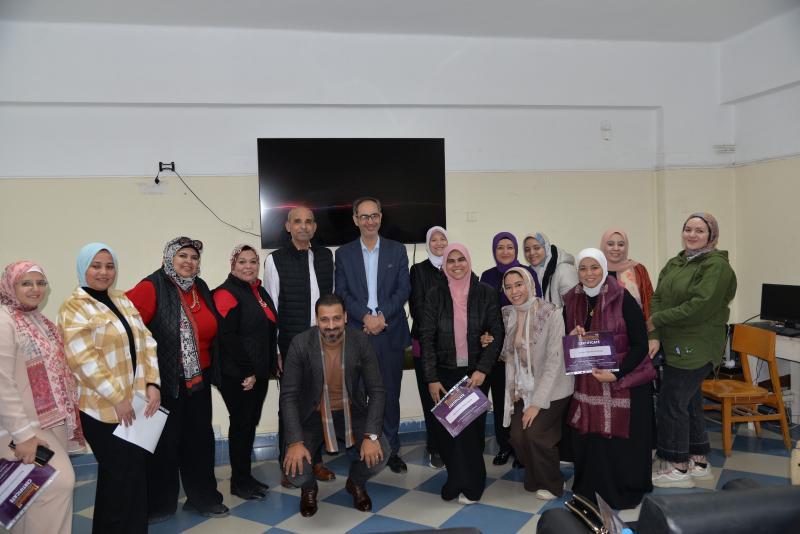
واختُتمت فعاليات المؤتمر بتكريم عدد من القيادات والشخصيات البارزة، حيث تم تقديم الدروع التذكارية لكلٍ من الأستاذ الدكتور أحمد المنشاوي رئيس جامعة أسيوط، والأستاذ الدكتور أحمد عبد المولى نائب رئيس الجامعة لشئون التعليم والطلاب، والأستاذ الدكتور علاء عطية عميد كلية الطب ورئيس مجلس إدارة المستشفيات الجامعية، وتحت إشراف الأستاذ الدكتور محمد اليمني، رئيس قسم الأمراض الباطنة، والأستاذ الدكتور، والأستاذ الدكتور محمد زين مستشار محافظ أسيوط لشئون السياسات الصحية، والأستاذ الدكتور ضياء عبد الحميد نقيب الأطباء بأسيوط، تقديرا لدورهم وجهودهم في دعم وإنجاح فعاليات المؤتمر.
جدير بالذكر، أن المؤتمر في نسخته هذا العام ناقش من خلال أربع جلسات علمية متخصصة، أحدث المستجدات في أمراض الدم الحميدة والخبيثة، واضطرابات النزف والتجلط، وأمراض الغدد الليمفاوية، والخلل المناعي المزمن بعد العلاج الكيماوي.









 Do you have any questions?
Do you have any questions? 


















