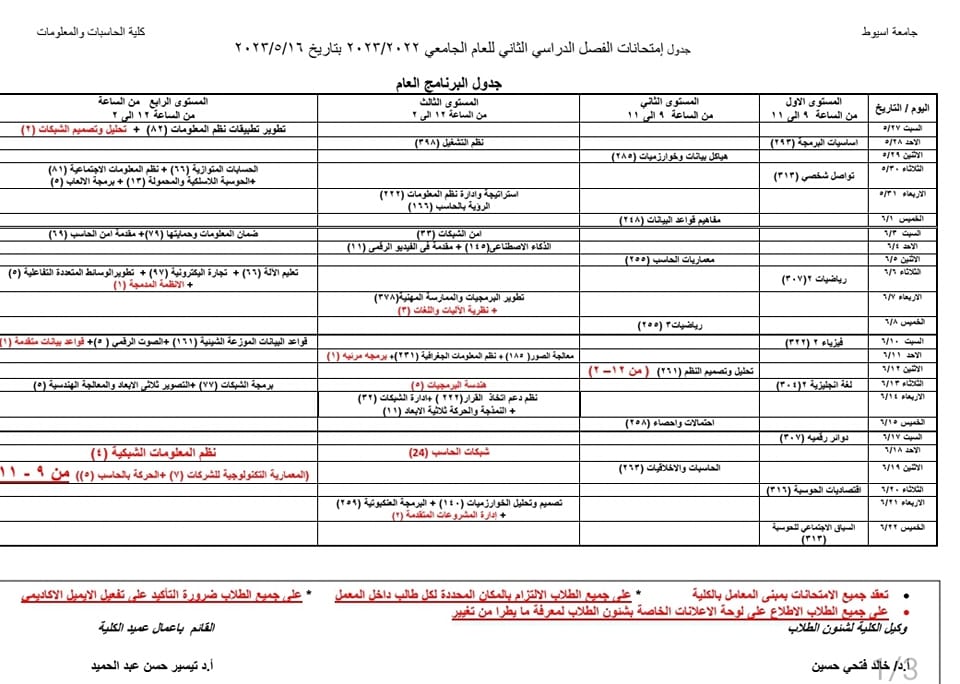
جدول إمتحانات الفصل الدراسي الثانى2022-2023 البرامج الخاصة
Examination schedule for the second semester 2022-2023 special programs
Practical exams schedule for the second term 2022/2023 General program schedule
Practical exams schedule for the second term 2022/2023
Examination schedule for the second semester 2022-2023, Al-Ahlia University
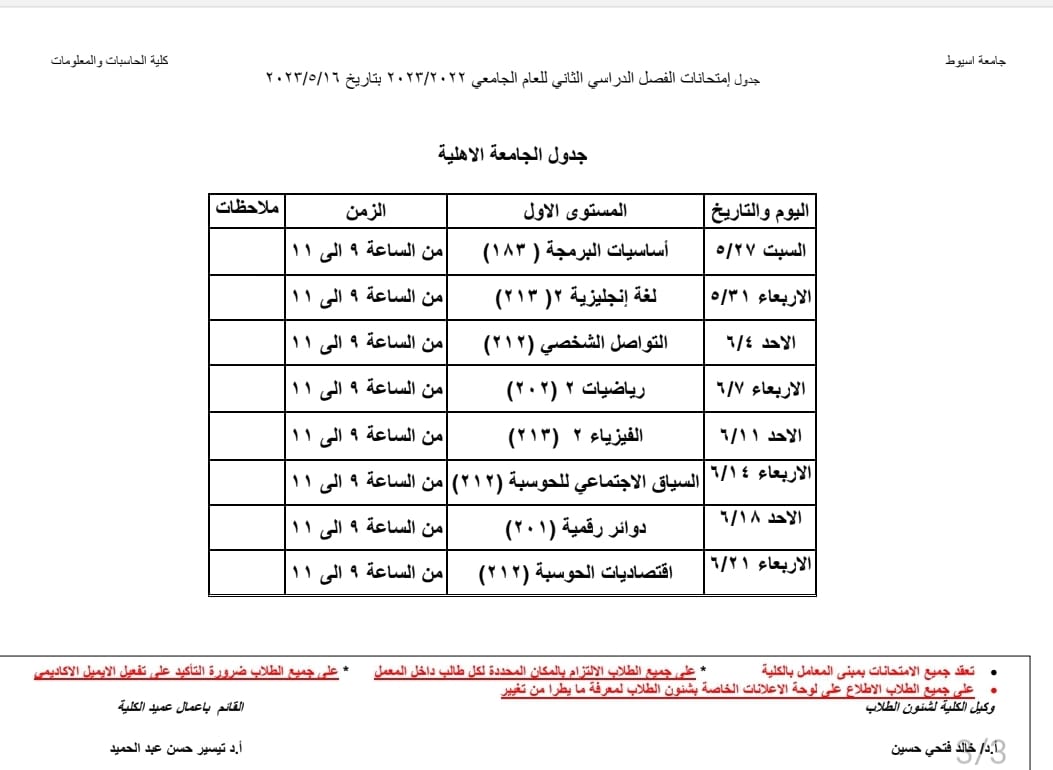
جدول إمتحانات الفصل الدراسي الثانى 2022-2023 الجامعة الاهلية
The Information Technology Institute announces the opening of registration to grant intensive training in distinguished technological specializations to graduates of Egyptian universities from 2014 to 2023 at the Institute's headquarters

**** دورات تدريبية مقدمة بمحافظة أسيوط ****
يعلن معهد تكنولوجيا المعلومات عن فتح باب التسجيل لمنح التدريب المكثف في تخصصات تكنولوجية متميزة لخريجي الجامعات المصرية من عام ٢٠١٤ وحتى عام ٢٠٢٣ بمقر المعهد بمحافظة أسيوط، وهي كالآتي:
UI/UX Designer
لمزيد من المعلومات حول التخصص ادخل على الرابط التالي:
https://drive.google.com/.../1qXHm8t3j0k9sCjrxOAs.../view...
Software Engineering Fundamentals
لمزيد من المعلومات حول التخصص ادخل على الرابط التالي:
https://drive.google.com/.../1S8g.../view...
E-Learning
لمزيد من المعلومات حول التخصص ادخل على الرابط التالي:
https://drive.google.com/.../1TbPRffsjQu1YVKkx8gU.../view...
Frontend & Cross-Platform Mobile Development
لمزيد من المعلومات حول التخصص ادخل على الرابط التالي:
https://drive.google.com/.../1bSC.../view...
- المستندات المطلوبة ومراحل التسجيل موضحة برابط التسجيل
- نظام الحضور بالدورات التدريبية هو نظام مختلط Blended Learning
- يبدأ التسجيل اعتباراً من يوم الأحد الموافق ١٤ مايو ٢٠٢٣ ويستمر حتى يوم الأربعاء الموافق ٢٤ مايو ٢٠٢٣
- يتم التسجيل من خلال الرابط التالي على الموقع الرسمي لمعهد تكنولوجيا المعلومات
Congratulations to Dr. Ali Hussein Bakhit
The College of Computers and Information welcomes the guests of the judging committees for the best environmentally friendly university competition
A final schedule for mid-term exams for the second semester 2022/2023
The opening of the Vice President for Education and Student Affairs exhibition of hand-painting
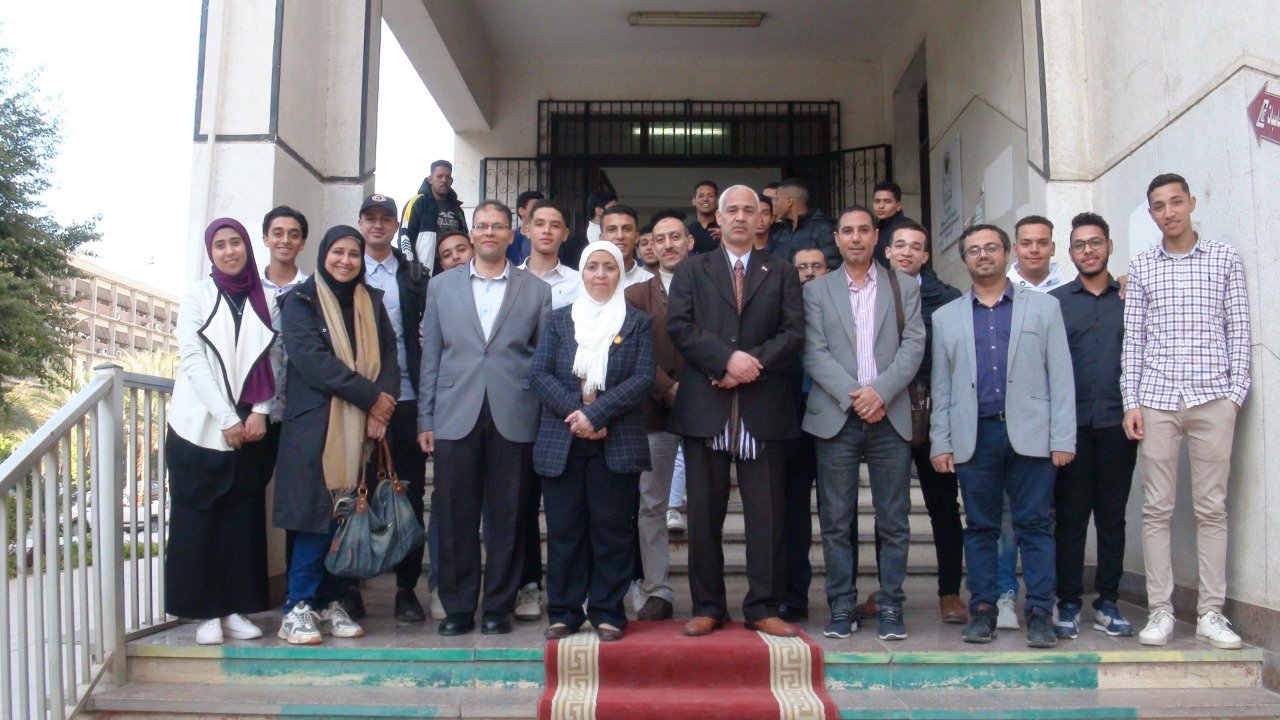

It opened today, Tuesday, 12/27/2022
Prof. Dr. Ahmed Abdel Mawla, Vice President for Education and Student Affairs
Hand drawing exhibition for students of the Faculty of Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Al-Ahlia University, Assiut
Where he was received by Mrs. Prof. Tayseer Hassan, Dean of the Faculty of Computers and Information, Assiut University, and Program Coordinator
And Mr. Dr. / Khaled Fathi, Vice Dean of the College of Computers and Information for Education and Student Affairs
And a group of faculty members and students, within the framework of His Excellency's keenness to encourage students and continuous participation in student activities and urge them to further creativity and development