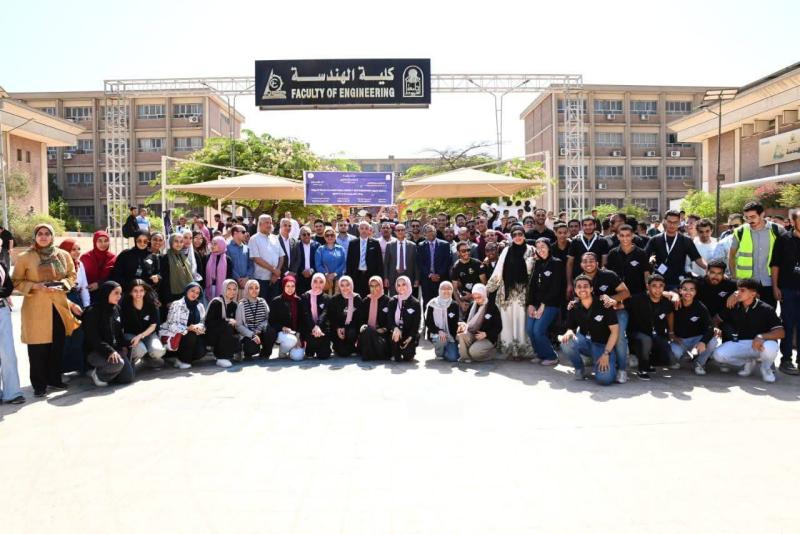
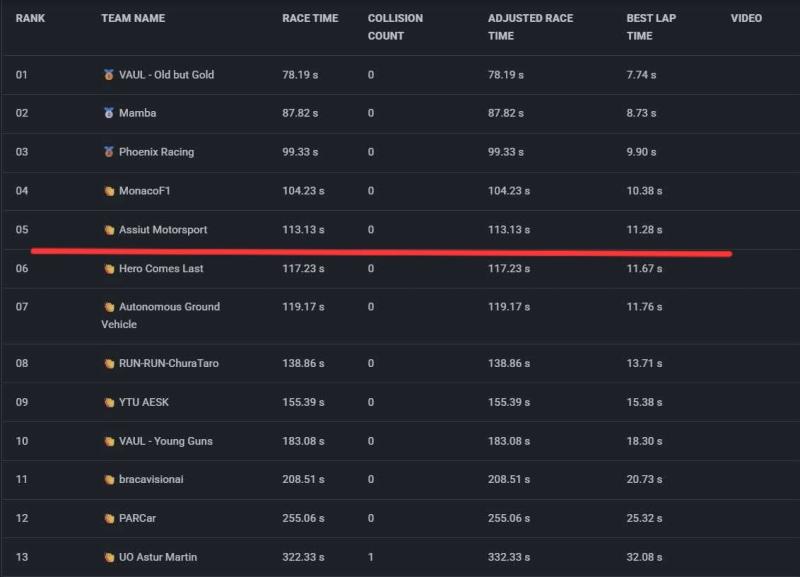
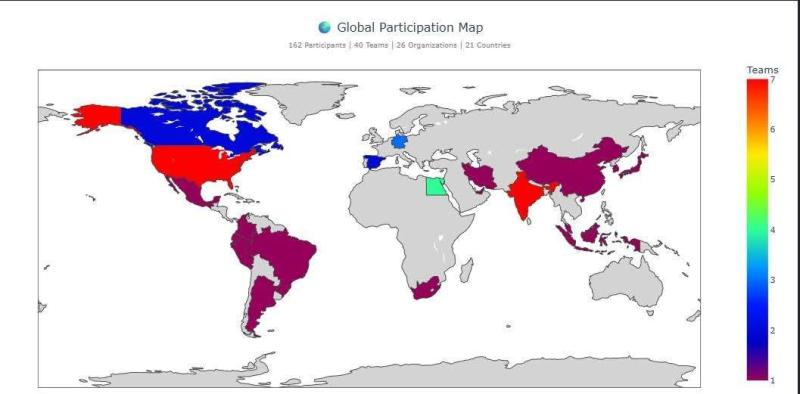
The Assiut Motorsport team achieved fifth place globally and first place among Egyptian universities in the Roboracer Sim Racing CDC TF 2025 international competition, part of the AutoDRIVE Ecosystem, held concurrently with the IEEE CDC conference. Forty teams from 21 countries participated in the competition.
The competition involved developing an autonomous AI algorithm capable of driving a car on a track at maximum speed and without errors, through programming and path planning.
The RoboRacer competition is an international competition organized by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers).
It is open to undergraduates, hobbyists, graduate students, and others, with a maximum of five team members. Participation can be entirely remote or in the host country (Romania). The team participated remotely.
Professor Dr. Khaled Salah, Dean of the Faculty, expressed his delight with the team and its honorable achievements, as well as its outstanding representation of Egypt, the university, and the faculty. He commended the efforts of all team members and their leader, student Mohamed Wael.
The Dean also expressed his deep gratitude to the university leadership, represented by Professor Dr. Ahmed El-Menshawy, President of the University, and Professor Dr. Ahmed Abdel-Mawla, Vice President for Education and Student Affairs, for their continuous support of student scientific activities.
Furthermore The Dean of the College expressed his gratitude to all those involved in student activities at the college, under the supervision of Professor Dr. Mohamed Safwat Abu Raya, Vice Dean for Education and Student Affairs, the team's academic supervisor, Dr. Gamal Abdel Nasser, the Student Welfare Department, and the department's scientific activity coordinators.
It is worth noting that the Assiut Motorsport team was first established in 2018 and consists of 80 students. The team participated in the electric car rally competition, which included 22 teams from Egyptian universities, in 2020, 2022, and 2024. The team has also participated in numerous international competitions, achieving high rankings.
Furthermore, the team participated in the Formula July 2025 competition and secured 15th place out of 42 teams. They are now aiming to participate in the Silverstone Formula Student competition.
The Assiut Motorsport team is one of the college's most active scientific teams, operating under the umbrella of the Student Union's Scientific Committee and with the academic supervision of Dr. Gamal Abdel Nasser and his assistants. At the college, and under the administrative supervision of the Scientific Activity Department of the Student Welfare Administration at the college.