Abstract
Background : Home bleaching is a promising option for addressing discolored teeth conservatively. However, its
impact on the physical and mechanical properties of indirect restorations remains unknown. This study provides
comparative insights into the material responses to aesthetic treatments by assessing the effects of home bleaching
agents on two hybrid ceramics: VITA ENAMIC® and Grandio Blocs. The focus is on evaluating color stability and biaxial
flexural strength.
Methods : 60 discs (12 × 1 mm) were prepared from hybrid ceramics. Specimens were divided into two groups
according to type of hybrid ceramic (30 specimens in each group); group A: VITA ENAMIC®, group B: Grandio Blocs.
Each group was further subdivided into 3 subgroups according to the concentration of home bleaching agents used
(10 specimens in each subgroup); subgroup C: unbleached control group, subgroup C10%: carbamide peroxide 10%
bleaching agent, and subgroup C35%: carbamide peroxide 35% bleaching agent. Samples of subgroup C10% were
bleached with Home Bleaching Opalescence PF (10%) for 8 h per day for 14 days, as directed by the manufacturer.
Samples of subgroup C35% were bleached using WHITEsmile Carbamide Peroxide (35%), following the manufacturer’s
directions for 30 min every day for 14 days. Color change (ΔE) was assessed using of the CIE L*a*b* system. Then, the
biaxial flexural strength test was done. The data were analyzed using two-way ANOVA tests and Weibull analysis.
Results: VITA ENAMIC samples exhibited significantly higher color change than Grandio Blocs (p < 0.001), while
Grandio Blocs showed significantly higher biaxial flexural strength (p < 0.001). The concentration of the bleaching
agent had no significant effect on color change (p = 0.086). However, regardless of its concentration, bleaching
significantly reduced biaxial flexural strength in both materials (p < 0.001). Weibull analysis showed that Grandio Blocs
had higher characteristic strength, while VITA ENAMIC demonstrated more reliable failure behavior.
Conclusions: Compared to Grandio Blocs, VITA ENAMIC® exhibited a greater color change with both 10% and 35%
carbamide peroxide home bleaching agents. Additionally, both concentrations of carbamide peroxide reduced the
biaxial flexural strength of hybrid ceramics. These findings can guide clinicians in selecting hybrid ceramics based
on clinical demands for aesthetics and durability. VITA ENAMIC® offers greater structural reliability and predictability
for aesthetic restorations, while Grandio Blocs provide superior durability and stress resistance for high-stress clinical
applications.

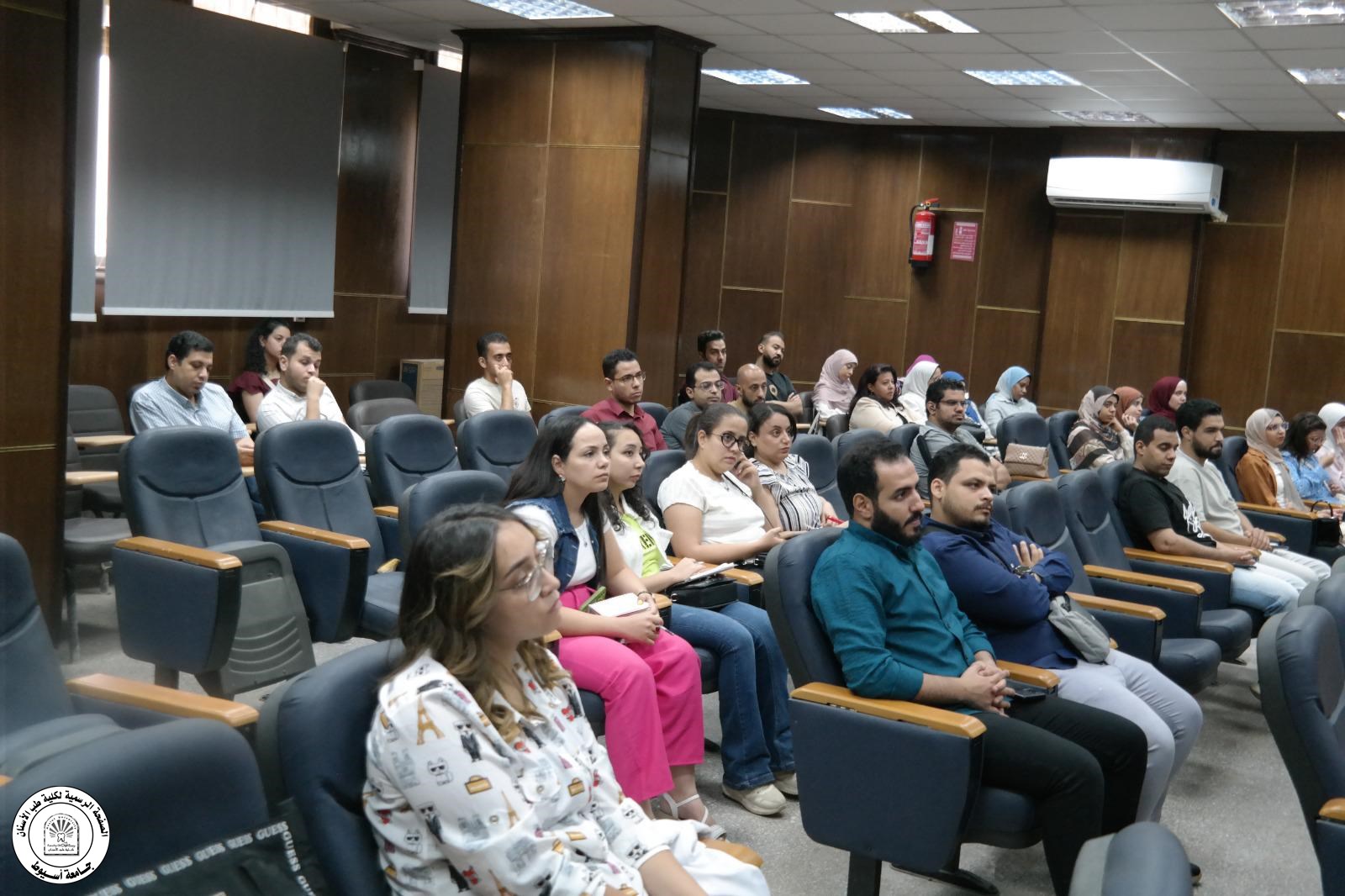
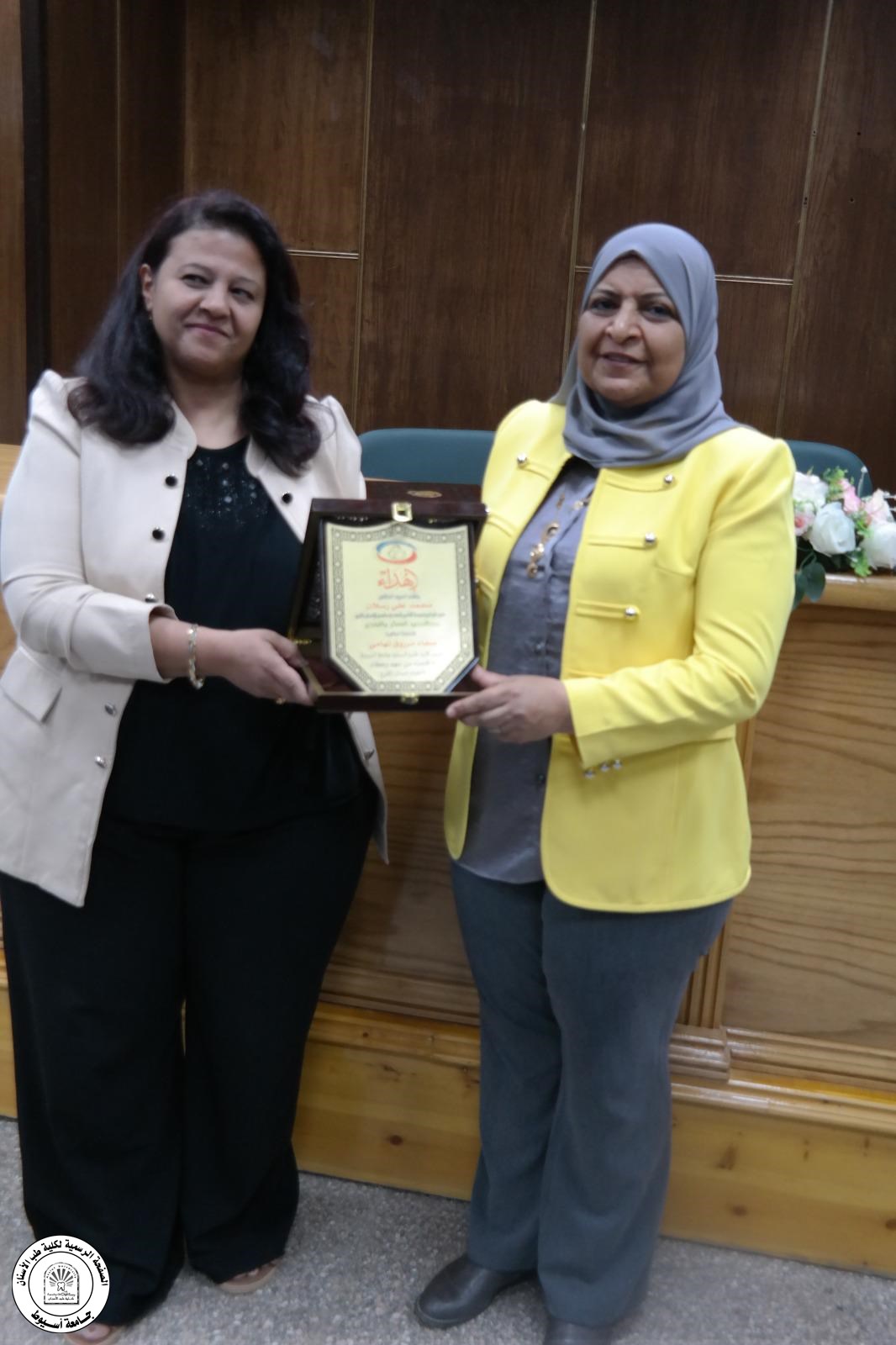
بحضور معالي الأستاذ الدكتور / صفاء تهامي - عميد الكلية - اختتام فعاليات الأيام العلميه لأطباء وزارة الصحه و التأمين الصحي تحت رعاية أ.د أحمد المنشاوي - رئيس الجامعه أ.د محمود عبد العليم - نائب رئيس الجامعه لشئون خدمة المجتمع و تنمية البيئة أ.د صفاء تهامي - عميد الكلية أ.م.د محمد ناهض عطيه - وكيل الكلية لشئون خدمة المجتمع و تنمية البيئة استكمالا لخطة قطاع خدمة المجتمع و تنمية البيئه بكلية طب الأسنان للعام الجامعي ٢٠٢٤ - ٢٠٢٥ و التي تتضمن المساهمه في رفع كفاءة اطباء الأسنان بالمحافظه و المشاركه في التعليم الطبي المستمر لجميع الخريجين ، بفضل من الله انتهت فعاليات اليوم العلمي السابع و الأخير الذي نظمه قطاع خدمة المجتمع و تنمية البيئه لأطباء الأسنان بوزارة الصحه و التأمين الصحي … حاضر في هذا اليوم أ.م.د / محمد ناهض عطيه - أستاذ مساعد جراحة الفم و الوجه و الفكين - حيث القي سيادته محاضره عن التعامل الآمن في تخصصات طب الأسنان المختلفه مع مرضي القلب شهد اليوم حضور أكثر من ٥٠ طبيبا من وزارة الصحه و التأمين الصحي بالإضافه إلي أعضاء الهيئة المعاونه و أطباء الإمتياز بالكليه و علي هامش اختتام فعاليات الأيام العلميه قامت مشكوره الدكتوره نيڤين كمال عبد السيد - مسئول قطاع الأسنان بالتأمين الصحي و الدكتور حمزه حسن نيابا عن الدكتور محمد علي رسلان - مدير عام الهيئة العامه للتأمين الصحي فرع وسط الصعيد بتسليم درع التأمين الصحي لمعالي الأستاذ الدكتور - صفاء تهامي - عميد الكلية و الأستاذ الدكتور محمد ناهض عطيه - وكيل الكلية لشئون خدمة المجتمع تقديرا لجهود سيادتهم في خدمة أطباء الأسنان بالمحافظه و بدورها تقدمت معالي الاستاذ الدكتور عميدة الكلية بالشكر و العرفان لهذه اللفته الكريمه و تقدمت بالشكر لجموع الأطباء علي حضورهم المميز و حرصهم علي تحصيل العلم و أضاف الأستاذ الدكتور وكيل بالكلية بأنه سيتم إضافة ورش العمل و تطوير الايام العلميه للأعوام القادمة بمشيئة الله تعالي دمتم في حفظ الله و امنه







تحت رعاية
أ.د أحمد المنشاوي - رئيس الجامعه
أ.د محمود عبد العليم - نائب رئيس الجامعه
لشئون خدمة المجتمع و تنمية البيئة
أ.د صفاء تهامي - عميد الكلية
أ.م.د محمد ناهض عطيه - وكيل الكلية لشئون خدمة المجتمع و تنمية البيئة
يعلن قطاع خدمة المجتمع و تنمية البيئه بكلية طب الأسنان عن الإنتهاء من فعاليات ثامن القوافل الطبيه و التوعويه التي نظمها القطاع بالتعاون مع مستشفي الأطفال الجامعي
تأتي هذه القافلة ضمن خطة قطاع خدمة المجتمع لتسيير قوافل طبيه تستهدف العاملين بالمستشفيات الجامعيه و المرضي بالأقسام المختلفه
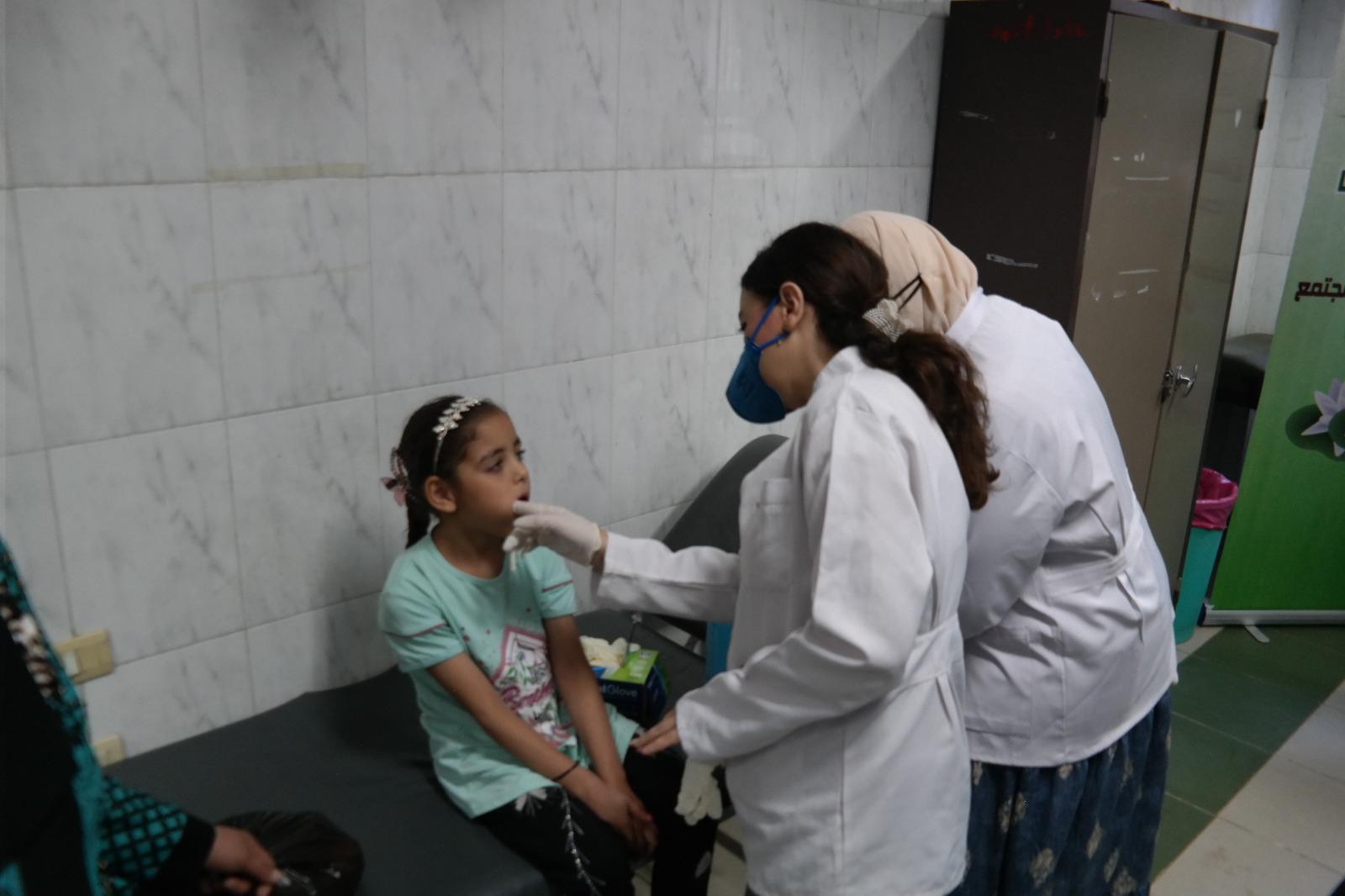
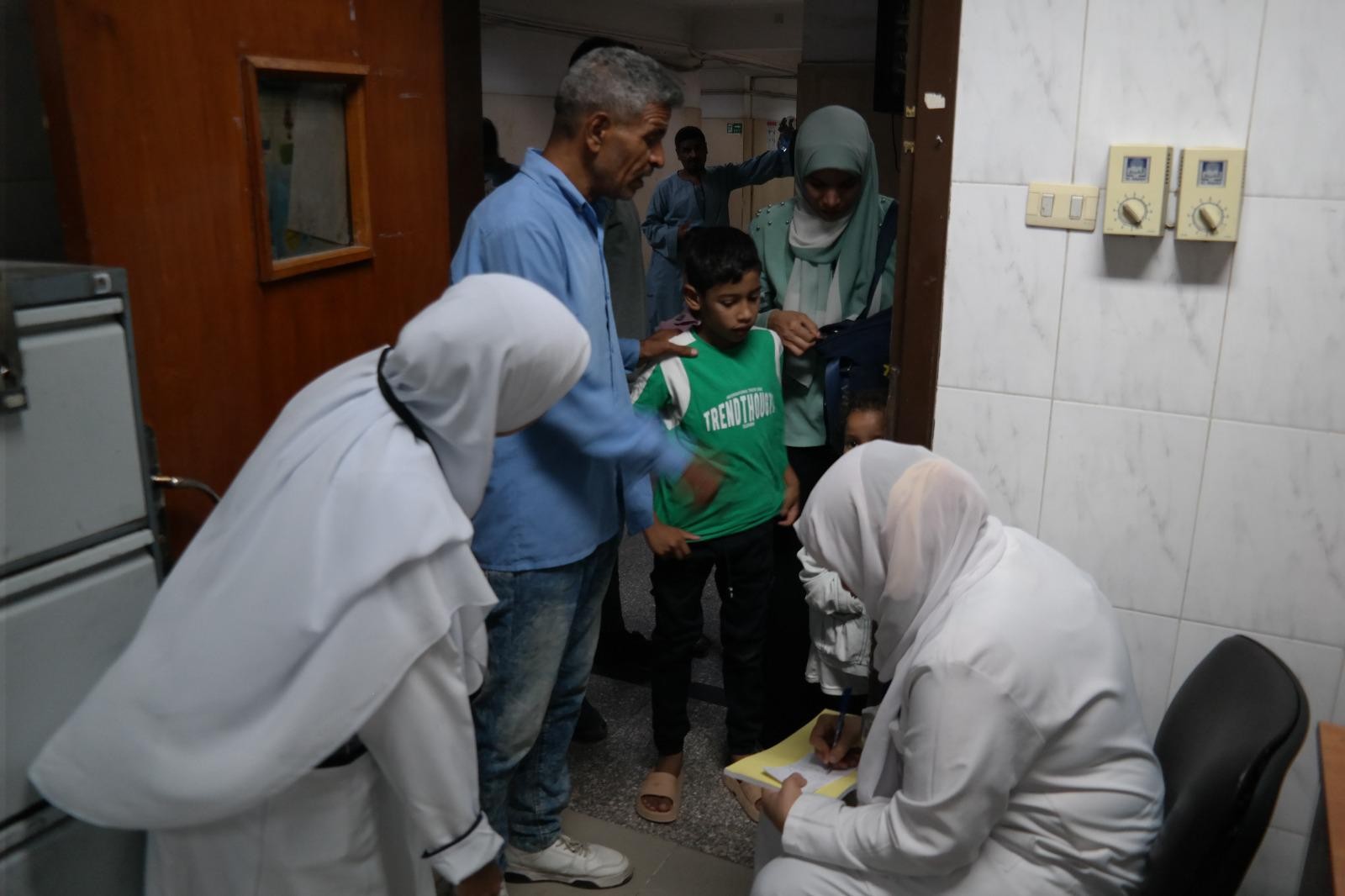
استقبلت القافله أكثر من ١٠٠ طفل ، قدمت خلالها خدمات التشخيص و الخدمات توعوية للأطفال و أولياء الأمور بالإضافه إلي تحويل الحالات التي تتطلب امكانيات و اجراءات علاجيه معينه إلي مستشفي طب الأسنان الجامعي لتلقي الخدمات العلاجيه الازمه.
أشرف علي القافله أ.م.د محمد ناهض عطيه - وكيل الكلية لشئون خدمة المجتمع و تنمية البيئه و د. محمود القاضي - مدرس العلاج التحفظي
خالص الشكر و التقدير و العرفان لأعضاء الهيئة المعاونه و الأطباء المقيمين المشاركين في القافله:
- ط/ چورچ ناصر ( طب الفم و أمراض اللثه )
- ط/ رحاب عاطف ( التركيبات المتحركه )
- ط/ عبد الرحمن محروس ( طب أسنان الأطفال )
- ط/ مورا مجدي ( التركيبات الثابته )
- الطالبه / وعد حيدر ( الفرقه الثانيه )
- الطالبه / إيريني مجدي ( الفرقه الخامسه )
دمتم في حفظ الله و امنه