Complaints and suggestions
Announcement of writing in the Arab magazine for boys 2023
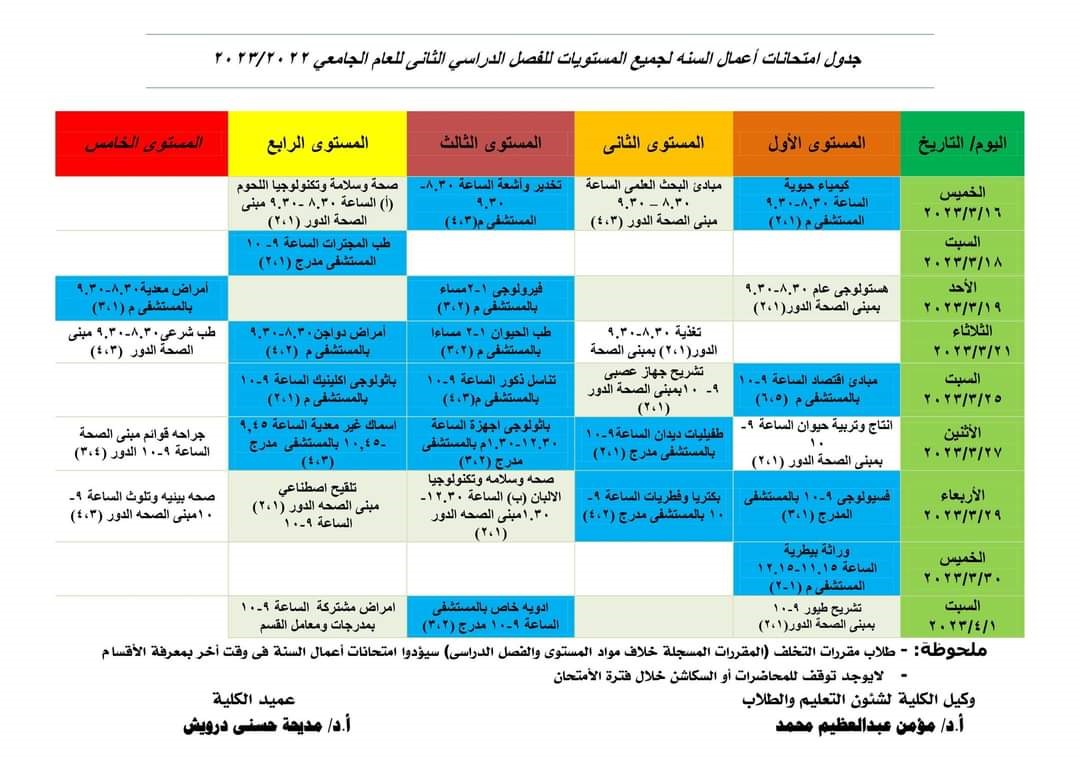
Midterm Examination schedule for all levels, second semester 2022-2023
The announcement of the National Training Academy for the training program Women Lead the Executives
Changes in clinicomorphometrical findings, lipid profiles, hepatorenal indices and oxidant/antioxidant status as thermoregulatory adaptive mechanisms in poikilothermic Dabb lizard (Uromastyx aegyptia)
Wildlife has exposed to various environmental stressors. Reptiles (ectothermic) are highly susceptible
to climatic changes due to their behaviour, physiology, and life history that were so heavily reliant
on the ambient environmental temperature. The present work aims to monitor different biochemical
and haematological indices of Dabb lizards (Uromastyx aegyptia) at various thermal gradients as well
as their adaptation to oxidative stress. This has been reflected through assessment of their impact on
some adaptive physiological traits i.e. thermoregulation, and muscle metabolic biomarkers, blood
pictures and oxidant/antioxidant status. This experiment is carried out on non-hibernating adult male
Dabb lizards (U. aegyptia; n = 24) of age of 18–24 months. These Dabb lizards are divided into four
equal groups (n = 6 for each one) where they are exposed to different thermal treatments for one week
as following; control group [Exposed to terrarium temperature 38–39 °C], low temperature exposed
group [Exposed to 12–14 °C], Gp. C; moderate temperature exposed group [Exposed to 41–43 °C] and
high temperature exposed group [Exposed to 43–45 °C]. Each independent group (n = 6) are kept at
separated glass terraria. The investigated lizards are monitored for body temperature, morphometric
measurements i.e. body weight (g) and total body length (cm; TBL), muscle biochemical analysis,
haematological pictures indices and serum biochemical assays including mainly oxidant/antioxidants
biomarkers throughout the current experiment. The results state that the thermoregulatory behaviour
of Dabb varies with the increase of concentration of muscular metabolic enzymes. In low temperature
exposed group, the increase in red blood corpuscles (RBCs), haemoglobin concentrations (Hb),
white blood cell (WBC), serum antioxidant biomarkers and anaerobic Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
enzyme are associated with a marked reduction in serum levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides
(TGs), total proteins (TPs), albumin, glucose and electrolytes. In moderate temperature exposed
group, a significant elevation in serum values of TC, TGs, TPs, glucose, urea and uric acids levels are
mentioned. In high temperature exposed Dabb group, a remarkable increase in blood values of RBCs,
Hb, haematocrit value (HCT), WBC, T. chol., TGs, TPs, glucose, urea, uric acids, triiodothyronine (T3)
and thyroxine (T4) levels are also observed. Moreover, significant increases in muscular anaerobic/aerobic metabolic enzymes as well as stimulation of antioxidant defence system have been reported.
Different significant correlations have been stated between variably estimated laboratory indices
in the investigated Dabb lizards under different thermal treatments. The study concludes that the
Dabb lizards have a strong antioxidant defence system and undergo physiological thermoregulatory
adaptive mechanisms, that involve biochemical and metabolic acclimatization as a response to
environmental temperature changes that act as a protective mechanism against oxidative stress as
well as maintained homeostatic responses and normal physiological functions.
Diagnostic investigations of lumpy skin disease in crossbred‑cattle infected with Theileria annulata infection
The current work was carried out to reveal-up the probable cause that increases the seriousness of lumpy skin disease (LSD) in crossbred dairy cattle in villages of Assiut and Sohag Governorates, Upper Egypt. The serious form of LSD infected twenty-eight crossbred dairy cows. Diagnosis is based on the clinical background and histopathology. All cows were adult and previously vaccinated against LSD using the sheep pox “Romanian-strain” vaccine. Clinically, enormous numbers of hideous necrotic dermal lesions, similar to starred-shaped craters, were the prominent signs of the diseased cases in association with systemic reactions anorexia pyrexia, tachycardia, tachypnea, and edematous lymphadenitis in superficial nodes. Detailed clinical findings are described. Histopathologically, fibrinoid vasculitis, with severe perivascular mononuclear inflammatory cellular infiltration and ambulance of eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions in the dermis were conspicuously histopathological findings. Blood films and lymph smears of the diseased cases revealed both erythrocytic and lymphocytic forms of Theileria infection. Theileria annulata was identified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Theileria annulata infection and LSD interactions were discussed. This tick-borne-protozoan is an endemic infection in our villages and plays a pivotal role in the frustration of the humoral and cell-mediated immune statuses of the infected cattle inducing a reduction of the efficiency of the applied vaccine, and increasing the seriousness of the endemic lumpy skin disease. A national strategy for reducing or minimizing the infection rate with Theileria infection should be warranted in paralleling vaccination programs to avoid the insufficiency of immune responses. The current work concludes that bovine theileriosis is an endemic disease in our villages and the existence of Theileria annulata infection minimizes the efficiency of the vaccination programs and increases the seriousness of LSD in crossbred cattle. The existence of sporadic cases of cattle infected by LSD precipitates the disease as a circulating disease in our villages in Egypt.
Keywords Histopathology · PCR · Lumpy skin disease · Theileria annulata
Clinical and Molecular Epidemiological Study on Herpesviruses Infection among Equid Populations in Upper Egypt
The present study was carried out to record the clinical signs of equine herpesviruses (EHVs) infection
and to detect the prevalence of EHVs infection among working equids in different provinces of Egypt. A total number of 115 working equids (92 horses and 23 donkeys) were clinically examined and sampled from November 2018 till November 2019 for this study.
Two samples were collected from each animal (nasal swab and blood sample) and were subjected to multiplex-PCR to detect the prevalence of different EHVs infection among equids. In the current study, the overall prevalence of EHVs infection among equid populations in Egypt was 80% by using multiplex-PCR. Moreover, the most prevalent equine herpesvirus (EHV) among equids in Upper Egypt was EHV-2 (61.
74%), followed by EHV-5 (43. 48%), EHV-1 (20%), and EHV-4 (13. 04%). The recorded clinical signs of the examined equids harbored EHVs (PCR-positive) can be summarized as follow: a higher percentage was detected among equids with a history of acute onset (59. 78%), pyrexia (57. 61%) and/or systemic illness (45. 65%) with or without respiratory signs (56. 52%) and ocular signs (35. 87%). Furthermore, 4. 35% and 1. 09% of EHV-1 PCR-positive equids displayed neurological signs and abortion, respectively.
Keywords: Working equids; Egypt; EHVs; Clinical signs; multiplex PCR.
Impact of Epidermal Growth Factor and/or β-Mercaptoethanol Supplementations on the in vitro Produced Buffaloes' Embryos
Background: The present study investigated the effects of epidermal growth factors
(EGF) and/or b-Mercaptoethanol (bME) supplementations to oocyte maturation,
fertilization, and culture media on the buffalo in vitro embryo production. Methods: The
ovaries were collected and transferred within 2 h to the laboratory. The cumulus
oocytes complexes were aspirated from 3 to 8mm diameter follicles. Firstly, EGF;
0, 10, 20, or 50 ng/mL or bME; 0, 25, 50, 100, or 200μM were supplemented
to the in vitro maturation (TCM-199), fertilization (IVF-TALP), or culture (IVC:
SOF) media. Results: Our results revealed that supplementing EGF (20 ng/mL) to the Q22
TCM-199, IVF-TALP, or SOF media could efficiently improve the growth rates
and development of buffalos’ embryos, while EGF (50 ng/mL) could stimulate
the embryo production only after treatment of the IVF-TALP /or SOF media, but
not the IVM medium. However, bME was less efficient than EGF; it stimulated
the growth rates of buffalo embryos when supplemented with the maturation
and fertilization (IVF-TALP) media in a 50μM concentration. Secondly, combined
EGF (20 ng/mL) and bME (50μM) were supplemented to the maturation media
as effective concentration. Conclusion: The combined treatment of EGF (20 ng/mL) and bME
(50μM) showed no significant enhancing effect on the buffalo embryos compared
to each alone. For future perspectives, further study is required to examine the
effects of combined EGF and bME on the maturation and fertilization of buffalo
oocytes at different categories of age and seasonal localities.
The relationship between ovarian hormones and mast cell distribution in the ovaries of dromedary camel (Camelus dromedaries) during the follicular wave
Background and Aim: Mast cells (MCs) play an essential role in regulating tissue homeostasis through various non-allergic immune reactions. This study aimed to describe the salient features of MCs during different phases of the estrous cycle and evaluate the relationship between ovarian hormones and the presence of MCs in camel ovaries. Materials and Methods: Genital tracts (n = 28) of healthy, non-pregnant camels were collected from a local slaughterhouse. The follicular wave stage was determined according to structures on the ovaries using an ultrasound device. Stages were classified as "growing" (n = 12, FØ = 0.3–0.8 cm), "mature" (n = 9, FØ = 0.9–2.2 cm), or "regression" phase (n = 7, FØ >2.5). Blood samples were collected at slaughter to determine serum estradiol-17β and progesterone levels using an immunoassay. Safranin-O, periodic acid/Schiff, alcian blue, or methylene blue stains were used to detect MCs. Results: Follicular numbers at the growing, mature, and regression phases were determined to be 36, 14, and 7 follicles, respectively. Mast cells were widely but sparsely distributed within the ovarian tissue (9.3 MCs in the growing phase, 10.7 in the mature phase, and 7.0 in the regression phase). Typical histological features of MCs were observed in ovarian stromal tissue. Some MCs were found in the interstitial tissue, either near the follicular wall or the interstitial gland. Mast cells were present at a higher density during the mature phase than in the growing and regression phases in the ovarian matrix. A significantly reduced presence of MCs was found in the regression phase than in both the growing and mature phases (p < 0.05). A very strong positive correlation was observed between serum estradiol-17β concentrations and MC density in the ovaries (r = 0.9; p < 0.001). In addition, a strong negative correlation (r = –0.65; p = 0.03) was observed between the presence of MCs and serum progesterone concentrations. Conclusion: These findings suggest that the follicular wave phase and the associated hormonal concentration induce changes in the number of MCs in the camel ovary.







