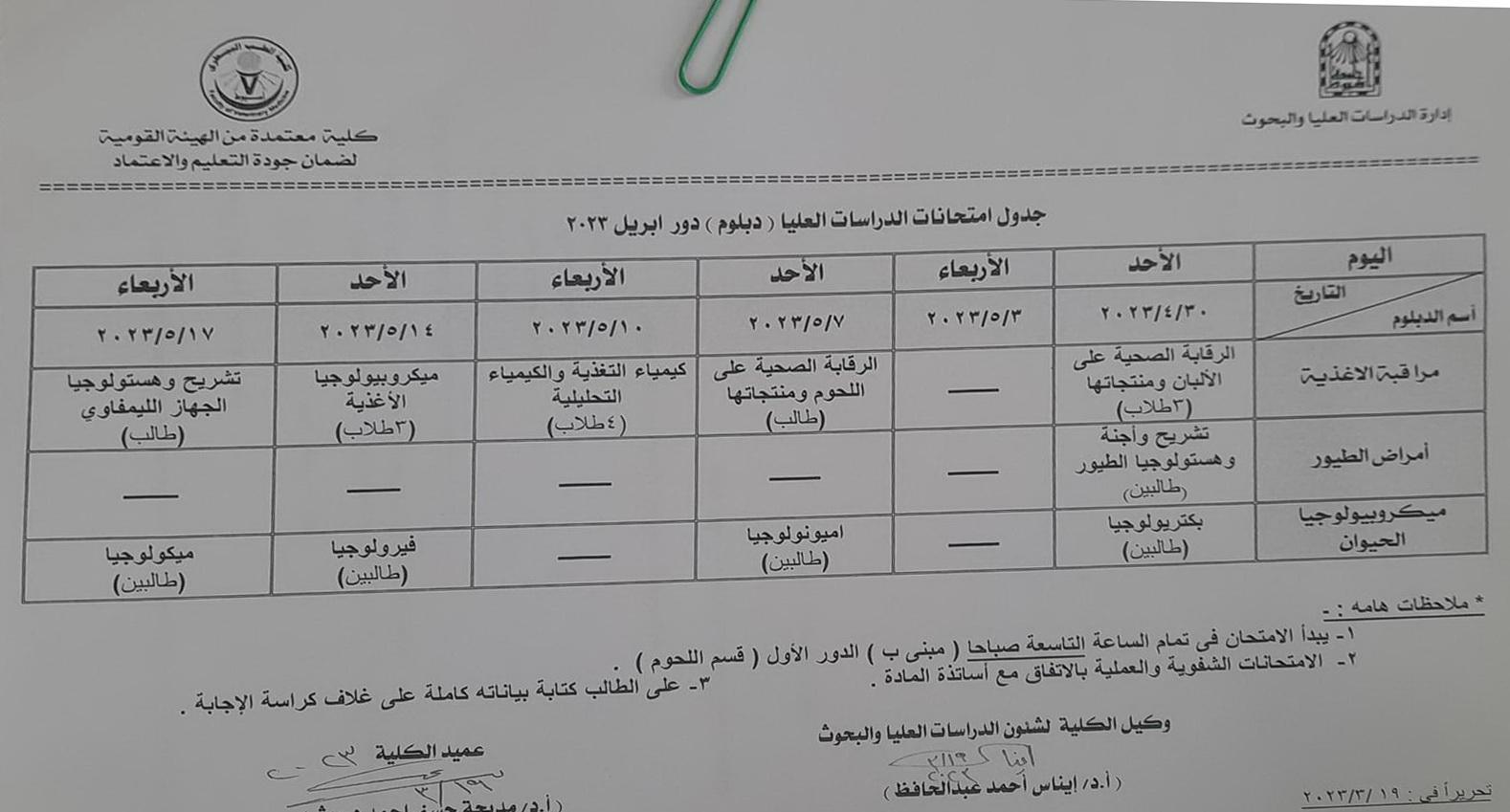
Postgraduate diploma exams schedule - April 2023
In vitro assessment of PEG-6000 coated-ZnO nanoparticles: modulating action to the resisted antibiotic activity against APEC
Avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) are considered a growing health problem to both poultry and the public, particularly due to its multi-drug resistance. Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) are a promising multi-benefit candidate. This study focused on boosting the antimicrobial effect of the chemically synthesized ZnO-NPs using Polyethylene glycol-6000 (PEG-6000) and evaluating their potential to recover the sensitivity of Florfenicol and Streptomycin-resistant APEC to these drugs in a concentration range of 0.1–0.4 mg/mL. Four samples of ZnO-NPs were formulated and tested microbiologically. The physicochemical characterization showed well-crystallized spherical in situ synthesized ZnO-NPs using PEG-6000 (surfactant) and ethanol (co-surfactant) of ∼19–67 nm particle size after coating with PEG-6000 molecules. These ZnO-NPs demonstrated a strong concentration-dependent antibacterial effect against multidrug-resistant APEC strains, with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 0.1 mg/mL, Combining PEG-6000 coated in situ synthesized ZnO-NPs and Florfenicol induced 60% high sensitivity (30 mm inhibitory-zone), 30% intermediate sensitivity, and 10% resistance against APEC strains. The combination with Streptomycin revealed 50% high sensitivity, 30% intermediate sensitivity, and 20% resistance with a 20 mm maximum zone of inhibition using agar well diffusion test. In situ preparation of ZnO-NPs using PEG-6000 and ethanol followed by coating with PEG-6000 enhanced its antibacterial activity in minimum inhibitory concentration and regained the efficacy of Florfenicol and Streptomycin against APEC, referring to a …
فاعلية وحدة جغرافية مقترحة قائمة على مدخل مونتيسوري في تنمية الحس الجغرافي وبعض مهارات قراءة الخريطة لطفل الروضة
The effectiveness of proposed geographic unit depending on Montessori approach in Developing geographic sense and some of map reading skills
استخدام انشطة منتسوري في تنمية الطلاقة اللغوية لأطفال الروضة ذوي صعوبات التعلم
"أثر استخدام نموذج أبعاد التفكير في تنمية مهارة قراءة الخريطة وبعض
قدرات التفكير اإلبداعي لدى تالميذ المرحلة االبتدائية" بحث مشترك
وعرض في المؤتمر الدولي في جامعة ديكارتية باريس الفرنسية )2-4
2
يوليو 2008 )
[Universitè Paris Descartes www.icieconfere
أحمد حسن
فاعلية وحدة جغرافية مقترحة قائمة على مدخل مونتيسوري في تنمية الحس الجغرافي وبعض مهارات قراءة الخريطة لطفل الروضة
د. يارا إبراهيم محمد
اثر برنامج تربية حركية قائم على استراتيجية القبعات الست لتنمية بعض مهارات القيادة لدى طفل ما قبل المدرسة
د. غادة كامل سويفى
د.يارا ابراهيم محمد
ا. زينب عباس عبد المنصف




