Skip to main content
Invitation to discuss the master's thesis of Veterinarian / Nada Mohamed Mahmoud
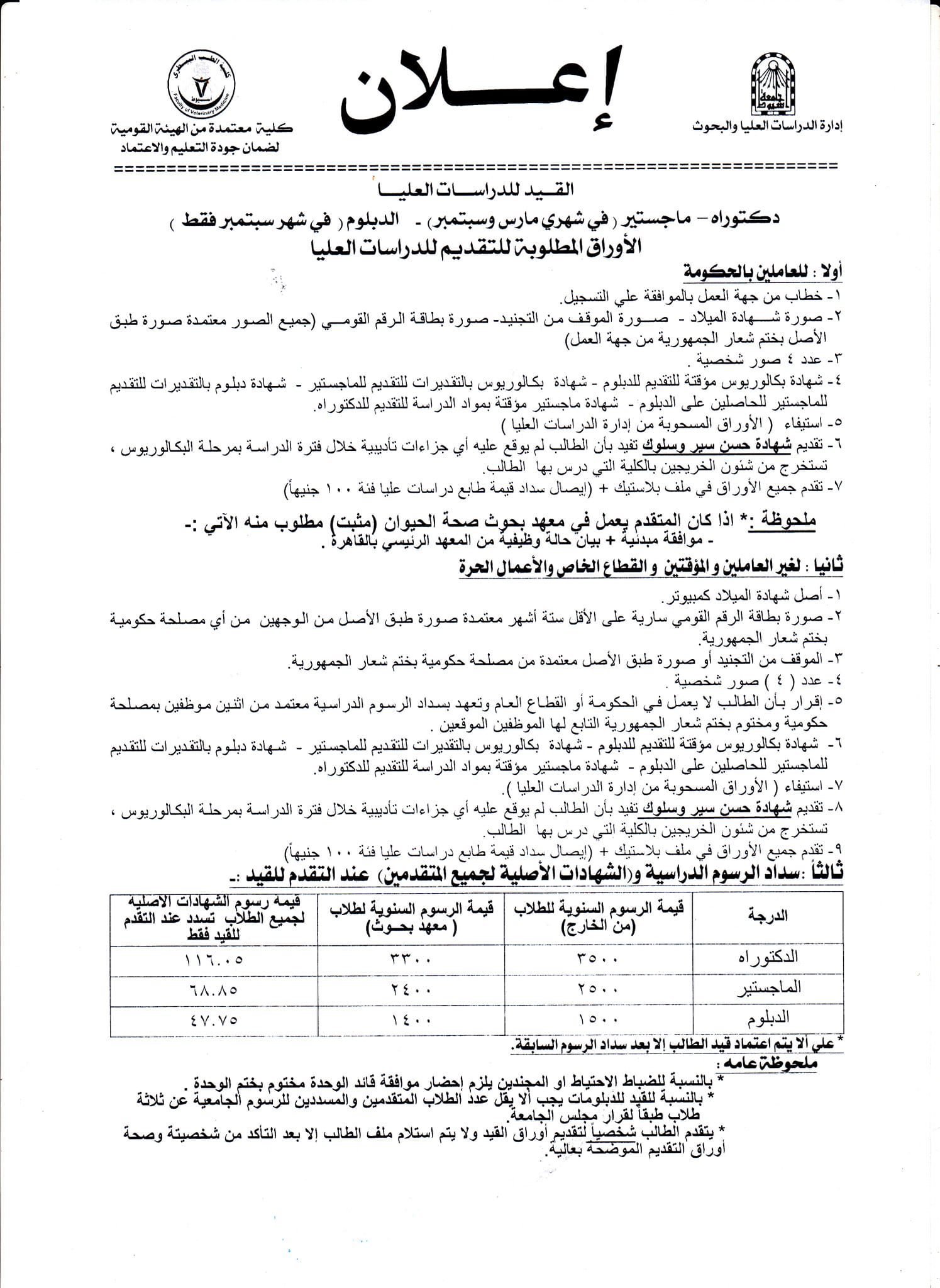
Announcement of enrollment for postgraduate studies
Invitation to discuss the master's thesis of Veterinarian / Hoda Jamal Sayed Hussein
Invitation to discuss the doctoral thesis of Veterinarian / Mervat Milad Thabet Gerges
Invitation to discuss the doctoral thesis of a veterinarian / Doaa Sameh Sayed Khalaf
Invitation to discuss the master's thesis of Female Veterinarian / Amira Jamal Abdullah Mohammed
Invitation to discuss the master's thesis of Veterinarian / Dalia Abdel Maaboud Ismail Mohamed
Invitation to discuss the doctoral thesis of a veterinarian / Wissam Samih Sayed Galal
Invitation to discuss the master's thesis of a veterinarian / Ahmed Abu Haroun Abdel Jaber
Subscribe to