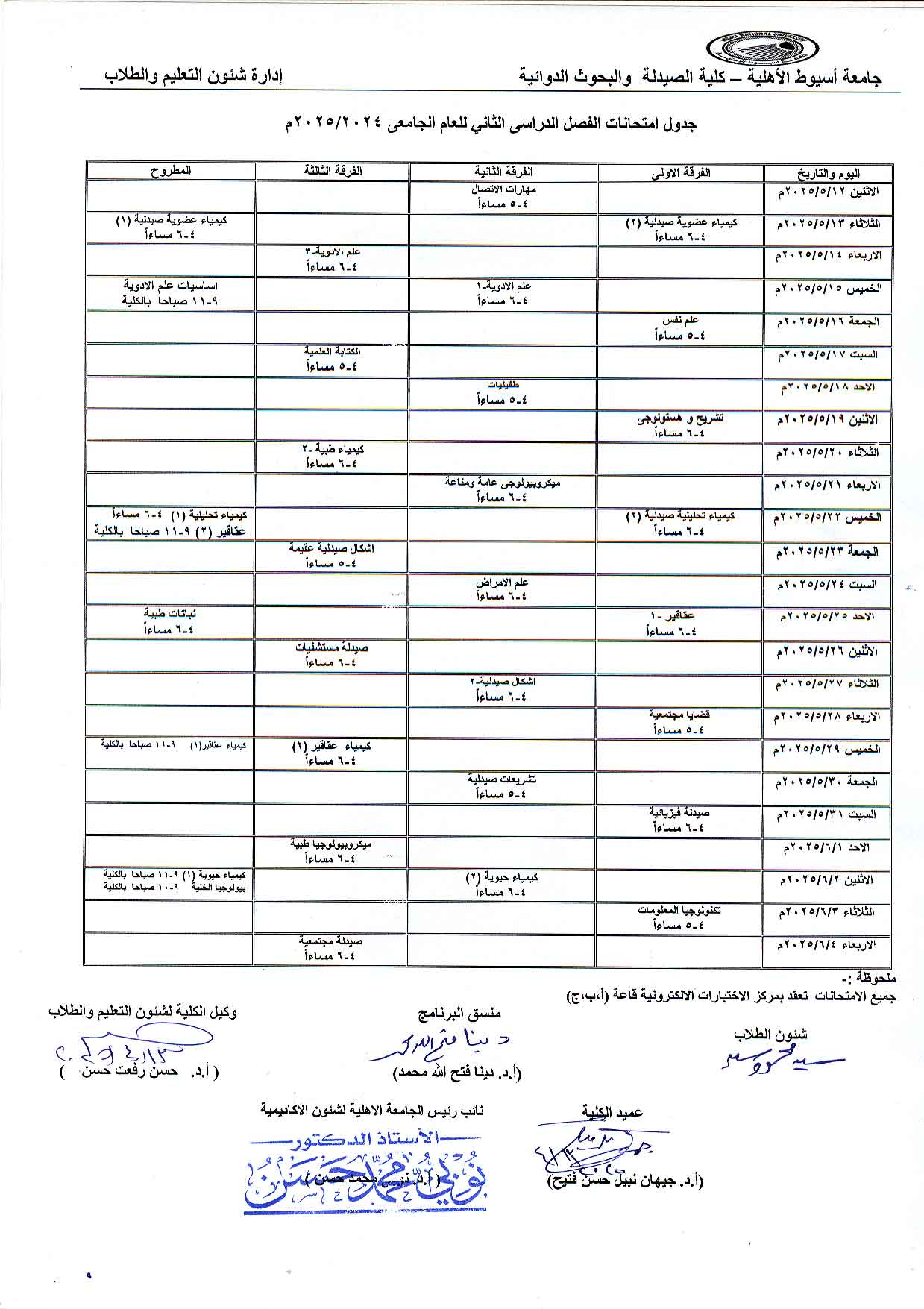
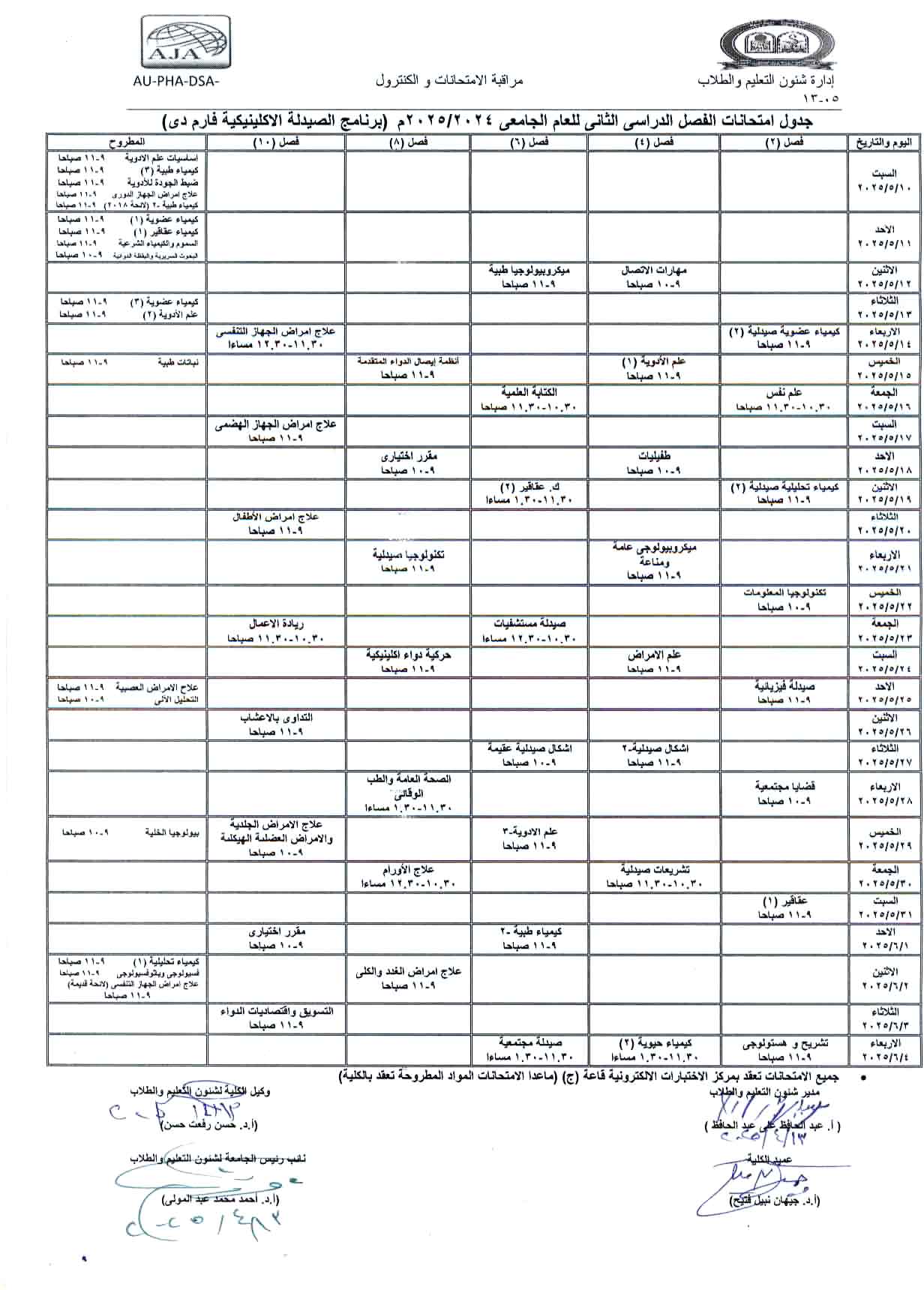
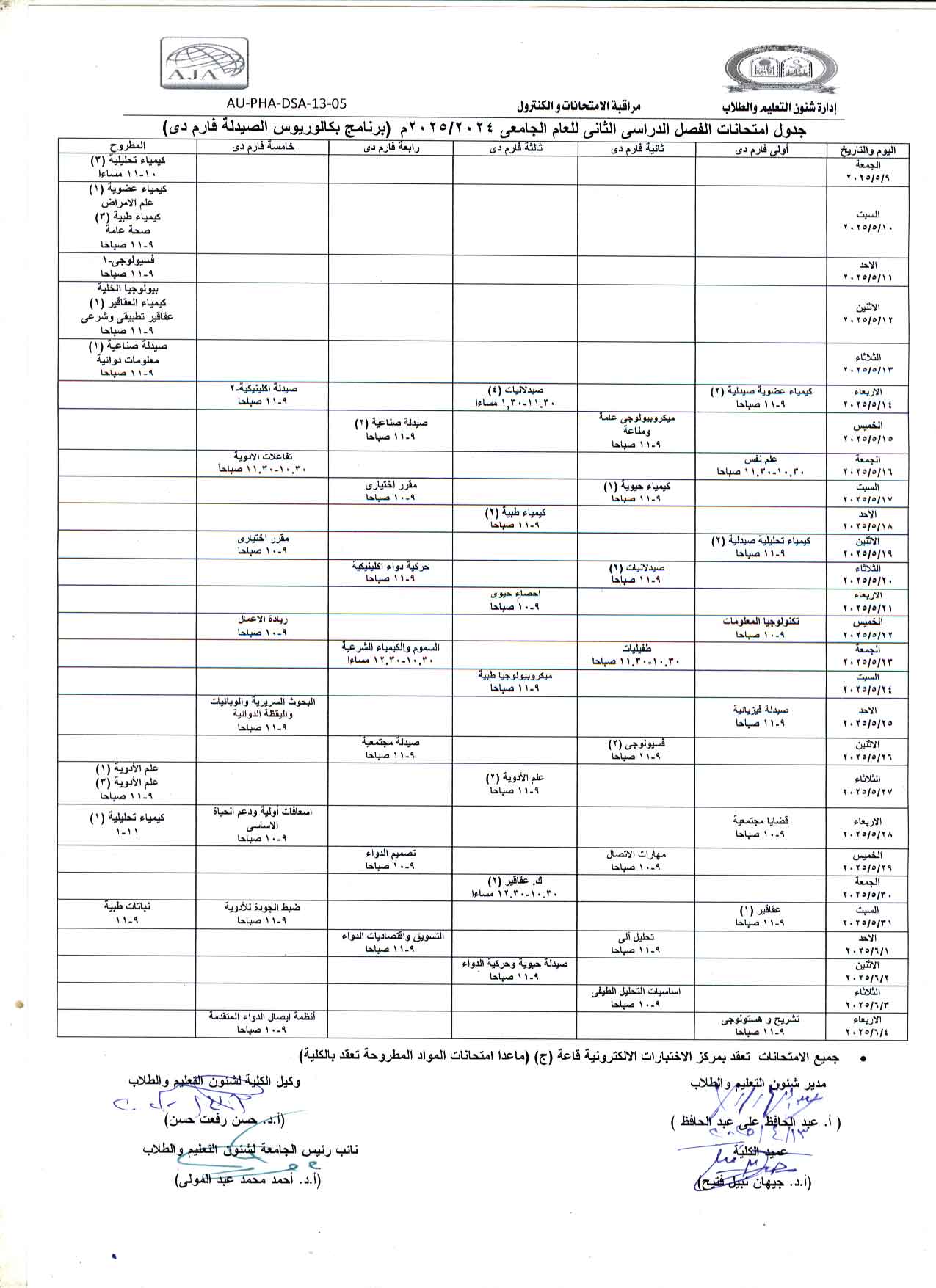
Announcement for First-Year, Clinical Pharmacy, and National University Students: The second-term mid-term exam and the theoretical and practical exam for the course "Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry-1" will be held on Sunday, May 4, 2025.

The department announces that the second mid-term exam and the second practical theory exam for the course Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry - 1 (offered course) will be held on Sunday, May 4th, 2025, from 11:30 AM to 12:30 PM.
Please make sure to attend on time, as the exam will not be repeated.
Exam Venues:
- Pharm D : Hall 1
- Pharm D National University: Hall 2
- Pharm D Clinical: Department Lecture Hall