The First Scientific Conference of the Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy – Saturday, May 3, 2025.


 Do you have any questions? (088) 2080369 - 2345622 Pharmacy_QAAU@pharm.aun.edu.eg
Do you have any questions? (088) 2080369 - 2345622 Pharmacy_QAAU@pharm.aun.edu.eg


With deep sorrow and heartfelt condolences, we mourn the passing of
Professor Dr. Ihsan Hafiz Ibrahim,
Emeritus Professor, Department of Pharmaceutics.
We pray that Allah grants her mercy and forgiveness, and we extend our sincere condolences to her family.
“Indeed we belong to Allah, and indeed to Him we shall return.”
The funeral will take place today, Monday, following Dhuhr prayer at Suleiman Al-Hakim Mosque,
and the burial will be at Assiut Cemeteries – Arab Al-Madabigh.
Condolences will be received today, Monday, after Maghrib prayer at the Ceremony Hall next to the Health Directorate.

By the will of Allah, the scientific conference of the Pharmacology at the Faculty of Pharmacy will be held on Tuesday, April 29, 2025, at 11:00 AM. The conference will take place in the Department Council, 5th floor, Building (A).
The aim of this work is to develop and evaluate self‑nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems (SNEDDS) containing simvastatin to increase its oral bioavailability. Formulation EO 5 (Ethyl oleate 9.3% w/w: Tween 80 49.4% w/w: Propylene glycol 39.3% w/w) and Formulation CL 14 (Clove oil 54.3% w/w: Tween 80 34.4% w/w: Transcutol‑P 9.3% w/w) were thoroughly studied. They showed emulsification time less than 1 min, droplet size in the nanometric range, and almost a complete drug release after 2 h. The in‑vitro dissolution profile of both formulations was found to be significant in comparison to the pure drug in pH 1.2 and 7.4 buffers (P < 0.0001). Furthermore, they demonstrated superior anti‑hyperlipidemic activity in comparison to simvastatin suspension (10 mg/kg/day). In order to investigate the impact of oil type on oral bioavailability, the selected formulations have been examined in terms of the in‑vivo pharmacokinetic study, and formulation EO 5 was found to have higher bioavailability. After oral administration of a single dose (40 mg/kg) of simvastatin‑loaded SNEDDS (CL14 and EO 5), a 1.5‑fold and 1.95‑fold increase in bioavailability were observed, respectively, as compared to simvastatin suspension. Hence, the results indicated that the developed SNEDDS could enhance the therapeutic efficacy and oral bioavailability of simvastatin.


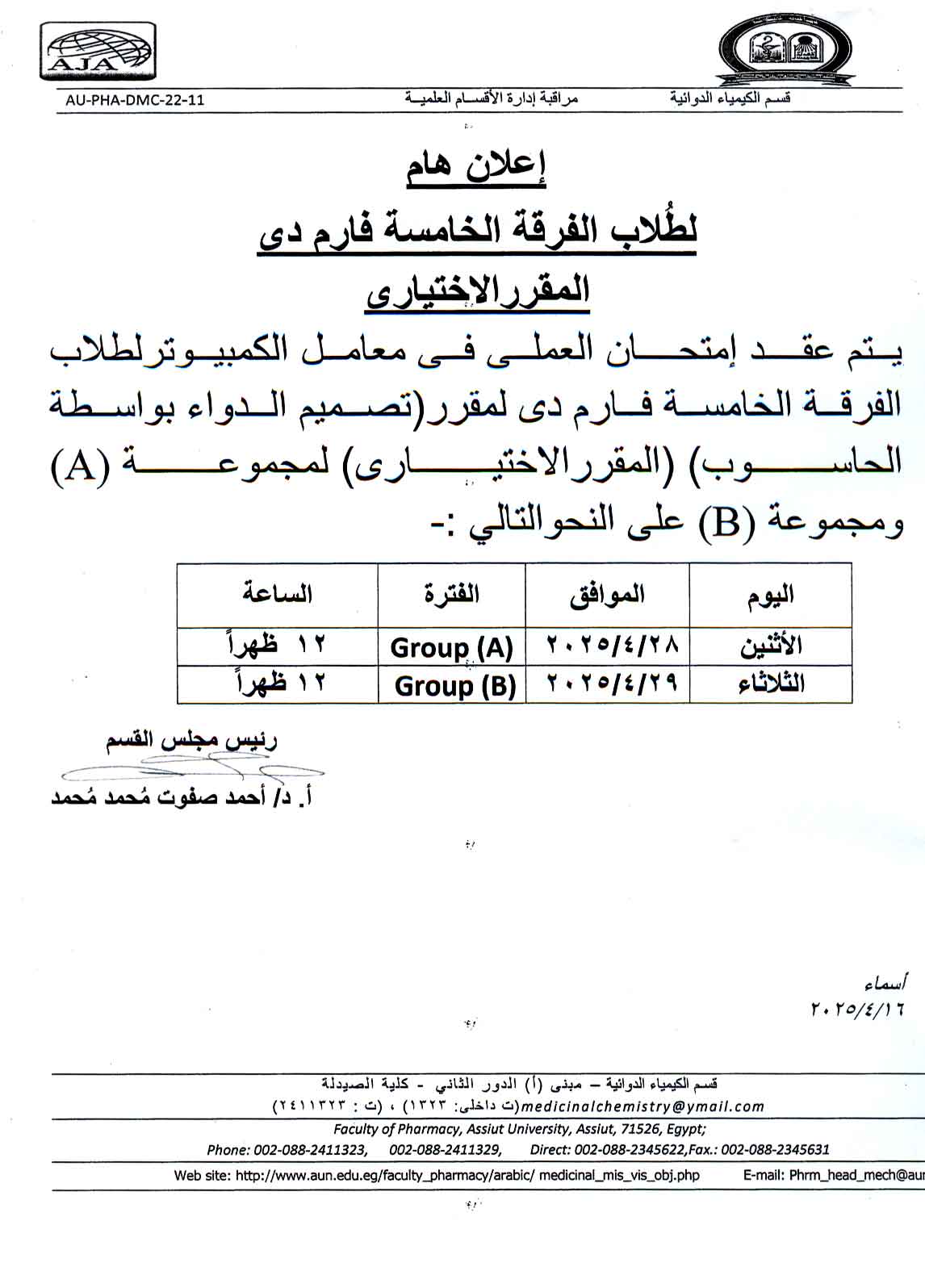
The practical exam for the elective course
"Computer-Aided Drug Design" for 5th-Year Pharm D students will be held in the computer labs
for Group (A) and Group (B) as follows:
|
Day |
Date |
Group |
Time |
|
Monday |
28/04/2025 |
Group (A) |
12:00 PM |
|
Tuesday |
29/04/2025 |
Group (B) |
12:00 PM |
All students must attend according to their assigned group and time.
No makeup exam will be given without an officially approved excuse.

The department announces that the second mid-term exam and the practical theory exam will be held on Saturday, April 26th, from 11:30 AM to 12:30 PM.
Please make sure to attend on time, as the exam will not be repeated.
Venue: Hall 2, beneath Lecture Hall B
Course Content for the mid-term Exam (10 Marks):
Course Content for the Practical Theory Exam (15 Marks):

