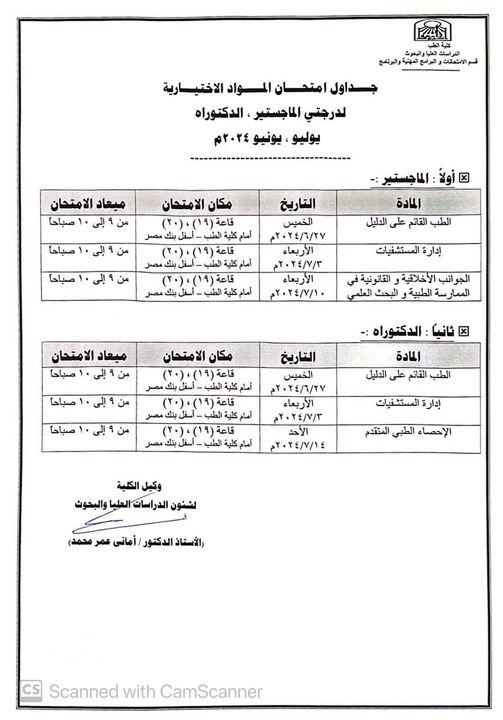
Examination schedule for elective subjects for the master’s and doctoral degrees, June, July 2024


Background: Balancing opioid stewardship and the need for adequate analgesia following discharge after surgery is challenging. This
study aimed to compare the outcomes for patients discharged with opioid versus opioid-free analgesia after common surgical
procedures.
Methods: This international, multicentre, prospective cohort study collected data from patients undergoing common acute and
elective general surgical, urological, gynaecological, and orthopaedic procedures. The primary outcomes were patient-reported time
in severe pain measured on a numerical analogue scale from 0 to 100% and patient-reported satisfaction with pain relief during
the first week following discharge. Data were collected by in-hospital chart review and patient telephone interview 1 week after
discharge.
Results: The study recruited 4273 patients from 144 centres in 25 countries; 1311 patients (30.7%) were prescribed opioid analgesia at
discharge. Patients reported being in severe pain for 10 (i.q.r. 1–30)% of the first week after discharge and rated satisfaction with
analgesia as 90 (i.q.r. 80–100) of 100. After adjustment for confounders, opioid analgesia on discharge was independently associated
with increased pain severity (risk ratio 1.52, 95% c.i. 1.31 to 1.76; P < 0.001) and re-presentation to healthcare providers owing to sideeffects
of medication (OR 2.38, 95% c.i. 1.36 to 4.17; P = 0.004), but not with satisfaction with analgesia (β coefficient 0.92, 95% c.i. −1.52
to 3.36; P = 0.468) compared with opioid-free analgesia. Although opioid prescribing varied greatly between high-income and lowand
middle-income countries, patient-reported outcomes did not.
Conclusion: Opioid analgesia prescription on surgical discharge is associated with a higher risk of re-presentation owing to side-effects
of medication and increased patient-reported pain, but not with changes in patient-reported satisfaction. Opioid-free discharge
analgesia should be adopted routinely.
Objectives: To test the feasibility of sonographic measurement of the umbilical cord (UC) length index in prediction of UC length and subsequent abnormalities at birth.
Methods: This study was done at tertiary University. We included 300 pregnant women who were ≥37 weeks admitted to labor ward. Sonographic evaluation of UC length index was calculated by counting the UC rings in each amniotic fluid quadrant. One point was given for each quadrant that contained UC ring and 0.5 point was given for each UC ring in one quadrant then the total score was calculated. After delivery of the fetus, the UC length was measured by flexible tape in cm. Any UC abnormalities at birth as true knots and neck loops were noted.
Results: Thirty-six cases (12%) were delivered vaginally while 264 (88%) of cases were delivered by CS. The mean UC length index was 3.35±1.17. Ten cases (3.3%) had short UC and their mean UC length index was 1.9±0.51. Normal UC cases were 269 (89.7%). Their mean UC length index was 3.27±1.07. Long UC cases were 21 (7%) and their mean UC length index was 5.09±0.86. Neck loops and true knots were significantly higher among newborns with long UC; 11 (52.3%) & 6 (20.6%) cases respectively (P=0.001). Meanwhile, placental separation was significantly higher among cases with short UC; 2 (20%) (P<0.001).
Conclusions: The calculation of UC length index before delivery can be used for predicting cord abnormalities due to short and long UCs.
Keywords: Umbilical cord; Ultrasonography; True knots; Fetal distress
Background: There is no justification for any reason to have a caesarean delivery (CD) rate higher than 10–15%. CD rates higher than 10% are not associated with substantial decrease in maternal and neonatal mortality rates. Robson Group Classification System has the advantage of analyzing the caesarean delivery rate in well-defined sub-groups of women that are totally inclusive and mutally exclusive.
Objective: The aim of the current work was to make comparative analysis of increasing trends of caesarean delivery in two hospitals at Assiut Governorate in Egypt.
Patients and methods: This retrospective cross-sectional study included a total of 2702 cases, attending for delivery at Assiut University Hospital; a tertiary hospital and Assiut Police Hospital; a secondary hospital, both present in Assiut Governorate. This study was conducted over 3-month between Jan 2016 to Mar 2016.
Results: Robson Group 5 constituted the most in both hospitals regarding the relative size of the group with higher and significant percentage at the secondary hospital (53%) compared to (32.3%) at the tertiary one. Robson Group 5 contributed the most in both hospitals regarding the overall CD rate with higher and significant percentage at the secondary hospital (74.8%) compared to (49.4%) at the tertiary one. Robson Group 5 also contributed the most in both hospitals regarding the absolute contribution rate of all deliveries with higher and significant percentage at the secondary hospital (50%) compared to (28.7) at the tertiary one.
Conclusion: On the basis of the study, TGCS is only a starting point, but it is important to have a common starting point. Having implemented TGCS, we have concluded that Group 5 (previous caesarean delivery) is the largest of the overall CD rate in both secondary and tertiary hospitals.
Keywords: Caesarean delivery, Assiut Governorate, Robson Ten Group Classification
Background: Missed abortion, significant birth defects, and some women’s decision not to carry a pregnancy to term are all reasons for mid-trimester pregnancy
termination. The aim of this work was to assess evening primrose oil’s (EPO) effect on the duration of induction of abortion.
Methods: This prospective registered, randomized controlled study included 144 women in their missed abortion singleton mid-trimester of pregnancy (14 - 28
weeks). The assignment was random to one of two equal groups. Group I: received 200 mcg Misoprostol and EPO. Group II: received Misoprostol only. The
induction to onset of cervical dilatation time was the primary outcome.
Results: Temperature was insignificantly different in all times of measurements except at 48 h, it was significantly lower in group I compared to group II. Pulse was
significantly lower in group I compared to group II at all times of measurements. Pain was insignificantly different at all times of measurements between both groups
except at 8 (h), 24 (h) and 48 (h), it was in group I significantly lower than group II.
Conclusion: In women with second trimester missed abortion, vaginal administration of EPO with misoprostol had no additional significant effect on duration of
induction of delivery, duration to cervical dilatation, maternal satisfaction, vaginal bleeding, fetal expulsion, and surgical removal of placenta.
Keywords: Evening primrose oil, Misoprostol, Second trimester missed, Miscarriage
Background: Episiotomy is a surgical increase of the perineum made to increase the vulval outlet during childbirth, 85% of women who have a spontaneous vaginal birth will have some form of perineal trauma and up to 69% will need to have sutures. The aim of this study is to establish if there was clear scientific evidence that the technique used for perineal skin repair, following childbirth, had influenced postoperative pain and wound healing occurring in perineal area and to compare after suturing techniques with respect of time taken to complete skin closure (in minutes).
Methods: This is a prospective RCT of 150 women who gave birth at Women health hospital aged 21-35 years old and with normal vaginal delivery, at term (37 weeks – 40 weeks), live baby and vertex presentation. The women (Primigravida or multipara) ae assigned equally to 3 groups: simple continuous group, subcuticular group and interrupted skin suturing group. All patients were subjected to perineal pain intensity assessment, perineal wound healing assessment and postoperative scar assessment.
Results: NPRS after 10 days and SBSES were significantly lower in simple continuous group and subcuticular group than interrupted skin sutures group (P value<0.05). Suturing time significantly lower in simple continuous group was than subcuticular group and interrupted skin sutures group and in subcuticular group than interrupted skin sutures group (P value<0.05). There was an insignificant difference in NPRS and SBSES between simple continuous group and subcuticular group, in NPRS after 1month and in REEDA after 10 days and 1 month among the studied groups.
Conclusions: Suturing time significantly lower in simple continuous group was than subcuticular group and interrupted skin sutures group and in subcuticular group than interrupted skin sutures group.
Keywords: Episiotomy; 2nd-Degree perineal tears; Simple continuous suturing; Subcuticular suturing; Interrupted skin suturing
Background and aim
The close proximity of the urinary tract to the female genital system makes it vulnerable to
damage during pelvic surgical procedures. The objective of the current study was to evaluate
iatrogenic urinary tract injuries (UTIs) caused by obstetrical and gynecological procedures.
Patients and methods
The current study was conducted at Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Assiut University
Hospitals, in the period between March 2018 and March 2021. All women with UTIs secondary
to obstetrical or gynecological surgeries during the study period were recruited in the study.
Results
A total of 20 636 women were scheduled for different obstetric or gynecological surgeries,
and 170 (0.82%) of them experienced iatrogenic UTIs, 161 (94.7%) women had injury during
obstetric surgeries, whereas the other nine (5.3%) had gynecological surgeries. Operations
were repeated cesarean section (34.2%) and placenta previa (54.1%) in obstetric surgeries
and repeated section in gynecological surgeries (33.3%). Iatrogenic UTIs were detected
intraoperatively in 167 (98.2%) women, whereas in only three patients, detection was delayed.
Overall, eight (4.7%) patients had both bladder and ureteric injuries, whereas bladder injury
alone occurred in 154 (90.6%) patients and another eight (4.7%) patients had ureteric
injuries alone. ICU admission was needed in 43 (25.3%) patients.
Conclusion
Although frequencies of UTIs in obstetric and gynecological surgeries were found to be
relatively low, yet it may lead serious morbidity and outcome. Proper antenatal care and good
knowledge of pelvic anatomy may help in decreasing its frequency.
Keywords:
assiut, gynecologic, iatrogenic, obstetric, operation, placenta previa, procedure, recurrent
cesarean section, urinary tract injury
Abstract: Zinc (Zn) and copper (Cu) have been shown to have the potential to improve glucose metabolism through interactions with cytokines and signaling events with multiple genes. miRNA375 and the Calpin-10 gene are potential genetic biomarkers for the early prediction of diabetic nephropathy (DN). 128 healthy controls and 129 type 2 diabetic (T2DM) participants were matched for age and sex. Three subgroups were identified from the T2DM group: 39 patients had microalbuminuria, 41 had macroalbuminuria, and 49 patients had renal problems. Circulating miR375 expression levels were measured via qPCR. Calpain-10 SNP 19 (rs3842570) genotyping was assessed with allele-specific PCR in all the included participants. Spectrophotometry was used to measure the concentrations of serum copper, zinc, and magnesium, while ELISA was used to measure the levels of TGF-β and IL-17. There was significant up-regulation in the expression of miR375 and serum levels of TGF-β, IL-17, Cu, and the Cu/Zn ratio, whereas, in contrast to the control group, the Zn and Mg levels were lower in the T2DM group. The DN groups had significantly lower miR-375, TGF-β, IL-17, Mg, and Zn levels compared with the T2DM without nephropathy group. Furthermore, between TGF-β, IL-17, and miRNA-375, there were notable correlations. Calpain-10 SNP 19 genotype 22 and allele 2 were linked to a higher incidence of T2DM and DN. SignificantTGF-β, Cu, Cu/Zn ratio, HbAc1, and creatinine levels, but insignificant miRNA-375 levels, were associated with genotype 22 of Calpain-10 SNP 19. interactions between the Calpain-10 SNP 19 genotype 22 and IL-17, TGF-β, mineral levels, and miRNA-375 might contribute to the aetiology of DN and T2DM and may have clinical implications for diagnosis and management.
Background Serum adenosine deaminase (ADA) measurement is a biochemical test that is believed to play a role in diagnosing tuberculosis (TB). However, few studies have been conducted in this area and there have been contradictory reports on the diagnostic value of serum ADA in TB. Objective The aim of the study was to evaluate the usefulness of ADA measurement in the serum for diagnosing TB. Materials and methods In all, 97 participants were included in this study; 28 with pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB), 20 with extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB), 32 with non-TB lung disease, and 17 heathy individuals. Serum ADA activity was determined in all participants using the semiautomated biochemistry analyzer ERMA AE600N (ERMA Inc.). Results We found that serum ADA levels were significantly high in patients with TB (PTB and EPTB) compared with non-TB lung disease cases and healthy control. The best cutoff value in this study of serum ADA in diagnosing TB was more than 21.1 IU/l for PTB and more than 21.2 IU/l for EPTB as obtained by the receiver operating characteristic curve with high sensitivity and specificity. Conclusion According to the results indicating high sensitivity for serum ADA level, this test is a helpful tool for the diagnosis of TB. On the basis of high specificity for serum ADA level, this test is also a useful test to rule out TB in questionable cases

