Exam schedule for second semester - May 2025, second year (regularity - directed affiliation)
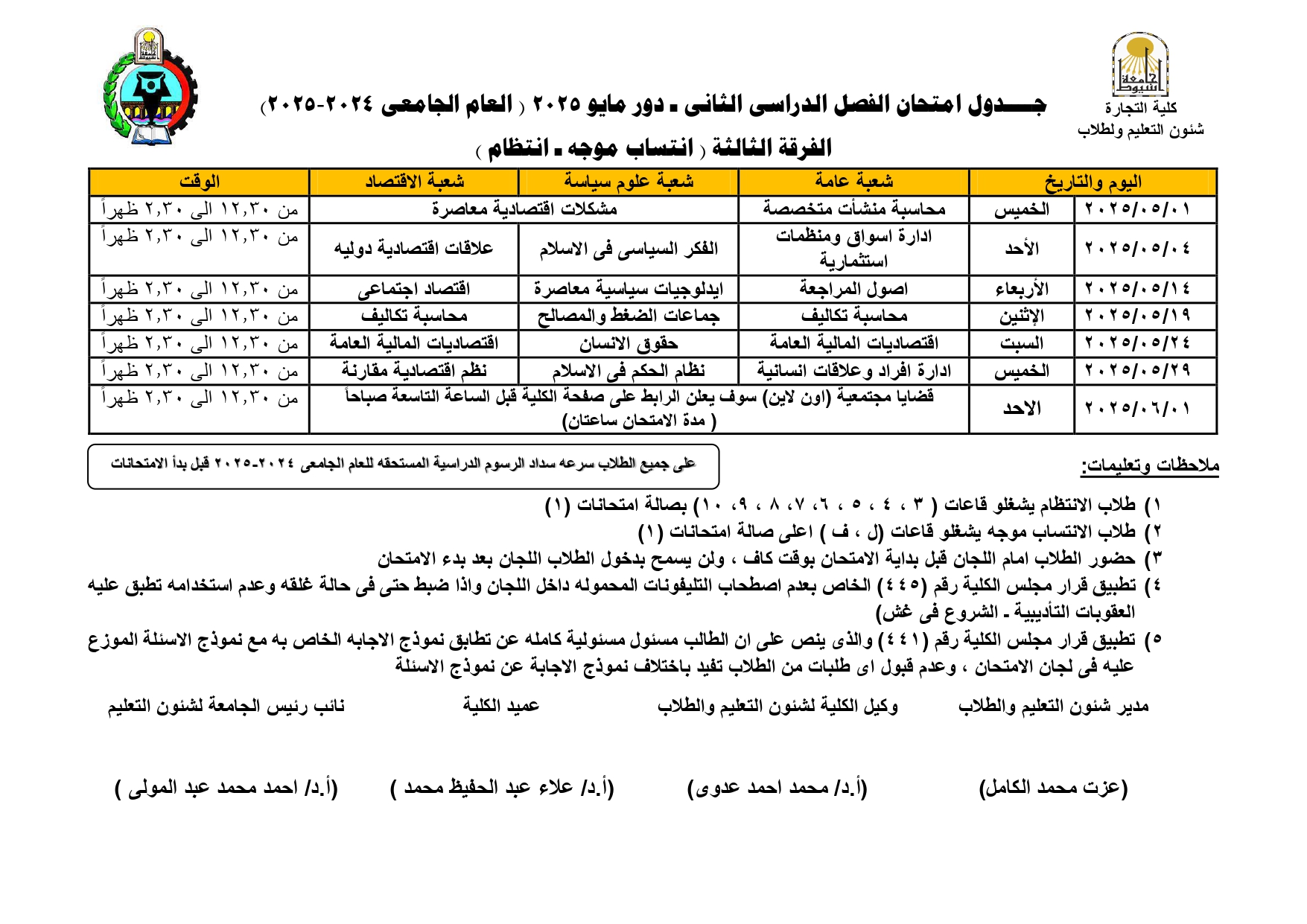
Exam schedule for second semester - May 2025, third year (regularity - directed affiliation)
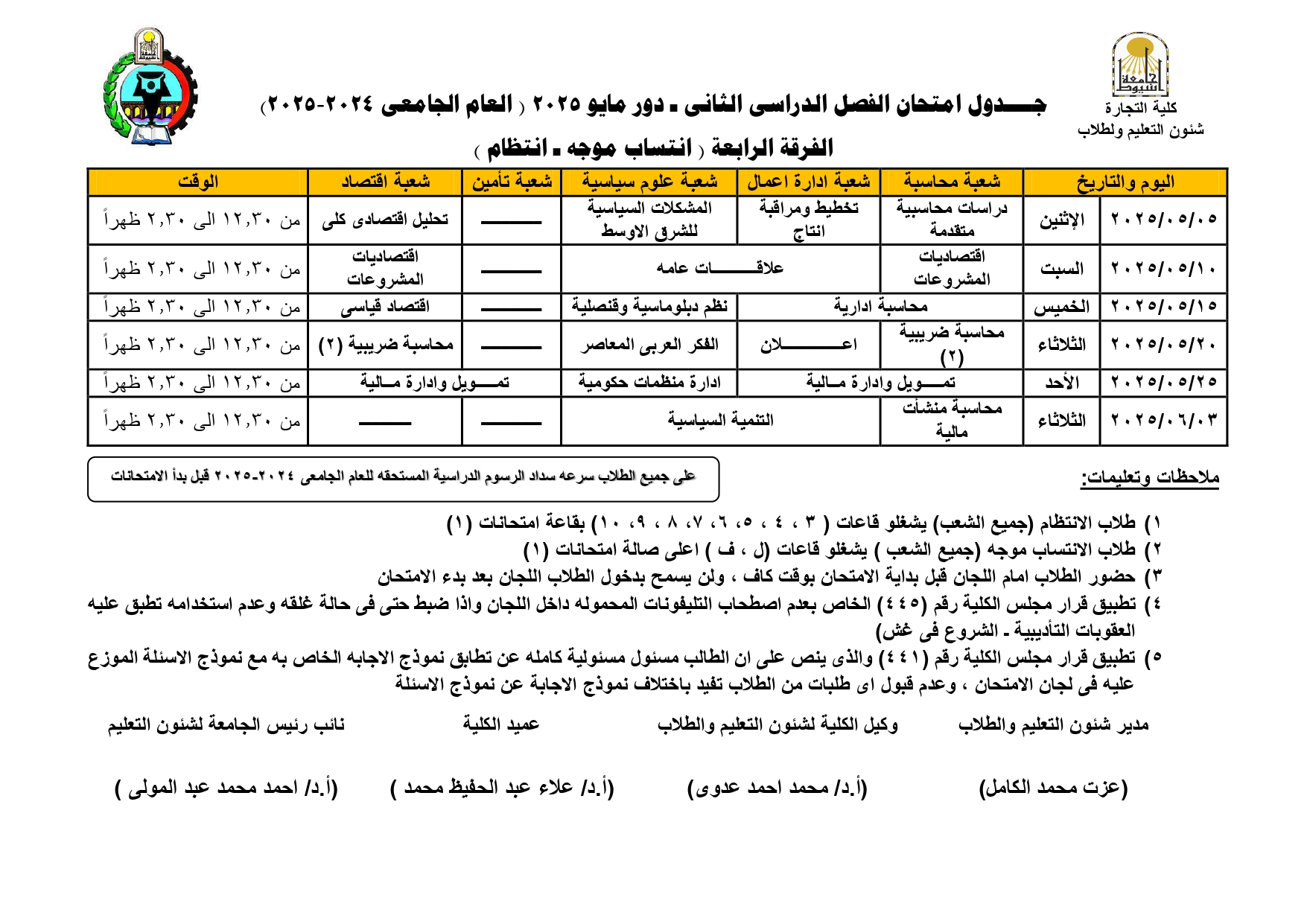
Exam schedule for second semester - May 2025, fourth year (regularity - directed affiliation)
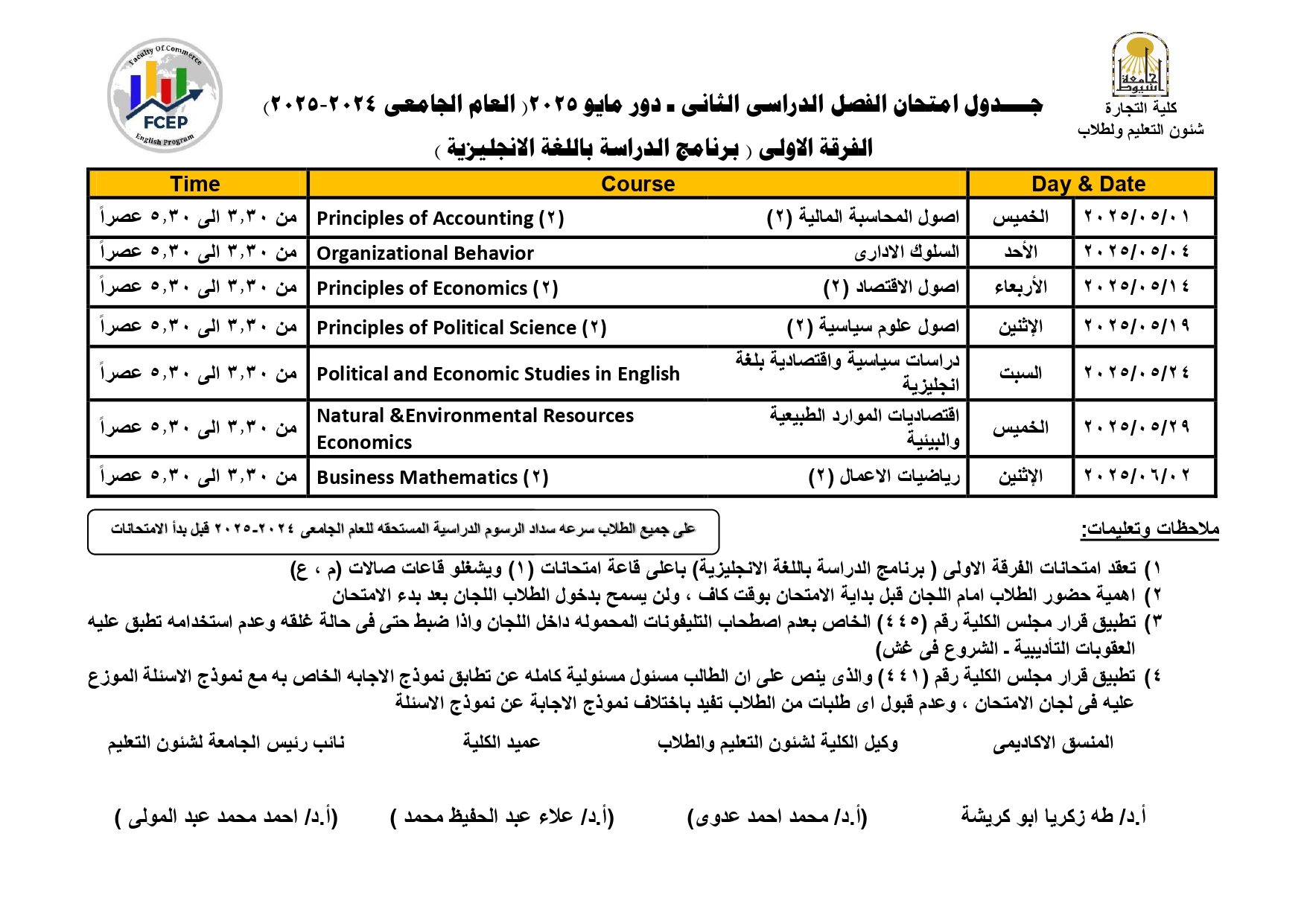
Exam schedule for second semester - May 2025, first year (study program in English)
The impact of integrated reporting quality on the cost of equity capital: evidence from Asia
Purpose– This paper aims to examine the impact of the quality of integrated reporting (IR) on the cost of equity capital in the voluntary Asian context. Design/methodology/approach– This study uses OLS regression to analyze the impact of IR quality on the cost of equity, using a sampleof Asian firmsthat issued IR andarepresented on theInternational Integrated Reporting Council website from 2015 to 2022. IR quality is evaluated through content analysis. To ensure the robustness of the findings, this study incorporates alternative cost of capital measures, propensity score matchingandinstrumental variable estimation. Findings– IR quality negatively influences the cost of capital. Additional analysis shows that this negative impact is more pronounced in profitable firms and firms with a higher need for external financing. In addition, further analysis shows that the negative impact remains significant during the COVID-19 pandemic period. In addition, the findings reveal that earnings quality and analyst forecast accuracy serve as mediators in the relationship between IR quality and the cost of capital. Practical implications– Understanding how IR quality influences the cost of capital is vital for investors, policymakers, regulators and companies. Originality/value– This study is unique in concentrating on the effect of the quality of IR on the cost of capital in the voluntary Asian context. This region has received little attention in previous research. This study also adds to the literature by showing the mediating role of earnings quality and analyst forecast accuracy on the relationship between IR quality and cost of capital. Keywords Integrated reporting, Cost of capital, Earnings quality, Asia Paper type Research paper
Does ERP Adoption Affect Stock Price Volatility? Evidence from Egypt
This study explores the association between ERP adoption and stock price volatility (SPV). An ERP software reshapes information collected, processed, and disseminated. We examine whether ERP usage influences the stock price volatility of Egyptian firms. Our investigation is among the first to examine how ERP usage affects SPV, an overall outcome measure of a firm’s information environment. The Findings document that ERP has a significant and negative association with SPV. Stock price volatility (SPV) relationships have expanded the literature on ERP facts. ERP is essential for both strategic and operational logistics decisions. This study also gives strong evidence that ERP-adopted firms help to reduce the risk of stock price volatility and build a good relationship with the shareholders. Overall, it showed the financial effect of ERP in the emerging economy context of Egypt. OLS Regression Analysis 115 organizations in Egypt were edited in 1150 observations registered from 2011 to 2020 on the Egyptian Stock Exchange (ESE). The main results of tests are robust after analysis with a cluster of the standard errors by companies' change of critical variables.
The impact of integrated reporting quality on the cost of equity capital: evidence from Asia
Purpose – This paper aims to examine the impact of the quality of integrated reporting (IR) on the cost of equity capital in the voluntary Asian context.
Design/methodology/approach – This study uses OLS regression to analyze the impact of IR quality on the cost of equity, using a sample of Asian firms that issued IR and are presented on the International Integrated Reporting Council website from 2015 to 2022. IR quality is evaluated through content analysis. To ensure the robustness of the findings, this study incorporates alternative cost of capital measures, propensity score matching and instrumental variable estimation.
Findings – IR quality negatively influences the cost of capital. Additional analysis shows that this negative impact is more pronounced in profitable firms and firms with a higher need for external financing. In addition, further analysis shows that the negative impact remains significant during the COVID-19 pandemic period. In addition, the findings reveal that earnings quality and analyst forecast accuracy serve as mediators in the relationship between IR quality and the cost of capital.
Practical implications – Understanding how IR quality influences the cost of capital is vital for investors, policymakers, regulators and companies.
Originality/value – This study is unique in concentrating on the effect of the quality of IR on the cost of capital in the voluntary Asian context. This region has received little attention in previous research. This study also adds to the literature by showing the mediating role of earnings quality and analyst forecast accuracy on the relationship between IR quality and cost of capital.
Keywords Integrated reporting, Cost of capital, Earnings quality, Asia
Does the chairman’s political and royal authority matter? Evidence from ESG disclosure in Gulf Cooperation Council
Abstract Purpose– This study aims to explore the influence of the chairman’s political and royal authority on environmental, social and governance (ESG) disclosure within the context of nonfinancial companies listed in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
Design/methodology/approach– The authors adopt a mixed-methods approach, analyzing a data set of 262 nonfinancial GCC companies from 2016 to 2021. The authors use content analysis to collect the ESG disclosure data based on the ESG Disclosure Guidance provided by the GCC Financial Markets Committee. Quantitative methods are applied to investigate the effect of the chairman’s political and royal authority on ESG disclosure. The credibility of the findings is fortified through rigorous robustness and endogeneity tests.
Findings– Consistent with the resource-based view and servant leadership theory, the authors found a positive impact of the chairman’s political and royal authority on ESG disclosure.
Practical implications– The findings of this study insight investors to consider the complex relationship between political affiliations and governance practices to align investments with sustainability and ethical criteria, thereby improving investment strategies in these contexts. This research offers a solid foundation for regulatory craft governance frameworks that acknowledge and incorporate the unique influence of royal family members and politically connected individuals within corporate boards.
Originality/value– This study enhances the discourse on ESG disclosure by focusing on the underrepresented GCC region. This research breaks new ground by focusing on the impact of the chairman’s political and royal authority on ESG disclosure. In addition, it addresses previous methodological limitations by incorporating more comprehensive ESG data for the GCC market.
Keywords ESG disclosure, Chairman’s political and royal authority, GCC companies, Servant leadership theory
The effect of board culture diversity on ESG disclosure: Evidence from the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
This study examines the influence of board culture diversity on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) disclosure within the context of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). Drawing on a sample of 762 observations spanning from 2016 to 2021, a content analysis approach was employed to collect ESG disclosure scores. The results suggest a positive impact of board culture diversity on ESG disclosure. To reinforce the validity of these findings, robustness tests, including a lag model and an alternative proxy model, were conducted. Moreover, potential endogeneity concerns were addressed using a two-stage least squares (2SLS) analysis, strengthening the study's reliability. This research contributes to the literature on the interplay between corporate board diversity and ESG reporting practices, especially within the specific context of the KSA-listed companies.
Keywords: Board culture diversity; ESG disclosure; Kingdom of Saudi Arabia