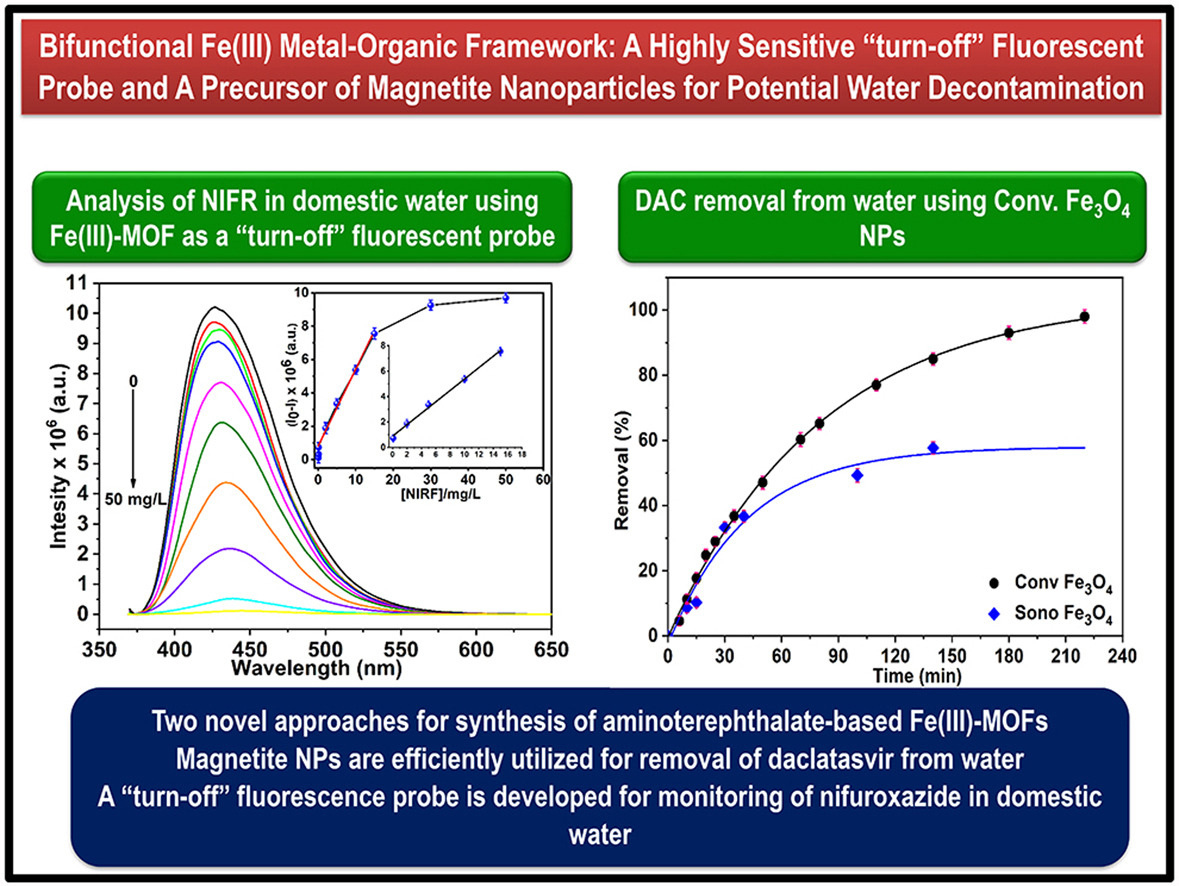
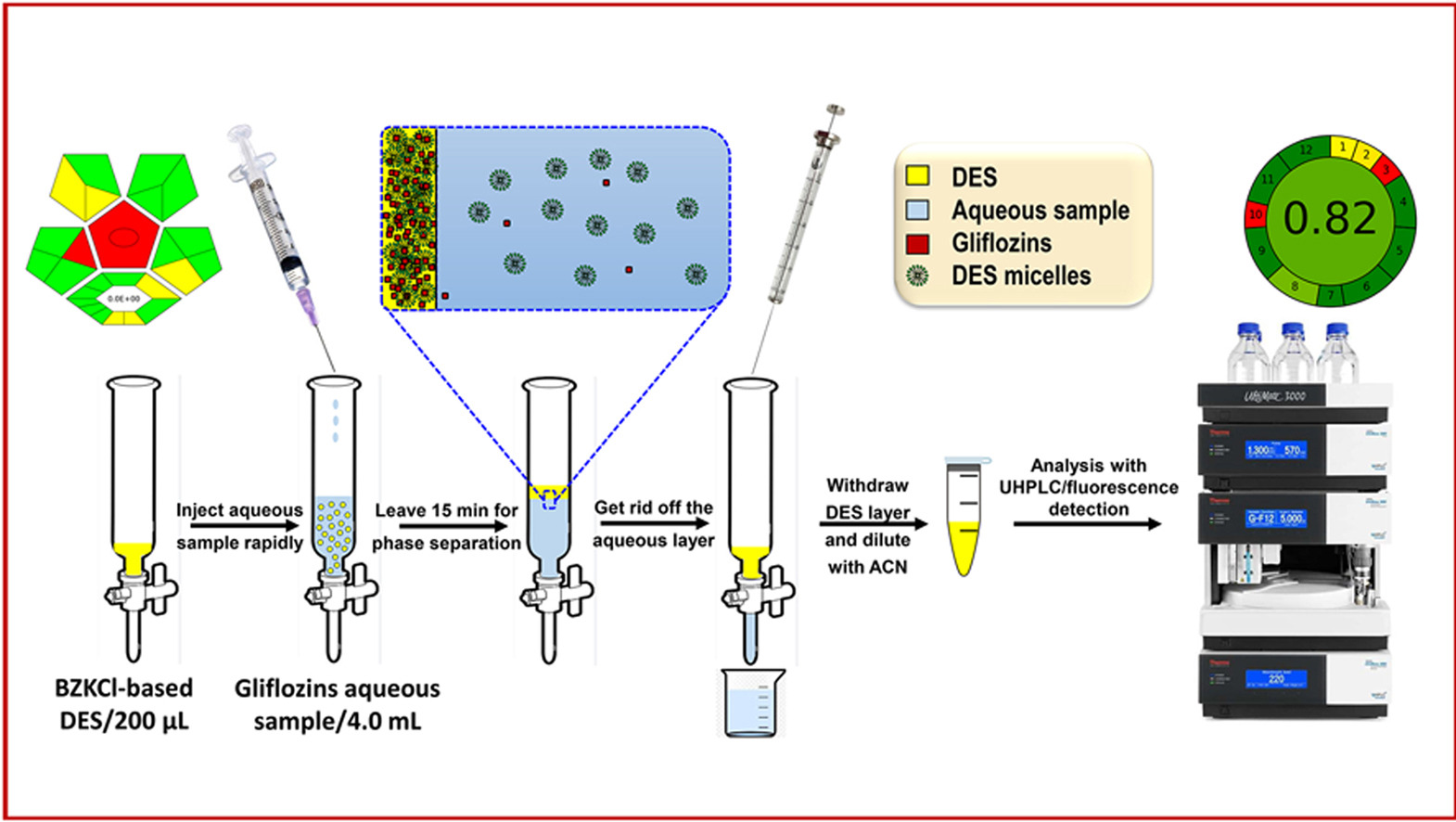
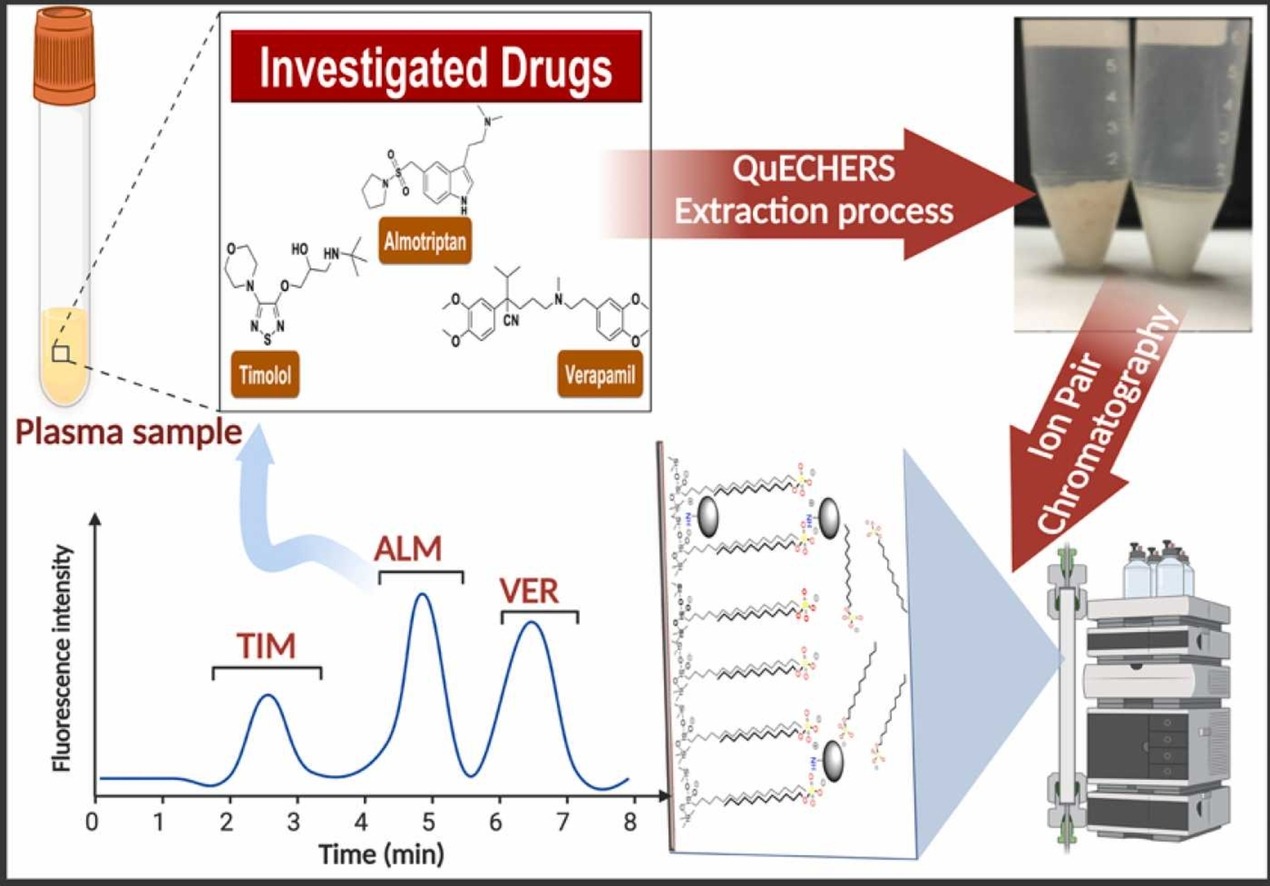
Announcement for third year Pharm-D students: The practical and mid-term exams will be held for the offered course, Phytochemistry-1.

The practical and mid-term exams will be held on Thursday, March 28, 2024, from 9 to 10:20 a.m. in the C and D laboratories, third floor.