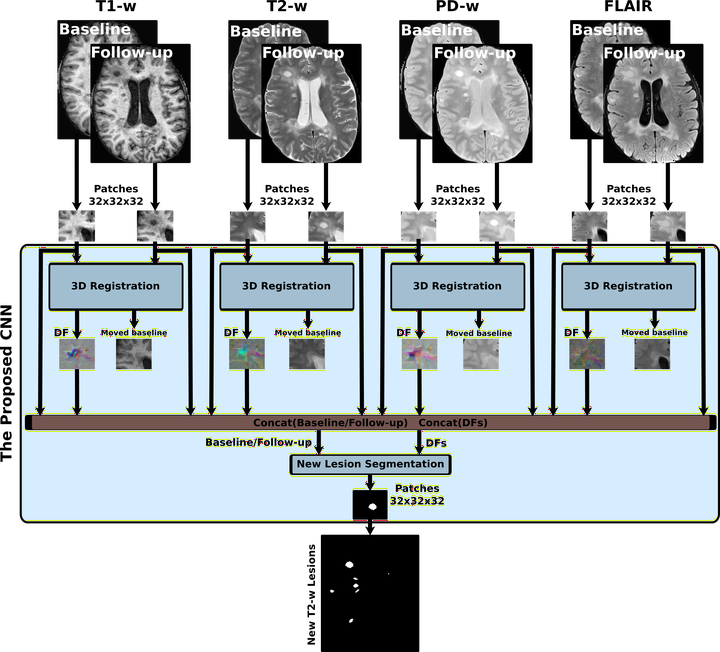
Introduction: Longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has an important role in multiple sclerosis (MS) diagnosis and follow-up. Specifically, the presence of new T2-w lesions on brain MR scans is considered a predictive biomarker for the disease. In this study, we propose a fully convolutional neural network (FCNN) to detect new T2-w lesions in longitudinal brain MR images. Methods: One year apart, multichannel brain MR scans (T1-w, T2-w, PD-w, and FLAIR) were obtained for 60 patients, 36 of them with new T2-w lesions. Modalities from both temporal points were preprocessed and linearly coregistered. Afterwards, an FCNN, whose inputs were from the baseline and follow-up images, was trained to detect new MS lesions. The first part of the network consisted of U-Net blocks that learned the deformation fields (DFs) and nonlinearly registered the baseline image to the follow-up image for each input modality. The learned DFs together with the baseline and follow-up images were then fed to the second part, another U-Net that performed the final detection and segmentation of new T2-w lesions. The model was trained end-to-end, simultaneously learning both the DFs and the new T2-w lesions, using a combined loss function. We evaluated the performance of the model following a leave-one-out cross-validation scheme. Results: In terms of the detection of new lesions, we obtained a mean Dice similarity coefficient of 0.83 with a true positive rate of 83.09% and a false positive detection rate of 9.36%. In terms of segmentation, we obtained a mean Dice similarity coefficient of 0.55. The performance of our model was significantly better compared to the state-of-the-art methods (p < 0.05). Conclusions: Our proposal shows the benefits of combining a learning-based registration network with a segmentation network. Compared to other methods, the proposed model decreases the number of false positives. During testing, the proposed model operates faster than the other two state-of-the-art methods based on the DF obtained by Demons.